Stem Cell Therapy for Parkinson’s Shows Exciting Results
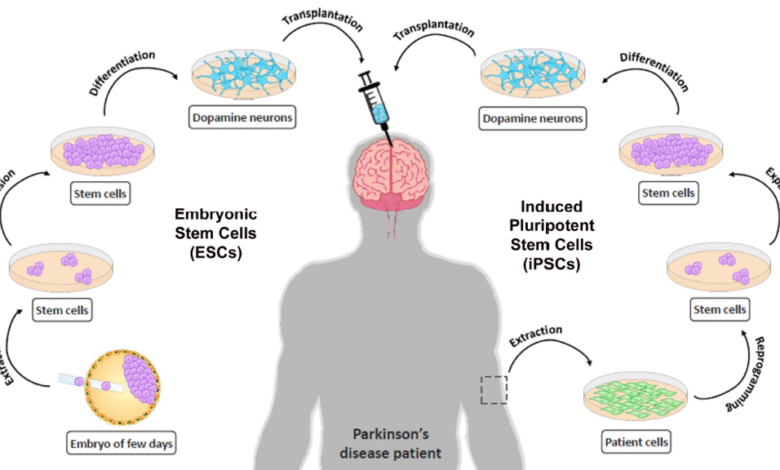
Stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s is emerging as a promising treatment option for those affected by this debilitating disease. With over one million individuals living with Parkinson’s disease in the United States alone, researchers are exploring innovative methods to combat its symptoms and progressive nature. Recent advancements in stem cell research, particularly involving embryonic stem cells, have shown potential in regenerating lost dopaminergic neurons that are critical for movement and coordination. Initial clinical trials for Parkinson’s have shown that introducing these cells can lead to significant improvements in motor function, heralding a new era in Parkinson’s disease treatment. As more studies unfold, the possibility of harnessing stem cells to effectively manage and even reverse certain aspects of Parkinson’s presents a beacon of hope for patients and researchers alike.
The exploration of stem cell interventions for managing Parkinson’s disease represents an exciting frontier in neuroscience. This innovative approach aims to restore brain function by utilizing advanced cellular therapy, specifically targeting the regeneration of neurons damaged by the disease. Researchers are focusing on utilizing both embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells to replace the lost dopaminergic neurons that lead to the characteristic symptoms of tremors and rigidity. As we observe the progress in clinical trials for treatments aimed at this neurological condition, the potential to alter the course of Parkinson’s could revolutionize the landscape of neurological therapies. Moreover, the ongoing investigations promise to deepen our understanding of cellular dynamics and their applications in other neurodegenerative disorders.
Understanding Parkinson’s Disease and Its Challenges
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions globally, causing debilitating symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and balance issues. As the brain gradually loses dopamine-producing neurons, the challenges faced by patients escalate, hindering their daily activities. The complexity of this disease necessitates a multifaceted approach to treatment, involving medication, therapy, and cutting-edge research to develop innovative solutions that can halt or reverse the impacts of the illness.
Recent advancements in neuroscience highlight the importance of early intervention and tailored treatment strategies. With the progression of Parkinson’s, patients often experience an increase in symptoms and a decrease in quality of life. Addressing these issues through comprehensive treatment plans, including lifestyle modifications and ongoing medical support, plays a crucial role in managing the disease effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s and how does it work?
Stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s involves the use of stem cells, specifically derived from early-stage embryos, to create dopaminergic neurons. These neurons are transplanted into the brains of Parkinson’s patients, where they can produce dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter that alleviates common symptoms such as tremors and stiffness.
What recent clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s?
A recent phase 1 trial conducted by researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center showed that stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s is not only safe but also leads to noticeable improvements in motor function. Participants who received a higher dose reported 2.7 hours of additional ‘on time’ each day, indicating significant enhancement in daily life.
Are there any side effects associated with stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease?
According to the findings from the initial clinical trial, stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s did not result in serious side effects, as the transplanted stem cells successfully integrated into patients’ brains. Long-term effects are still being studied, especially with larger phase 3 clinical trials set to investigate efficacy further.
What is the role of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease treatment?
Dopaminergic neurons are vital for movement and coordination, which are impaired in Parkinson’s disease due to the progressive loss of these cells. Stem cell therapy aims to replenish these neurons, potentially reversing motor dysfunction and improving patient quality of life.
How promising is embryonic stem cell research for treating Parkinson’s disease?
Embryonic stem cell research shows considerable promise for treating Parkinson’s disease, as demonstrated by studies that have successfully generated dopaminergic neurons from these cells. Early results from the clinical trials suggest that this approach may slow disease progression and improve motor functions, marking a significant breakthrough in Parkinson’s treatment.
What is the next step for stem cell therapy following the recent studies on Parkinson’s disease?
Following successful phase 1 trials, the next step for stem cell therapy in Parkinson’s disease is the commencement of phase 3 clinical trials involving a larger cohort of around 100 patients. This phase aims to confirm the efficacy of this promising therapy and bring it closer to becoming a standardized treatment option.
What are the limitations of the current research on stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s?
The current research on stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease is primarily limited by its small sample size and the focus on safety rather than efficacy. Researchers emphasize the need for larger, well-controlled studies in phase 3 trials to establish the long-term effectiveness of this innovative treatment.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Overview | Researchers at MSK developed a stem cell therapy for advanced Parkinson’s in a phase 1 trial with 12 patients. |
| Cells Used | Donated embryonic stem cells were differentiated into neurons and transplanted into patients’ brains. |
| Outcome | 18 months post-injection, patients showed improvements in Parkinson’s symptoms with no serious side effects. |
| Dopamine Production | Injected cells produced dopamine, important for movement, addressing low levels common in Parkinson’s. |
| FDA Approval | Following positive phase 1 results, the FDA approved a phase 3 trial with around 100 patients for 2025. |
| Expert Opinions | Experts hailed the study as groundbreaking, emphasizing potential for motor function improvement and disease progression halting. |
| Next Steps | Further larger studies are needed to validate findings and explore therapy’s efficacy. |
Summary
Stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s holds significant promise following the successful phase 1 trial conducted by researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. This innovative therapy, which involves transplanting stem cell-derived neurons into the brains of patients, showed encouraging improvements in symptoms. With the FDA’s approval for a phase 3 trial, the future looks bright for those affected by Parkinson’s disease. If the upcoming studies confirm the efficacy of this treatment, it could revolutionize how Parkinson’s is managed, offering hope for better motor function and quality of life for millions.




