Semaglutide Liver Disease: Revolutionary Injections Revealed
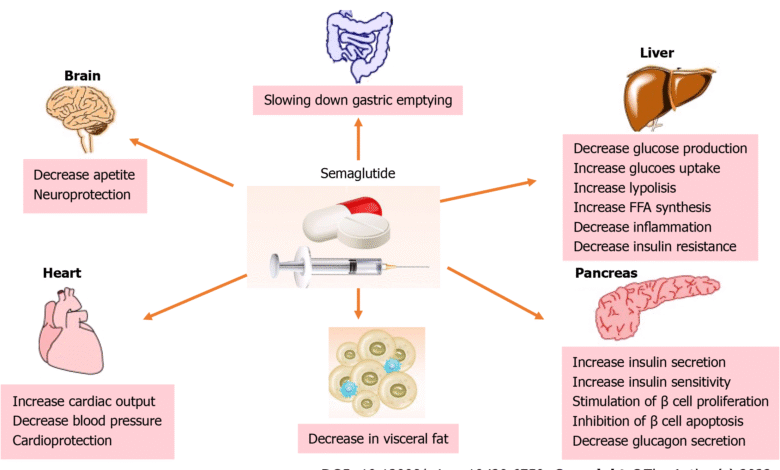
Semaglutide liver disease represents a groundbreaking development in the treatment of serious liver conditions, particularly metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). Recent studies have shown that semaglutide injections, primarily known for managing obesity and type 2 diabetes, can significantly reduce liver inflammation and excess fat deposits. With nearly 63% of participants experiencing improved liver conditions, this promising outcome underscores the potential of semaglutide as a vital tool in liver inflammation treatment. This innovation not only benefits those battling fatty liver disease but also opens new avenues for metabolic dysfunction therapies. As researchers continue to explore its effects, semaglutide may very well emerge as a front-line treatment for liver diseases that affect millions worldwide.
The advent of semaglutide as a treatment for liver diseases highlights an exciting shift in the medical landscape, especially for conditions associated with severe liver dysfunction. Known as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide has traditionally been used in diabetes treatment and weight management but is now showing promise in addressing metabolic disorders like MASH. This revolutionary approach aids in mitigating liver fat accumulation and inflammation, which is crucial for improving overall liver health. With further research on its long-term efficacy, semaglutide could potentially redefine therapeutic strategies for those suffering from liver-related complications. As health professionals seek effective solutions for fatty liver conditions, the role of semaglutide could become increasingly significant.
Understanding Semaglutide and Its Role in Fatty Liver Disease
Semaglutide, originally developed as a treatment for type 2 diabetes, has recently shown promising results in tackling fatty liver disease, specifically metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). This severe liver condition is characterized by significant fat accumulation within the liver, leading to inflammation and long-term liver damage. In clinical trials, semaglutide injections demonstrated not just weight loss, but also substantial reductions in liver fat and inflammation, showcasing the potential for this drug to be an effective treatment alternative in managing liver disease.
The significance of semaglutide’s application extends beyond its diabetes treatment background; it represents a dual approach in combating metabolic dysfunction. As lifestyles contribute increasingly to obesity and associated liver diseases, the need for innovative treatment solutions becomes paramount. Recent studies involving semaglutide injections have illustrated a marked improvement in liver enzymes and blood markers, highlighting its efficacy in reversing fatty liver disease complications, hence deserving attention both from healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Clinical Efficacy of Semaglutide in Liver Inflammation Treatment
In a groundbreaking clinical trial, over half of the participants treated with semaglutide injections exhibited notable improvements in liver inflammation and fat accumulation after 72 weeks. Specifically, 62.9% of those receiving semaglutide displayed reduced liver fat, significantly outpacing the 34.3% observed in the placebo group. This stark contrast underscores the effectiveness of semaglutide as a viable option in liver inflammation treatment, offering hope to patients who previously faced limited therapeutic avenues.
Additionally, the findings indicated that semaglutide not only facilitated weight loss (averaging 10.5%) but also improved liver fibrosis in participants. With 36.8% showing advancements in their liver condition compared to the 22.4% in the placebo group, these results suggest a transformative potential of semaglutide for individuals suffering from severe forms of liver disease. As researchers delve deeper into the impact of GLP-1 therapies on liver health, semaglutide stands out as a pivotal treatment option contributing to both weight management and liver recovery.
