Vaccine Hesitancy: Tackling Trust in Vaccines Today
Vaccine hesitancy remains a pressing issue even years after the COVID-19 pandemic’s onset, as highlighted by experts like Professor Margie Danchin from the Royal Children’s Hospital in Melbourne. This phenomenon not only affects the acceptance of COVID-19 vaccinations but also hinders overall vaccine confidence across various demographic groups. Danchin emphasizes the critical need to address fears surrounding vaccine safety to combat declining rates of immunizations, particularly among children. With new advancements such as maternal vaccination against RSV—an illness responsible for many infants’ hospitalizations—it’s disheartening that public perception continues to lag behind scientific progress. This gap underscores the importance of fostering dialogue around vaccine safety and effectiveness to restore trust and protect public health.
The lingering skepticism surrounding vaccinations, often referred to as vaccine reluctance, poses significant challenges in public health initiatives. As communities grapple with the efficacy of COVID-19 immunizations, the broader context of maternal immunization and emerging treatments like RSV monoclonal antibodies cannot be overlooked. The erosion of confidence in vaccinations reflects a broader crisis of trust in health systems, necessitating that healthcare professionals actively engage in transparent communication. Addressing misconceptions about vaccine safety, particularly in vulnerable populations, is vital for reversing the decline in immunization rates. Efforts to enhance vaccine assurance must pivot towards building relationships and conveying informative narratives that resonate with community members.
Understanding Vaccine Hesitancy: Factors and Challenges
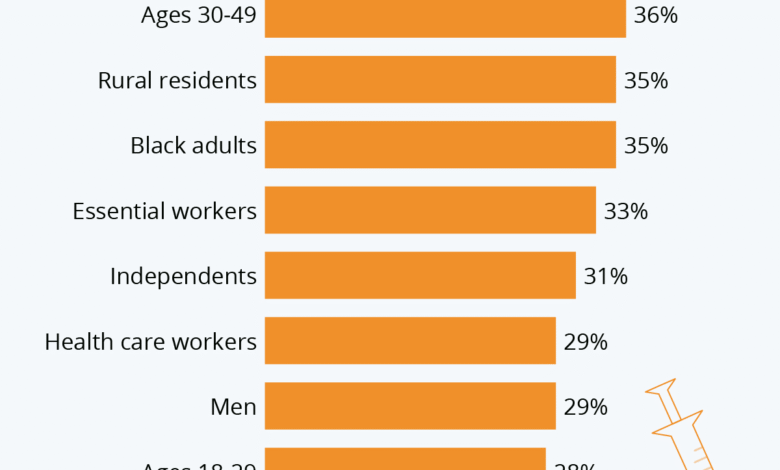
Vaccine hesitancy remains a significant challenge, especially in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many individuals have developed doubts about vaccine safety, influenced by fears of adverse events, misperceptions, and a general distrust in healthcare systems. According to Professor Margie Danchin, vaccine expert at the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, the erosion of vaccine confidence can be attributed to cognitive biases and worldviews that skew public perception. As a result, parents are increasingly cautious about vaccinating their children, despite the overwhelming benefits of vaccines in preventing serious illnesses.
The impacts of vaccine hesitancy are being felt globally, with lower childhood vaccination rates leading to outbreaks of preventable diseases like measles and whooping cough. Danchin highlights that during the COVID-19 vaccine rollout, even rare adverse events led to a significant decrease in public trust. Addressing these fears is imperative, and Danchin emphasizes the importance of educating parents about vaccine safety and the risks associated with the diseases vaccines prevent.
The Role of Maternal Vaccination in Child Health
Maternal vaccination has emerged as a groundbreaking strategy to safeguard newborns against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and improve overall public health preemptively. Professor Danchin advocates for the new maternal RSV vaccine, which has shown to effectively reduce hospitalizations in newborns by 80% in certain areas of Australia. This innovative approach not only protects infants from serious health complications but also bolsters vaccine confidence among expecting mothers, who often seek ways to ensure the health of their unborn children.
The success of maternal vaccination programs can help shift public perceptions about vaccine safety and efficacy. When mothers are empowered with information about the protective benefits of vaccinations for both themselves and their babies, they are more likely to demonstrate vaccine confidence that can resonate with their families and communities. By integrating education on maternal vaccination into healthcare discussions, we can foster a proactive approach to childhood immunization and prevent the resurgence of vaccine-preventable diseases.
Building Vaccine Confidence Through Education and Trust Strategies
Frequently Asked Questions
What is vaccine hesitancy and how does it affect vaccine confidence?
