Cancer Statistics: New Insights on Death Rates and Diagnoses
Cancer statistics reveal a mixed bag of outcomes as we navigate the complexities of cancer diagnostics and treatment in today’s world. Recent reports indicate that the rate of cancer diagnoses has shown a declining trend across various demographics, while cancer death rates have also seen a significant reduction over recent years. Between 2018 and 2022, mortality rates dropped by 1.7% annually for men, and 1.3% for women, highlighting advancements in early detection and targeted therapies. Notably, the 2025 cancer report showcases progress, particularly in the treatment of smoking-related cancers which have significantly decreased due to tobacco control measures and improved screening recommendations. As we explore these cancer trends, it becomes clear that ongoing advancements in medical science are shaping a brighter future in the fight against this relentless disease.
When discussing statistics on oncology, one can’t overlook the current data surrounding cancer incidence and mortality. The latest findings highlight pivotal trends in cancer cases, emphasizing both the struggles and strides made within the medical field. With a focus on understanding how many people are diagnosed with cancer each year and the evolving death rates, these insights are essential for informing public health strategies. Significant progress from recent therapies and enhanced diagnostic techniques underlines the importance of ongoing research in this area. As we delve into the advancements in cancer care, it’s crucial to recognize the collective efforts that are leading to improved outcomes for patients.
Current Cancer Statistics in the United States
The latest cancer statistics report reveals vital information regarding the fight against cancer in America. It highlights a significant 1.7% annual decrease in cancer death rates among men and a 1.3% decline among women from 2018 to 2022. This progress indicates a hopeful trend towards improving cancer diagnoses and outcomes, underscoring the importance of early detection and advanced treatment strategies. The National Cancer Institute’s data serves as an important reference for healthcare providers and policymakers aiming to reduce the cancer burden.
In addition to the overall decline in mortality, certain cancer types exhibited remarkable progress. Smoking-related cancers have seen substantial drops, attributed to reduced tobacco use and improved screening practices. This indicates advancements not only in medical technology but also in public health initiatives aimed at smoking cessation. As reported, the efforts toward better health education and preventative measures are crucial in shaping the future of cancer care and health outcomes.
Trends in Cancer Diagnoses: Insights from the 2025 Report
The 2025 cancer report indicates a nuanced landscape of cancer diagnoses in both men and women over recent years. While a notable decline in new cases was reported among men, various cancers such as prostate and pancreas show increasing rates, particularly concerning the rise of prostate cancer diagnoses by 2.9% per year. This complex set of statistics reflects shifting trends in disease prevalence and may be influenced by factors such as lifestyle, aging population, and advancements in diagnostic techniques.
For women, the report notes that new cancer cases increased by 0.3% per year between 2003 and 2021, with specific cancers such as stomach and breast cancer witnessing significant upticks. The researchers linked these trends to risk factors including lifestyle changes and societal influences, such as alcohol consumption and obesity. The upward trend in cancer cases among women calls for targeted public health strategies to address these emerging patterns.
Impact of Advancements on Cancer Death Rates
The advancements in cancer treatment have a profound impact on reducing cancer death rates, as reported in the annual statistics. For instance, innovative technologies in screening, surgery, and targeted therapies contribute significantly to early diagnosis and effective management of the disease. Dr. Marc Siegel highlighted the advancements in robotic surgeries and immunotherapies, particularly for lung cancer, which saw the most substantial decline in death rates among men, showcasing that cancer advancements play a critical role in patient outcomes.
Moreover, the increase in personalized medicine and precision therapies has elevated the effectiveness of treatment protocols significantly. This evolution in healthcare has led to better survival rates for previously hard-to-treat cancers, reinforcing the importance of ongoing research and development in oncology. As cancer treatment continues to advance, it is imperative to continue the focus on early detection and tailored approaches to maximize the potential for positive health outcomes.