The Connection Between Diabetes Treatment and Liver Health
The interplay between diabetes and liver health is a critical area of focus, particularly with the rising prevalence of fatty liver disease among diabetic patients. Managing diabetes effectively can not only stabilize blood sugar levels but can also mitigate the risks associated with liver complications. Semaglutide’s dual functionality as a diabetes treatment and a contender against liver disease encapsulates the strides pharmaceutical developments are making towards integrated healthcare solutions.
As obesity often correlates with metabolic dysfunctions affecting the liver, therapies like semaglutide offer a comprehensive approach by addressing both conditions simultaneously. This forward-thinking perspective on managing diabetes includes proactive measures that strengthen liver health, ultimately reducing the burden of fatty liver disease in affected populations. Through continued research into semaglutide, it is anticipated that more robust treatment protocols will evolve, reinforcing the connection between effective diabetes management and enhanced liver health.
Future Implications of Semaglutide in Liver Disease Management
Looking ahead, the ongoing studies and trials surrounding semaglutide present exciting prospects for patients suffering from metabolic dysfunction and advanced liver disease. As the research team aims to expand their findings through a more extensive participant pool and long-term follow-ups, the anticipated data could unlock new biopharmaceutical pathways for therapeutic interventions. Should these upcoming results mirror initial findings, semaglutide may redefine standards in liver disease management and treatment methodologies.
Furthermore, with increasing awareness of the overlap between diabetes and liver health, healthcare practitioners are expected to adopt more integrated treatment approaches, utilizing semaglutide’s capabilities to tackle both conditions. Such innovations may lead to more effective prevention strategies and management plans aimed at reducing the incidence of fatty liver disease, promoting a healthier lifestyle among at-risk populations. Through proactive healthcare solutions, the future landscape of liver disease treatment is likely to be transformed, placing medications like semaglutide at the forefront of clinical practices.
Understanding MASH and Its Association with Semaglutide
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) has emerged as a critical concern in the realm of liver diseases, particularly due to its severe implications for patient health. As a form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, MASH is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and ultimately, liver failure if left untreated. Recent studies indicate that treatments like semaglutide may offer significant relief to individuals facing this debilitating condition, effectively reversing some of the damaging effects of MASH.
The connection between semaglutide and MASH lies in its mechanism of action, which targets metabolic dysfunction and promotes weight loss, key factors that contribute to liver health. By addressing the underlying metabolic abnormalities, semaglutide injections have shown substantial improvements in liver parameters among patients with MASH. The dual capability of semaglutide to manage weight and improve liver health underscores its potential as a frontrunner in the treatment of metabolic-associated liver diseases.
Weight Loss and Its Impact on Liver Disease Recovery
Weight loss has long been recognized as a significant contributor to improved liver health, especially for patients suffering from fatty liver disease. As obesity plays a crucial role in exacerbating liver inflammation and damage, effective weight management strategies can yield considerable benefits. Recent clinical trials surrounding semaglutide indicate that the drug not only assists in weight loss but also promotes liver recovery, highlighting its importance as a multifaceted treatment option.
Participants in semaglutide studies achieved an average weight reduction of 10.5%, a change closely associated with positive shifts in liver function and health. The parallel improvements in liver enzymes and reduced fat accumulation in the liver reinforce the role of weight loss as a vital component in treating liver diseases. As further research unfolds, a deeper understanding of this relationship will likely aid in refining treatment protocols aimed at leveraging weight management to support liver disease recovery.
Semaglutide: A Promising Future for Liver Health
As the body of evidence supporting semaglutide’s role in liver health continues to expand, its potential implications for future treatments cannot be overstated. The successful reduction of liver inflammation and fat among patients highlights the drug’s capacity to go beyond diabetes and obesity management—ventures that could redefine patient outcomes for those with liver diseases. Such findings represent a promising avenue for developing comprehensive strategies aimed at tackling the complex interplay between metabolic health and liver functionality.
Moreover, the proactive exploration of semaglutide across specialized areas of metabolic health, including liver disease, signifies a broader recognition of the interconnected nature of these conditions. The collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare institutions stands to revolutionize therapeutic approaches, providing patients with options that were once viewed as limited. With continued research anticipated in the months and years ahead, semaglutide is positioned to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of liver disease treatments.
Adverse Effects and Considerations in Semaglutide Treatment
While semaglutide presents an innovative solution for treating fatty liver disease, understanding its potential adverse effects is crucial for patient management. Participants in clinical trials reported common side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and vomiting, which necessitates a comprehensive evaluation before initiating treatment. Adverse effects, while generally manageable, underline the importance of careful patient selection and monitoring during therapy.
