Translation Services: Your Guide to Accurate Solutions
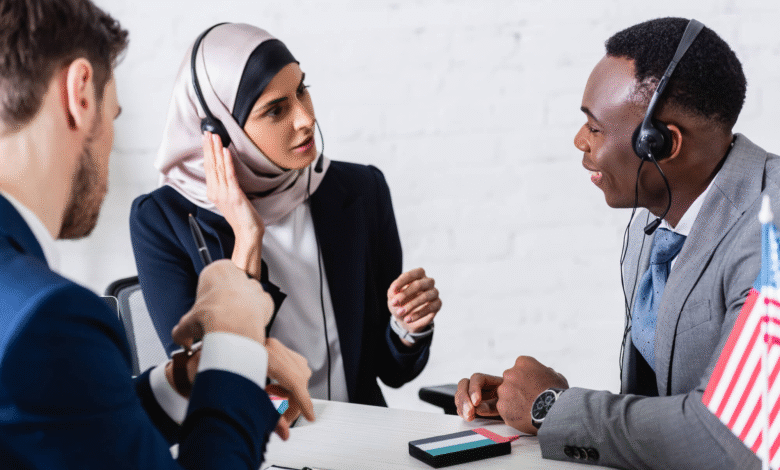

Translation services are essential in today’s globalized world, facilitating communication across diverse languages and cultures. Whether you require document translation for legal, medical, or business purposes, professional translators ensure an accurate translation that captures the nuances of the source material. With the rise in international commerce, investing in quality language translation has become vital for businesses aiming to expand their reach. Certified translation services bring credibility and assurance, often required for official documents to meet regulatory standards. By leveraging expert translators, organizations can overcome language barriers and connect more effectively with their audiences.
When we talk about linguistic conversion assistance, we reference tools and experts who bridge the gap between different tongues. This form of language facilitation is crucial for individuals and businesses needing to communicate efficiently in various contexts. With the demand for proficient text conversion rising, having access to skilled linguists can make a significant difference in message delivery and comprehension. Accuracy in these translations ensures that the intended meaning is preserved, especially in specialized fields such as healthcare and law. Utilizing certified experts in this area not only enhances understanding but also builds trust in communiqués across borders.
Importance of Accurate Translation in Global Communication
Accurate translation is fundamental in today’s interconnected world, where businesses seek to expand their reach across borders. Miscommunications due to translation errors can lead to misunderstandings, which may cost companies not only financially but also damage their reputations. For professionals and organizations, investing in high-quality translation services is crucial to ensure that the intended message resonates with the target audience without losing its essence.
When engaging with non-English-speaking clients or partners, the need for precise language translation becomes paramount. An accurate translation fosters trust and mutual understanding, enabling companies to establish stronger relationships. This is where professional translators come into play, offering specialized expertise that is vital for nuanced and culturally appropriate communication.
How Professional Translators Enhance Document Translation
Professional translators are trained to handle a variety of documents, ensuring that each piece is translated with the highest degree of accuracy. Document translation can range from legal contracts to marketing materials and scientific papers; each type requires distinct knowledge and skill. Utilizing certified translation services provides an additional layer of credibility, as these professionals adhere to rigorous standards and guidelines.
Moreover, professional translators possess an in-depth understanding of the subject matter, which is critical for conveying technical language and industry-specific jargon accurately. By choosing to work with experts, companies not only receive faithful translations but also benefit from insights that can improve the overall quality of their communications. This ensures their documents are not only translated but resonate well with the intended audience.
Certified Translation: A Necessity for Legal and Government Documents
When dealing with legal or government documents, certified translation is often required to authenticate the accuracy of translations. These documents may include birth certificates, court documents, or immigration papers, where an error could have serious consequences. Certified translators are equipped to produce documents that meet legal requirements, offering assurances to foreign authorities.
In many cases, both the source and the translated document must be accompanied by a certification statement that confirms the quality and fidelity of the translation. This process emphasizes the importance of choosing translators who are not only proficient in both languages but also knowledgeable about legal terminology and the specific requirements in different jurisdictions.
Leveraging Language Translation for Business Growth
Language translation has become a pivotal element in driving business growth in a globalized market. Companies that offer bilingual or multilingual content stand to attract a broader audience, which can result in increased sales and brand loyalty. By transforming marketing materials into several languages, businesses can effectively engage with prospective clients who may feel more comfortable reading in their native language.
Moreover, effective language translation helps businesses present their services or products in a compelling manner, enhancing overall customer experience. Combining this with the outreach strategies crafted by professional translators ensures that content not only translates words but also adapts culturally, which is essential for making lasting impressions in new markets.
Choosing the Right Translation Services for Your Needs
Selecting the right translation services can significantly impact the quality of your translations. It’s essential to consider the type of translations needed, as different providers specialize in various areas such as business, legal, or technical translations. Organizations should look for companies that offer professional translators specialized in their industry, ensuring that the nuances and terminologies are handled correctly.
Another key factor to keep in mind is the level of customer support provided by translation services. When questions arise or adjustments need to be made, reliable customer service can facilitate a smoother process. By evaluating potential service providers based on these criteria, businesses can make informed decisions that lead to better and more accurate translation outcomes.