Cancer Mortality: A Gender Perspective
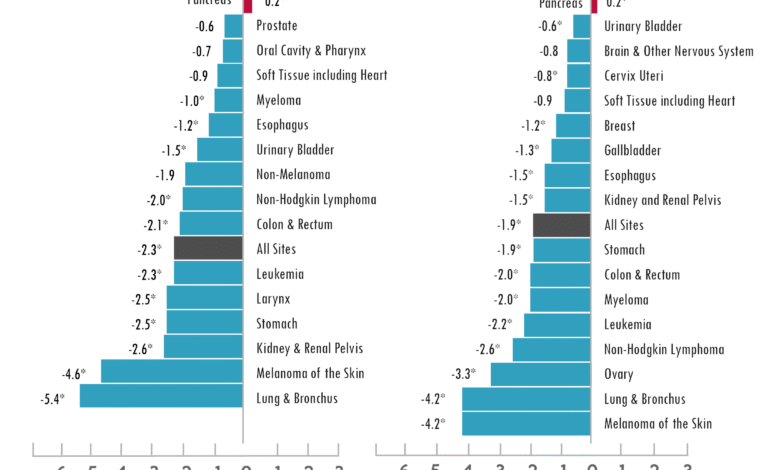
Cancer mortality trends indicate a notable difference in outcomes between genders. According to the recent report, while cancer death rates are declining overall, men are still experiencing higher mortality rates for several cancer types including lung and prostate. This discrepancy may arise from biological differences, lifestyle factors, and variations in healthcare access. With lung cancer mortality in men dropping by 4.5% annually, the effectiveness of early screening programs and other interventions is becoming increasingly evident.
Conversely, women’s cancer mortality rates have also demonstrated promising declines, particularly in lung cancer, where rates have decreased by 3.4% each year. The significant reduction in breast cancer death rates emphasizes successful screening methodologies and treatment breakthroughs. As both men and women face unique challenges in cancer prognosis, understanding these gender-based differences is essential for developing targeted interventions and improving overall survival rates.
Emerging Cancer Trends Among Young People
Recent data revealed changing patterns of cancer cases and mortality among younger populations, particularly children and young adults. For children, cancer deaths showed a slight decline of 1.5% per year between 2001 and 2022, reflecting potential improvements in treatment protocols and healthcare accessibility. Among teens and young adults, the mortality rate for cancer remained stable, though specific cancers like leukemia and lymphoma exhibited slight increases. These trends indicate the need for ongoing research to address cancer in younger demographics.
The stabilizing rates in both new diagnoses and mortality among young adults, despite the complexities of cancer, suggest a shift in the evaluation of cancer treatment. Experts note that a collaborative approach involving various specialists contributes to improved outcomes. This multi-disciplinary strategy aligns with the overall trend of decreasing cancer death rates, demonstrating that coordinated care is crucial in managing cancer effectively in vulnerable populations.
The Significance of Cancer Screenings in Survival Rates
The report underscores the critical role that cancer screenings play in improving survival rates across different demographics. Enhanced screening methods have been pivotal in the early detection of cancers, allowing for timely interventions. As identified in the latest statistics, the integration of routine screenings into healthcare practices significantly correlates with declining death rates, particularly in cancers such as colorectal and breast.
Furthermore, public health initiatives focusing on awareness and access to screenings contribute greatly to reducing cancer mortality. The relationship between early diagnosis and treatment effectiveness reinforces the necessity for educational programs aimed at promoting routine screenings among at-risk populations. Stakeholders must continue advocating for policies that improve access to these essential health services as a preventive strategy against cancer.
Analyzing the Rise and Fall of Specific Cancer Types
The latest cancer statistics reveal fluctuations in the prevalence of specific cancer types, highlighting a multifaceted landscape of cancer trends. While certain cancers such as lung and colorectal are witnessing significant declines, others like pancreatic and prostate cancers are on the rise. This intricate balance of cancer statistics may be influenced by varying factors, such as lifestyle changes, genetic predispositions, and the impact of innovative treatment methods over time.
A thorough analysis of these trends is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of public health interventions and therapeutic advancements. As healthcare providers monitor these rising and falling rates, adjustments in policy and resource allocation can be made to effectively combat the evolving nature of cancer. Staying ahead of these trends will ensure that response strategies remain effective and targeted.
Youth Cancer Statistics: Challenges and Opportunities
The fight against cancer in young populations presents both challenges and opportunities, as evidenced by the new data released. Cancer death rates among children and teens have been decreasing, reflecting advancements in treatment and increased awareness. However, the rise of certain cancers, such as leukemia, highlights the need for continued research and development in pediatric oncology. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from healthcare professionals, researchers, and policy-makers.
As we look to the future, the emphasis on collaborative care is paramount. Initiatives focused on multi-disciplinary approaches that involve oncologists, nurses, and specialists in various fields can revolutionize treatment protocols for young cancer patients. Reinforcing these efforts and driving funding towards pediatric research will be essential in overcoming the significant hurdles still present, ensuring that every young patient has the best chance for recovery and long-term survival.
Future Directions in Cancer Research and Treatment
The ongoing evolution of cancer research and treatment methodologies has set the stage for transformative advancements that could redefine patient outcomes. The promising data from the cancer report emphasizes substantial progress made in survival rates and diagnosis techniques. Innovations such as immunotherapy, personalized medicine, and advanced surgical approaches indicate that we are on the verge of even greater breakthroughs in cancer care.
