Prostate Cancer Screening: When Should Men Start Testing?
Prostate cancer screening is a critical aspect of men’s health screening, especially as more individuals face alarming statistics like those surrounding former President Joe Biden’s prostate cancer diagnosis. With the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommending discussions about prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening for men aged 55 to 69, the conversation about prostate cancer guidelines has never been more relevant. Understanding the risk factors for prostate cancer is essential for making informed health decisions that could save lives. As experts dive into the specifics of these guidelines, there is an urgent emphasis on initiating timely discussions with healthcare providers. By exploring prostate cancer screening options, men can take proactive steps in managing their health and reducing potential risks associated with late-stage detection.
When considering the timing for prostate cancer testing, it is important to recognize the various approaches to prostate health evaluations. Discussions around PSA tests—a common procedure for detecting prostate abnormalities—have gained momentum, fueled by significant cases such as Biden’s recent cancer journey. The emerging dialogue on men’s health assessments encourages individuals, particularly those in the 55 to 69 age bracket, to speak with their doctors about screening options tailored to their health profiles. Furthermore, awareness of prostate cancer risk factors plays a crucial role in determining the need for screenings, making it vital for men to stay informed. Ultimately, the pressing need to engage in preventative discussions cannot be overstated, as these conversations underpin the measures to better manage prostate cancer outcomes.
Understanding Prostate Cancer Screening Guidelines
Prostate cancer screening is essential for early detection and better treatment outcomes, especially given the rising cancer diagnoses across the United States. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) outlines that men primarily between the ages of 55 and 69 should engage in discussions about prostate cancer screening with their healthcare providers. This proactive approach allows individuals to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening, ensuring decisions are tailored to their unique health situations.
On the other hand, for men aged 70 and older, the recommendations become less clear, with a general consensus suggesting that routine PSA screenings should not be standard practice. Experts argue that men in this age group face a higher risk of over-treatment due to the nature of prostate cancer, which often grows slowly and may not pose an immediate threat to longevity. These factors highlight the importance of personalized conversations between patients and healthcare professionals.
The Importance of PSA Screening for Men
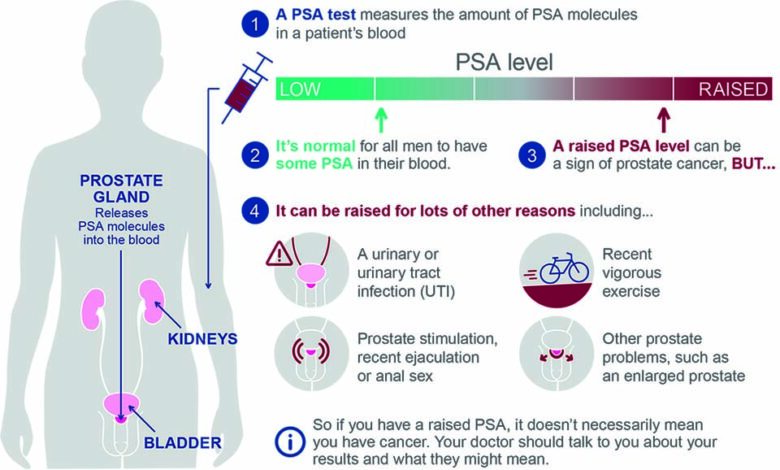
PSA screening plays a crucial role in the early detection of prostate cancer, enabling timely intervention. Despite the controversy surrounding its efficacy, particularly for older populations, it remains a vital tool for assessing prostate health. High levels of PSA can indicate the possibility of prostate cancer or other health conditions, prompting further investigation or monitoring. This is especially pertinent in the context of heightened awareness following notable cases, such as President Biden’s recent diagnosis.
Moreover, engaging in PSA screening is about empowering men to take charge of their health, especially as they age. The screening is recommended even for asymptomatic men who are at average risk. By initiating conversations with healthcare providers, patients can explore personal risk factors for prostate cancer, such as family history and lifestyle choices, to determine the need for this potentially life-saving screening. Early detection remains a critical strategy in fighting cancer and improving survival rates.