The Role of Technology in Document Translation
Technology plays an increasingly vital role in the field of document translation, providing tools that assist translators in delivering accurate translations efficiently. Translation software and machine translation tools can be particularly helpful in handling large volumes of text, but they should not be relied upon exclusively. Human oversight is crucial to ensure that context and cultural nuances are preserved in the final product.
Additionally, advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are continually improving the accuracy of machine-translated texts. However, professional translators still bring a level of understanding and intuition that technology cannot replicate, particularly when translating complex documents that require creative interpretation.
Cultural Sensitivity in Language Translation
Cultural sensitivity is a critical aspect of language translation that should never be overlooked. Professional translators not only translate words but also must understand the cultural context surrounding those words. This involves recognizing idiomatic expressions, regional dialects, and cultural references, which can vastly differ from one language to another.
Failure to incorporate cultural sensitivity can lead to translations that are not just inaccurate but also offensive or ill-received. Therefore, working with translators who possess cultural knowledge is essential for ensuring that the translated messages resonate positively with the target audience, thereby fostering greater engagement.
The Future of Translation: Trends and Innovations
The future of translation is poised for notable advancements, driven by both technological innovations and increasing globalization. As more businesses extend their operations worldwide, the demand for language translation services is set to rise. Companies are likely to adopt more sophisticated translation tools that can seamlessly integrate with their existing workflows.
In addition, trends like crowdsourced translation and collaborative platforms are emerging, allowing for quicker translation turns and cost-effective solutions. However, the need for skilled professional translators remains crucial, as the nuance and quality of translations can only be guaranteed by experienced linguists.
Pitfalls of Neglecting Professional Translation Services
Neglecting professional translation services can lead to several pitfalls that could adversely affect a business’s image. Companies that opt for free or low-quality translation services risk presenting their audience with inaccurate or poorly constructed content. This not only creates confusion but can also lead to a lack of trust in the brand, potentially costing them customers.
Additionally, overlooking the expertise of certified translators when dealing with critical documents can pose legal risks. Errors in legal translation can result in expensive lawsuits, penalties, or compliance issues. By understanding the clear disadvantages of inadequate translations, businesses can make a more informed decision regarding the importance of investing in professional translation services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are translation services and how do they work?
Translation services are professional services that convert text or speech from one language to another. They involve skilled human translators or advanced technology to ensure accurate translation while maintaining the original message’s context and tone. Professional translators often specialize in specific fields, providing necessary expertise in document translation.
Why is accurate translation important for businesses?
Accurate translation is crucial for businesses as it ensures clear communication with clients and partners across different languages. Misinterpretations can lead to substantial financial losses and damage to reputation. Utilizing reliable translation services helps companies convey their messages effectively, fostering trust and professionalism.
What should I look for in professional translators?
When seeking professional translators, ensure they have proven expertise, relevant qualifications, and experience in your specific industry. Look for certified translation providers who can demonstrate a track record of delivering high-quality, accurate translations that adhere to industry standards and cultural nuances.
How do certified translation services differ from regular translation services?
Certified translation services provide translations that are officially recognized by legal or professional authorities. These translations come with a signed statement affirming that the translated document is accurate and complete. This type of service is often required for legal proceedings, immigration applications, or academic purposes.
Can I get document translation for various file formats?
Yes, many translation services offer document translation for a variety of file formats, including Word, PDF, PowerPoint, and more. It’s essential to confirm with your chosen service provider that they can handle your specific file type while ensuring accurate translation and formatting.
How can language translation impact marketing strategies?
Language translation plays a vital role in global marketing strategies, allowing businesses to reach wider audiences. Effective translation services help tailor marketing materials to resonate culturally with local markets, enhancing engagement and increasing the likelihood of consumer conversions.
What is the average turnaround time for translation services?
The turnaround time for translation services varies depending on factors such as the document’s length, complexity, and language pair. Generally, standard projects can take anywhere from a few hours to several days. For urgent requests, many translation services offer expedited options.
Are there translation services available for rare languages?
Yes, many translation services offer support for rare and lesser-known languages. It’s recommended to inquire directly with the service provider about their language capabilities, as not all providers may have specialized translators for every language.
What are the benefits of using technology in translation services?
Technology in translation services, such as translation memory tools and machine translation, can enhance efficiency and consistency. However, it is crucial to combine these tools with human expertise to ensure accuracy and maintain the quality of the translation.
What factors influence the cost of translation services?
The cost of translation services can be influenced by several factors, including the language pair, the document’s complexity, turnaround time, and the amount of text to be translated. Specialized fields, such as legal or medical translation, may also incur higher rates due to the expertise required.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Lack of Base Content | No specific text has been provided for translation. |
| Request for Content | The user is prompted to submit the text for translation. |
Summary
Translation services are essential for effective communication across languages, especially when specific text is lacking. This highlights the need for individuals and businesses to provide clear and comprehensive content for translation to achieve accurate and impactful results. When the right material is available, translation services can truly bridge linguistic gaps and foster better understanding.