Vaccine hesitancy refers to the reluctance or refusal to vaccinate despite the availability of vaccines. This phenomenon can significantly reduce vaccine confidence, leading to lower vaccination rates, as seen in areas experiencing rising vaccine hesitancy. It is crucial to address and improve public perceptions to ensure higher rates of COVID-19 vaccinations and other essential immunizations.
How can addressing vaccine hesitancy improve COVID-19 vaccinations?
Tackling vaccine hesitancy directly influences the rates of COVID-19 vaccinations by building trust and informing the public. Engaging healthcare providers, community leaders, and using effective communication strategies help alleviate fears and misconceptions, thus encouraging more people to get vaccinated against COVID-19.
What role does maternal vaccination play in combating vaccine hesitancy among new parents?
Maternal vaccination, such as the new RSV vaccination, is essential in providing immunity to newborns and can help reduce vaccine hesitancy among parents. When mothers are educated about the safety and benefits of vaccines given during pregnancy, it increases vaccine confidence and encourages them to vaccinate their children.
How does vaccine safety relate to public perceptions of vaccine hesitancy?
Vaccine safety is a primary concern that fuels vaccine hesitancy. Misconceptions about adverse events can lead individuals to distrust vaccines. It is vital to provide clear, evidence-based information about vaccine safety to counteract fears and enhance public confidence in immunizations.
What strategies are effective in reducing vaccine hesitancy in communities?
Effective strategies to reduce vaccine hesitancy include community engagement through the Vaccine Champions Program, training healthcare workers, and using storytelling to convey the benefits of vaccinations. Building rapport and trust is crucial in addressing concerns respectfully and sharing trustworthy information.
What are the implications of declining childhood vaccination rates due to vaccine hesitancy?
Declines in childhood vaccination rates due to vaccine hesitancy can lead to a rise in vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles and whooping cough. This raises significant public health concerns, necessitating urgent actions to restore vaccine confidence and ensure the safety and health of children.
How can trusted sources combat vaccine hesitancy effectively?
Trusted sources, including healthcare professionals and scientists, play a crucial role in combating vaccine hesitancy. They are essential for providing accurate information and engaging in open conversations that address misconceptions and fears about vaccinations.
What impact does misinformation have on vaccine hesitancy and public health?
Misinformation significantly contributes to vaccine hesitancy by creating distrust in vaccines and health authorities. This can hamper public health efforts, resulting in lower vaccination rates and increased incidents of vaccine-preventable diseases.
How can parents be reassured about the safety of vaccines concerning their children’s health?
Reassuring parents about vaccine safety involves transparent communication about the extensive research confirming that vaccines do not cause conditions like autism. Engaging in respectful dialogues, addressing concerns, and providing clear facts about vaccine safety can enhance parents’ trust.
Why is it essential to maintain open conversations about vaccines in the context of vaccine hesitancy?
Maintaining open conversations about vaccines is crucial for dispelling myths and misunderstandings that contribute to vaccine hesitancy. Such dialogues promote clarity and trust, essential for guiding individuals toward informed decisions regarding vaccinations.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Vaccine Hesitancy | The reluctance to get vaccinated persists, despite advancements in vaccine technology. |
| Professor Margie Danchin | A pediatrician and vaccine expert addressing vaccine hesitancy at the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Melbourne, Australia. |
| New Vaccines | Recent vaccines like RSV maternal vaccination and monoclonal antibody treatment (nirsevimab) aim to combat serious respiratory illnesses in newborns. |
| Trust Decline | There’s the lowest level of trust in vaccines recorded in over a decade, leading to decreased coverage. |
| Risks and Fears | Fear of adverse vaccine effects during COVID-19 has heightened anxiety over vaccine safety despite low actual risks. |
| Building Trust | Professor Danchin emphasizes the importance of community engagement and honest communication to foster vaccine confidence. |
| Vaccine Champions Program | A program that trains healthcare providers and community leaders on effective vaccine communication. |
| Addressing Concerns | Danchin listens to parents’ concerns about vaccines and dispels myths about links to autism through evidence-based dialogue. |
| Need for Accurate Info | Access to trustworthy information is crucial to counter misinformation and misconceptions about vaccines. |
Summary
Vaccine hesitancy continues to challenge public health efforts worldwide, particularly in the context of childhood vaccinations. Despite the development of innovative vaccines and treatments, such as those targeting RSV, skepticism remains high. Key figures like Professor Margie Danchin work tirelessly to rebuild trust and encourage vaccination through transparent communication and community engagement. Addressing fears and misinformation is vital in turning the tide against vaccine hesitancy, ensuring more children are protected from preventable diseases.




