Web Scraping Techniques: Learn the Best Methods Today
Web scraping techniques have revolutionized the way we collect and analyze information online. With the rise of digital data, these data extraction methods are becoming essential for businesses and researchers alike. By leveraging powerful web scraping tools, users can automate the process of gathering large sets of data efficiently, while Python web scraping has emerged as a popular approach due to its simplicity and versatility. However, it is crucial to be aware of the legal issues of web scraping, as unauthorized data collection can lead to significant repercussions. This web scraping tutorial aims to guide you through the various methods and best practices to ensure successful and lawful data extraction.
The art of extracting data from websites, often referred to as online content harvesting or information mining, plays a pivotal role in today’s data-driven landscape. Techniques in data acquisition not only enable businesses to stay competitive but also provide researchers with invaluable insights. As programmers and analysts explore various data gathering strategies, understanding the capabilities of programming languages like Python becomes increasingly beneficial. Moreover, the importance of ethical practices in online data collection cannot be overstated, as the legal aspects are constantly evolving. This introductory guide will shed light on effective strategies for gathering information while addressing the crucial considerations for compliance.
Understanding Web Scraping Techniques
Web scraping techniques are essential for anyone looking to extract data from websites efficiently. These techniques involve using automated tools to gather data from web pages without manual intervention. Common methods include sending requests to web servers and parsing HTML or XML content to retrieve the desired information. Understanding these techniques is fundamental for anyone undertaking a web scraping project, as they form the backbone of all data extraction efforts.
In addition to basic scraping techniques, it’s important to consider more advanced methods such as API integration, where data is fetched directly from a website’s application programming interface (API). This process is generally more efficient and less prone to errors compared to traditional scraping, especially when dealing with large volumes of data. Combining different web scraping techniques can lead to more effective data extraction strategies.
A Comprehensive Web Scraping Tutorial
A web scraping tutorial is an excellent starting point for beginners looking to understand the nuances of data extraction. Such tutorials typically cover the basics of web scraping, including the necessary tools and programming libraries. Python, for instance, is widely favored for web scraping due to its simplicity and a rich ecosystem of libraries like Beautiful Soup and Scrapy that facilitate the scraping process. By the end of a comprehensive tutorial, learners should feel confident in writing their own web scraping scripts.
Furthermore, a good web scraping tutorial emphasizes best practices, such as respecting robots.txt files and implementing rate limiting to avoid overwhelming servers. These practices not only improve the efficiency of scraping but also help mitigate legal issues associated with web scraping. By adhering to these guidelines, beginners can ensure their scraping activities are ethical and within legal boundaries.
Popular Web Scraping Tools and Their Benefits
The market is flooded with various web scraping tools that cater to different user needs and expertise levels. Some of the most popular scraping tools include ParseHub, Octoparse, and Apify, each having unique functionalities that allow users to gather data from complex web pages without coding. These tools often come with user-friendly interfaces that enable individuals to drag and drop elements they wish to scrape, making the process accessible even for non-programmers.
On the other hand, open-source programming libraries such as Beautiful Soup and Scrapy are invaluable for those who are comfortable with coding and require more customization. Python web scraping with these tools provides maximum flexibility, allowing users to develop tailored scraping solutions that fit specific data extraction needs. A thorough understanding of both types of tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of data collection.
Exploring Data Extraction Methods in Depth
Data extraction methods can vary widely depending on the complexity of the task at hand and the specific requirements of the project. Depending on the target website, users can choose from several approaches, such as HTML parsing, which involves extracting relevant HTML elements to get the data needed. Techniques like XPath and CSS selectors are crucial when it comes to accurately pinpointing the data points of interest within the HTML structure.
Moreover, the choice of data extraction method can greatly influence the success of the web scraping project. For instance, when dealing with JavaScript-heavy websites, it may be necessary to use headless browsers or specialized scraping tools that can render the page dynamically. As such, it’s beneficial for aspiring web scrapers to equip themselves with knowledge of various data extraction methods to successfully adapt to different scraping scenarios.
Legal Considerations in Web Scraping
Navigating the legal landscape of web scraping is vital for anyone who engages in this practice. Legal considerations primarily revolve around copyright issues, terms of service violations, and the ethical implications of data harvesting. Websites often have specific terms of service that dictate how their content can be used or accessed, and failing to comply can lead to legal action. Therefore, it is crucial for scrapers to familiarize themselves with these terms before proceeding.
Additionally, understanding the implications of the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the U.S. is critical for web scrapers, as this act can make unauthorized access to computer systems a federal crime. Ethical scraping practices, such as respecting robots.txt directives and exercising caution when collecting personal data, can mitigate many legal risks. Staying informed about the laws surrounding web scraping can empower web scrapers to operate safely and responsibly.
Implementing Best Practices for Effective Web Scraping
Implementing best practices in web scraping can significantly enhance not only the efficiency of the scraping process but also the quality of the extracted data. It is essential to plan the scraping operation carefully, considering factors like the structure of the target website and the specific data required. For instance, ensuring that the scraping scripts are robust and able to adapt to minor changes in webpage layouts can save a lot of future time and effort.