Assessing Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Understanding the risk factors for prostate cancer is essential for informed decision-making regarding screening. Factors such as age, ethnicity, and family history play significant roles in individual susceptibility. For instance, men over 50, especially African Americans, are at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer. Furthermore, men with a family history of the disease should consider discussing earlier screening options with their healthcare providers.
Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and obesity have been linked to increased risk levels. Engaging in healthy lifestyle choices not only aids in reducing the likelihood of cancer but also enhances overall well-being. Thus, recognizing these risk elements enables individuals to adopt proactive measures and initiate timely conversations surrounding prostate cancer screening.
Challenges in Prostate Cancer Screening
Despite the importance of screening, there are inherent challenges that complicate prostate cancer detection. One significant concern is the over-treatment of indolent cancers, which may not pose a threat to life. This has led experts to re-evaluate guidelines to avoid unnecessary interventions that can affect life quality. The dialogue among men regarding the necessity of screening is not only about cancer detection but about balancing potential harm and benefit.
Furthermore, healthcare providers face the challenge of navigating patient anxiety regarding prostate cancer. The recent spotlight on prostate cancer due to public figures like President Biden has heightened awareness, but it also amplifies fear. Thus, clear communication and supportive educational resources become critical in guiding patients through the decision-making process surrounding their health.
Men’s Health Screening Beyond Prostate Cancer
While prostate cancer screening is an essential aspect of men’s health, it is critical to view it within the broader context of overall health screening. Regular check-ups and screenings for conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension are vital to comprehensive health management. Men should schedule annual physicals that include discussions about prostate health, as well as other potential risk factors and screenings relevant to their age and lifestyle.
Additionally, men must be encouraged to participate in preventive health measures beyond cancer screening. This includes cardiovascular health assessments, mental health evaluations, and lifestyle counseling. By approaching men’s health screening holistically, healthcare providers can help reduce the risk of serious health issues and promote longer, healthier lives.
Consulting Healthcare Providers About Screening
The conversation around prostate cancer screening is pivotal, and healthcare providers play a critical role in guiding men through it. Given the variability in screening recommendations, especially for older adults and those with specific risk factors, consultation with a doctor is crucial. Such discussions can lead to a personalized screening strategy that considers individual health history and risk profiles, helping men make informed decisions.
Moreover, providers are tasked with not only facilitating discussions around PSA screening but also addressing the anxieties and misconceptions men may have about prostate cancer diagnoses. By fostering an environment of transparency and trust, healthcare professionals can empower men to prioritize their health, ultimately leading to higher screening rates and improved health outcomes.
Decisions on Screening for Older Adults
For older adults, particularly men over 70, the decision to engage in prostate cancer screening must be carefully considered. The USPSTF does not recommend routine screenings in this age group, yet individual clinical judgment is paramount. Factors such as the man’s overall health, life expectancy, and personal preferences should inform whether screening is pursued.
Additionally, men in this age bracket often face unique health challenges that can impact the effectiveness and necessity of treatment should cancer be detected. Hence, this demographic requires tailored discussions that prioritize quality of life alongside potential cancer treatment outcomes, emphasizing the importance of personalized healthcare.
The Future of Prostate Cancer Screening
As medical research continues to evolve, so too do the guidelines and practices surrounding prostate cancer screening. Emerging studies are increasingly focusing on the balance between screening benefits and risks, particularly as awareness grows among healthcare providers and the public alike. The hope is that future guidelines will better address the nuances of individual risk factors and lead to improved outcomes for men.