Healthcare providers must weigh the benefits of semaglutide against these potential side effects when formulating treatment plans. Ensuring that patients are informed about possible experiences allows for better patient adherence and management during their treatment journey. With risk assessments in place, physicians can effectively navigate the intricacies of semaglutide treatment, enhancing the likelihood of successful outcomes in managing liver disease.
The Integration of Semaglutide into Holistic Liver Care Strategies
Incorporating semaglutide into comprehensive liver care strategies signifies a progressive approach to treating metabolic dysfunction and associated liver diseases. By focusing on the multifactorial aspects of liver health—including diet, exercise, and pharmacotherapy—healthcare professionals can optimize treatment efficacy while addressing patients’ broader health needs. The multidimensional benefits offered by semaglutide, particularly for patients struggling with both diabetes and liver conditions, illustrate the potential for cohesive care pathways.
Furthermore, as research continues to solidify semaglutide’s effects on liver health, its integration into standard treatment protocols might pave the way for enhanced patient outcomes. Holistic care strategies that embrace medication like semaglutide alongside lifestyle modifications provide patients with a robust framework for success. With an emphasis on collaborative care and continuous evaluation, the integration of semaglutide could lead to significant advancements in the management of liver diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of semaglutide injections in treating liver disease?
Semaglutide injections are primarily known for treating type 2 diabetes but have shown promising results in treating liver disease, specifically fatty liver disease and metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis (MASH). In clinical trials, semaglutide has been effective in reducing liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis, offering a new treatment avenue for patients suffering from serious liver conditions.
Can semaglutide help reduce liver inflammation in patients with fatty liver disease?
Yes, semaglutide has been shown to significantly reduce liver inflammation in patients with fatty liver disease. In a recent study, over 60% of participants administered semaglutide experienced improvements in liver inflammation compared to only 34.3% in the placebo group, indicating its efficacy as a liver inflammation treatment.
What benefits can semaglutide injections provide for those with metabolic dysfunction?
Semaglutide injections offer multiple benefits for individuals with metabolic dysfunction, including significant weight loss and improved liver health. Participants in clinical trials experienced a weight reduction of approximately 10.5%, alongside enhanced liver enzyme levels and reduced liver fat, which are crucial for reversing conditions like MASH.
Are there any side effects associated with semaglutide treatment for liver disease?
While semaglutide is effective in treating liver disease, it may cause side effects in some patients. Common adverse effects reported include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and vomiting. Patients should discuss these potential side effects with their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Is semaglutide effective for obesity-related liver disease?
Yes, semaglutide has proven effective for obesity-related liver disease. Clinical trials indicate that individuals with obesity and liver disease experienced improvements in liver fat and inflammation, along with substantial weight loss, showcasing the benefits of semaglutide as a dual treatment for obesity and related liver issues.
How does semaglutide compare to traditional treatments for liver diseases?
Semaglutide presents a new approach to treating liver diseases compared to traditional treatments, which often lack efficacy or are limited in options. The recent studies highlight semaglutide’s ability to specifically target and improve liver conditions, such as fatty liver disease and MASH, making it a valuable addition to existing treatment methods.
What results did clinical trials show for semaglutide in patients with liver disease?
In clinical trials, semaglutide was found to significantly improve liver health indicators in patients with liver disease. After 72 weeks of treatment, a majority of participants showed reduced liver fat and inflammation, with noteworthy improvements in liver fibrosis, marking a significant advancement in the treatment of severe liver conditions.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Treatment Efficacy | Semaglutide injections showed significant improvement in reversing severe liver disease (MASH) in a clinical trial. |
| Clinical Trial Overview | The study involved 800 participants across 37 countries receiving either semaglutide or a placebo. |
| Weight Loss | Participants treated with semaglutide experienced an average weight loss of 10.5%. |
| Results of Treatment | 62.9% of participants receiving semaglutide showed improvements in liver inflammation and fat accumulation. |
| Liver Fibrosis Improvement | 36.8% of the semaglutide group had improvements in liver fibrosis compared to 22.4% in the placebo group. |
| Adverse Effects | Common side effects included nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and vomiting. |
| Future Research | Ongoing studies aim to gather data from nearly 1,200 participants over five years for long-term impacts of semaglutide. |
Summary
Semaglutide liver disease has shown promising results in recent studies, marking a major breakthrough in treating severe liver conditions such as MASH. The clinical trial demonstrated that semaglutide not only reduces fat and inflammation in the liver but also indicates potential in improving liver fibrosis. As a treatment previously focused on type 2 diabetes and obesity, its efficacy against advanced liver diseases opens up new avenues for research and patient care. Ongoing investigations aim to solidify these findings and explore the long-term viability of semaglutide as a standard treatment for liver disease.