Additionally, establishing a logging mechanism to track requests and responses can aid in troubleshooting and ensuring compliance with website policies. Incorporating error handling in your scraping scripts also enhances resilience, allowing them to function correctly even when unexpected changes occur on the target site. By adhering to these best practices, web scrapers can create more reliable and effective data extraction solutions.
The Role of APIs in Web Data Extraction
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) play a key role in web data extraction, offering a structured way to access data from websites. Instead of scraping HTML content directly from web pages, utilizing an API can streamline the data extraction process, providing clean and structured data sets tailored to the user’s needs. Many platforms, such as social media sites and marketplaces, offer robust APIs that allow developers to fetch data securely and efficiently.
Moreover, using APIs generally comes with better performance and reliability compared to traditional web scraping methods. Since APIs are designed for data exchange, they can handle large volumes of requests without the risk of getting blocked, which is often a concern for web scraping. Familiarity with APIs and their documentation is increasingly becoming a crucial skill for data engineers and analysts engaging in web data extraction.
The Future of Web Scraping: Trends and Innovations
The future of web scraping is set to be shaped by emerging technologies and trends that enhance the efficiency and capability of data extraction processes. Innovations like machine learning and artificial intelligence are making it possible to automate complex scraping tasks and improve data accuracy. These technologies can assist in pattern recognition and data classification, allowing scrapers to extract relevant information from unstructured data sources more effectively.
Additionally, as websites evolve to implement more robust anti-scraping measures, the web scraping community is likely to innovate in response. Tools that employ sophisticated techniques such as browser automation or those that can adapt to changing web infrastructures will be crucial to remain competitive. Staying abreast of these trends will be essential for anyone interested in the future landscape of web scraping.
Learning Resources for Aspiring Web Scrapers
For those looking to dive into the world of web scraping, a plethora of learning resources are available. From online courses on platforms like Coursera and Udemy to comprehensive books on Python programming, aspiring scrapers can find a wealth of knowledge aimed at various skill levels. These resources often cover critical topics such as web scraping frameworks, data processing, and ethical considerations, ensuring that learners receive a well-rounded education.
In addition to formal educational resources, online communities and forums provide spaces for aspiring scrapers to ask questions and share experiences. Platforms like Stack Overflow and GitHub not only host vast libraries of code snippets and projects that can serve as learning tools but also facilitate connection with experts in the field. Engaging with these communities can enhance learning and assist individuals in overcoming common challenges encountered in web scraping.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best web scraping techniques for beginners?
For beginners, the best web scraping techniques include using libraries like Beautiful Soup and Scrapy in Python. These tools simplify the process of parsing HTML and extracting data efficiently. Additionally, online tutorials can guide you through fundamental data extraction methods, helping you to grasp the basics of web scraping.
How do data extraction methods differ in Python web scraping?
Data extraction methods in Python web scraping vary in complexity. Basic methods involve simple requests to fetch HTML content, while advanced techniques might include using APIs or handling JavaScript-rendered pages with tools like Selenium. Understanding these distinctions can enhance your web scraping efficiency.
What are some popular web scraping tools available today?
Some popular web scraping tools include Scrapy, Beautiful Soup, and Selenium for Python users, as well as Octoparse and ParseHub for a no-code approach. These tools offer various features for efficient data extraction and automation, catering to different user needs.
Are there legal issues associated with web scraping?
Yes, there are legal issues associated with web scraping. It’s crucial to read a website’s terms of service and understand copyright laws to avoid potential violations. Legal frameworks can vary by jurisdiction, so always ensure your web scraping techniques comply with local laws and ethical guidelines.
What should I know before using a web scraping tutorial?
Before using a web scraping tutorial, ensure you have a basic understanding of Python and HTML. Familiarize yourself with web scraping tools and libraries, which are often highlighted in these tutorials. Additionally, be aware of ethical and legal considerations surrounding data extraction.
How can I get started with Python web scraping?
To get started with Python web scraping, download Python and set up your environment with libraries like Requests and Beautiful Soup. Follow web scraping tutorials that guide you through making HTTP requests and parsing HTML. It’s a practical way to learn data extraction methods effectively.
What are the ethical considerations in web scraping techniques?
Ethical considerations in web scraping techniques include respecting website terms of service, avoiding excessive requests that could harm site performance, and not scraping personal data without consent. Always prioritize ethical practices to maintain a good relationship with web sources.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
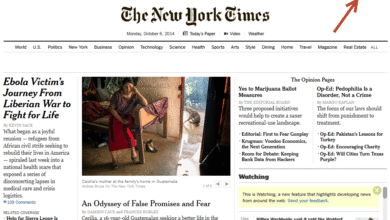
| Limitations of Web Scraping | Some websites, like nytimes.com, restrict access to their content, making scraping impossible. |
| Alternative Approaches | You can summarize articles or acquire information on web scraping techniques rather than extracting data directly. |
Summary
Web scraping techniques are essential tools for extracting data from websites, enabling users to gather and analyze information efficiently. Understanding the limitations, such as potential restrictions by certain sites, helps in developing effective scraping strategies. It’s important to explore alternative methods like summarization to stay compliant with legal boundaries while still obtaining valuable insights.