Looking ahead, the focus must remain on comprehensive research that prioritizes the unique needs of different patient populations, particularly in underserved communities. By channeling resources into developing more effective treatments and diagnostic tests tailored to various demographics, the medical community can work towards eradicating cancer disparities. This proactive approach is vital in not only enhancing survival rates but also providing hope and support to those affected by cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest cancer statistics for 2025 regarding diagnoses and death rates?
The latest cancer statistics report from 2025 indicates a decline in overall cancer death rates, with a decrease of 1.7% annually for men and 1.3% for women between 2018 and 2022. New cancer diagnoses have also shown a decrease, particularly for lung and bronchus cancers in men, which fell by 3.4% per year during the same period.
How have cancer death rates changed over the past few years according to the latest cancer report?
According to the latest cancer statistics report, cancer death rates have experienced a general decline, with significant reductions noted for various cancers among men and women. For instance, deaths from lung and bronchus cancers saw a 4.5% decrease in men and a 3.4% decrease in women per year from 2018 to 2022, attributed to advancements in screening and treatment.
What trends in cancer diagnoses are evident from the 2025 cancer report?
The 2025 cancer statistics suggest a downward trend in new cancer diagnoses among men, particularly for cancers such as lung and bronchus, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and colon and rectum, which fell by 1.6% to 2.2% yearly from 2001 to 2013. However, certain cancers such as prostate and pancreatic are on the rise, highlighting an ongoing shift in cancer trends.
Which cancers showed the most significant declines in death rates according to cancer statistics from 2025?
The 2025 cancer report revealed significant declines in death rates for various cancers, including lung and bronchus cancers for both genders, which had the highest reduction in mortality rates. Specifically, lung cancer deaths decreased by 4.5% per year for men and 3.4% for women between 2018 and 2022, reflecting improvements in medical interventions.
How have advancements in cancer treatment impacted cancer statistics in recent years?
Advancements in cancer treatment, such as improved screening methods, robotic surgeries, and targeted therapies, have directly contributed to the positive shifts observed in cancer statistics. The 2025 report notes that these factors have played a crucial role in decreasing cancer death rates, particularly for smoking-related cancers and breast cancer, which has seen death rates drop significantly since the late 1980s.
What factors are influencing rising cancer rates in specific demographics based on the latest cancer statistics?
The 2025 report on cancer statistics highlights that rising cancer rates, particularly among women, can be attributed to factors such as higher alcohol consumption, obesity, and changes in reproductive patterns. These influences have been linked to increasing rates of certain cancers, including breast and uterine cancers, showing a concerning trend in specific demographics.
What are the implications of the recent findings in cancer statistics for public health policy?
The recent findings in the 2025 cancer statistics report underscore the need for continued investment in cancer research, public health initiatives, and early screening programs. As cancer death rates decline, it is crucial to address the rising rates in specific cancer types and demographics to ensure equitable access to care and treatment advancements.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Overall Cancer Fate | Cancer death rates are decreasing for both men (1.7% annually) and women (1.3% annually) from 2018 to 2022, largely due to improved screening and treatment options. |
| Significant Cancer Types | Notable declines were observed in smoking-related cancers, colorectal cancers, and breast cancer among women, with lung cancer mortality dropping 4.5% for men and 3.4% for women. |
| Cancers with Rising Rates | Despite overall declines, certain cancers such as oral cavity and pharynx for men and uterine cancers for women saw increased mortality rates. |
| Trends in Young Population | Children’s cancer deaths have decreased by 1.5% per year from 2001 to 2022, while young adults (ages 15-39) saw varied rates of cancer-related mortality. |
| Factors Affecting Statistics | Social determinants like obesity, alcohol consumption, and lifestyle choices are increasingly linked to rising cancer rates in certain demographics, particularly among women. |
| COVID-19 Impact | The pandemic affected cancer diagnosis trends, with reports indicating a return to expected levels in 2021 after a decline in 2020. |
Summary
Cancer statistics reveal a poignant narrative of progress and challenges in the battle against cancer. The latest report highlights a notable decrease in deaths and new diagnoses across many cancer types, driven by advancements in treatment and prevention strategies. However, there remain significant disparities in outcomes and certain cancers on the rise, underscoring the need for continued efforts in cancer awareness, lifestyle modification, and healthcare access to ensure these statistics lead to improved health outcomes for all.