Looking ahead, advancements in technology and screening methods may also transform how prostate cancer is detected and monitored. Innovations such as genetic testing and imaging techniques can provide more precise assessments, potentially leading to targeted treatments that minimize the risk of over-treatment. As discussions around prostate cancer screening continue to evolve, staying informed will be critical for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Advocacy and Awareness in Prostate Cancer
With the recent diagnosis of high-profile figures like President Biden, advocacy and awareness efforts surrounding prostate cancer have gained significant traction. These events have sparked conversations on the importance of regular screenings and early detection as key preventive measures. Advocacy groups are working tirelessly to promote research, access to healthcare, and education about prostate cancer risk factors.
Increased awareness can empower men to take charge of their health by encouraging proactive engagement in health screenings. Public campaigns that target men’s health issues, including prostate cancer, are instrumental in breaking down stigmas and fostering open discussions about men’s health concerns. By uniting efforts towards education and advocacy, we can enhance the overall health outcomes for men nationwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is prostate cancer screening and who should consider it?
Prostate cancer screening includes methods like PSA screening that help detect prostate cancer early. Men aged 55 to 69 are advised to discuss the potential benefits and risks of PSA screening with their healthcare providers, considering individual health factors and risk factors for prostate cancer.
What are the current prostate cancer screening guidelines?
Current prostate cancer screening guidelines from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend shared decision-making regarding PSA screening for men aged 55 to 69, while generally advising against routine PSA screenings for men over 70, focusing on health and life expectancy.
How does PSA screening work in prostate cancer detection?
PSA screening measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood, which can indicate the presence of prostate cancer. However, elevated PSA levels can also result from non-cancerous conditions, so follow-up discussions with healthcare providers are essential.
What risks are associated with prostate cancer screening?
The risks associated with prostate cancer screening, particularly PSA screening, include the possibility of over-treatment, where men may undergo unnecessary procedures for cancers that would not have caused significant problems during their lifetime.
Why is there concern regarding prostate cancer screening after Biden’s diagnosis?
The concern stems from former President Biden’s aggressive prostate cancer diagnosis, highlighting the importance of ongoing discussions about prostate cancer guidelines and the necessity of early detection through PSA screenings, especially for men at high risk.
What factors influence the decision for prostate cancer screening in older men?
Factors influencing the screening decision for men over 70 include overall health, life expectancy, and individual risk factors for prostate cancer. It’s crucial for older men to consult their healthcare providers to weigh the pros and cons of screening.
Can asymptomatic men still benefit from prostate cancer screening?
Yes, asymptomatic men deemed at average risk for prostate cancer should engage in conversations about screening options. Prostate cancer screening can offer valuable insights into health, aiding preventive care.
What are the statistics regarding prostate cancer in men over 70?
Over 300,000 new prostate cancer cases are diagnosed annually in the U.S., raising awareness about the need for effective discussions on prostate cancer screening, including for men over 70 who may face unique risks and considerations.
How should men approach discussions about prostate cancer screening with their healthcare providers?
Men should prepare for discussions about prostate cancer screening by understanding their family history, any personal risk factors, and asking questions about the implications of PSA screening, its benefits, and associated risks.
Is prostate cancer screening important for men’s health?
Yes, prostate cancer screening plays a critical role in men’s health, especially for those in the target age groups. Early detection through PSA screening can reduce mortality risk and lead to better treatment outcomes.
| Age Group | Recommendation | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 55-69 years | Engage in discussions with healthcare providers about PSA screening risks and benefits | Individual health factors should guide decisions on whether to screen or not |
| Over 70 years | Generally not recommended for routine PSA screening | Screening should be individualized based on overall health and life expectancy |
| Asymptomatic men at average risk | Should discuss screening options with healthcare providers | Proactive measures can be crucial in preventive health care |
Summary
Prostate cancer screening is a crucial topic that men should consider, especially as they age. Experts recommend that men between the ages of 55 and 69 engage in discussions with their healthcare providers regarding the risks and benefits of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening. The guidelines emphasize that while screening can save lives, especially for those diagnosed early, treatment comes with risks, particularly for older individuals. Therefore, personalized discussions guided by health history and risk factors play a significant role in the decision-making process regarding prostate cancer screening.




