Pneumonia: Lessons from Val Kilmer’s Health Battle
Pneumonia is a formidable respiratory infection that has recently captured public attention due to the tragic passing of Val Kilmer, the beloved actor known for his iconic roles in films such as “Top Gun.” At the age of 65, Kilmer succumbed to pneumonia, a condition characterized by inflammation of the lung tissue that can be caused by bacteria or viruses. Pneumonia symptoms can range from mild to severe, often manifesting as a cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. The link between pneumonia and various health conditions, including Kilmer’s history of throat cancer, highlights the infection’s potential dangers. Understanding pneumonia treatment options and prevention strategies is crucial, particularly for those at higher risk.
Understanding the term “lung infection” encompasses the complexities of pneumonia, a serious ailment that affects numerous individuals each year. This respiratory condition can stem from various infectious agents, including bacterial strains such as Streptococcus pneumoniae as well as a spectrum of viral pathogens. Those experiencing symptoms of pneumonia often face significant health challenges, making timely medical attention imperative. The discussion around pneumonia, especially in cases involving high-profile figures like Val Kilmer, emphasizes its potential severity and the importance of preventive measures. With advancements in pneumonia treatment and public awareness, it becomes vital to recognize this condition’s implications on individual health.
Understanding Pneumonia: Causes and Risk Factors
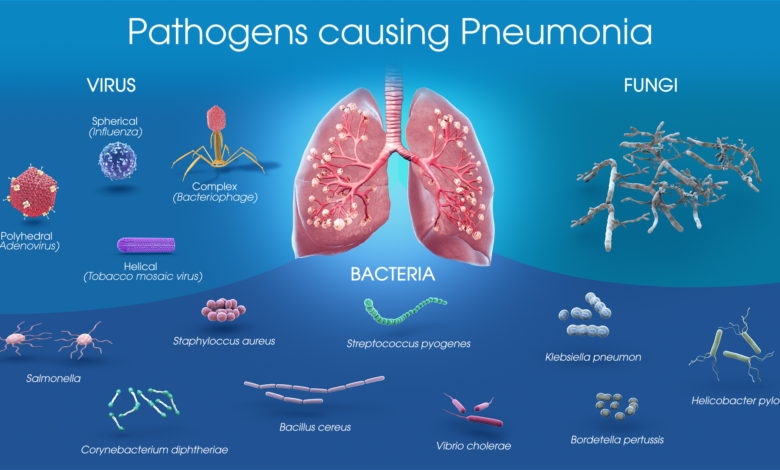
Pneumonia is a serious respiratory condition that can result from various infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It severely affects the lungs, causing inflammation and the accumulation of fluid or pus within lung tissue. The symptoms of pneumonia can range from a mild cough and fever to severe difficulty in breathing, making it crucial for individuals to be aware of the risk factors associated with this illness. Dr. Marc Siegel emphasizes that individuals with a compromised immune system, chronic health conditions, or recent illnesses, like those recovering from throat cancer, are particularly vulnerable to developing pneumonia.
Understanding the causes of pneumonia is essential in preventing its onset. Bacterial pneumonia, commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, is often more severe and requires prompt medical attention. Viral pneumonia may stem from infections like influenza and COVID-19 and, in some cases, can resolve without significant interventions. Awareness of one’s health status and the potential benefits of vaccination can help mitigate the risks associated with pneumonia.
Val Kilmer’s Battle with Pneumonia
The recent passing of Val Kilmer has spotlighted the devastating impact pneumonia can have, particularly for individuals with previous health battles like cancer. Kilmer’s death at 65 was linked to pneumonia, compounded by his earlier fight against throat cancer. His daughter, Mercedes, shared that pneumonia was ultimately the cause of his demise, emphasizing the importance of recognizing how underlying medical conditions can compromise the immune system. The impact of pneumonia, especially in someone with Kilmer’s medical history, illustrates the necessity for vigilance in managing respiratory health.
Val Kilmer’s story serves as a reminder that pneumonia can sometimes have fatal consequences, especially for high-risk patients. As the medical community highlighted, the type of pneumonia contracted can significantly influence recovery outcomes. For patients with recent or ongoing treatments for conditions like cancer, ensuring regular check-ups and monitoring lung health can be critical. The loss of such a beloved figure raises awareness about the dangers posed by pneumonia, encouraging individuals to remain informed about their health.
Bacterial vs. Viral Pneumonia: Key Differences
When discussing pneumonia, it is crucial to distinguish between bacterial and viral types as they differ in severity and treatment requirements. Bacterial pneumonia is often considered more serious, with higher mortality rates, especially among vulnerable populations like the elderly or those with chronic diseases. The presence of bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae can lead to aggressive onset symptoms. Dr. Siegel notes that the death rate from invasive pneumococcal disease can reach up to 20% in adults, underscoring the need for preventive measures like appropriate vaccinations.
In contrast, viral pneumonia typically arises from viral infections such as the flu or coronaviruses, including COVID-19. While still serious, viral pneumonia often resolves on its own, though it can progress to more severe conditions if not monitored closely. Understanding these differences not only helps in recognizing symptoms but also in guiding medical treatment and response, aiming for timely intervention to avoid complications.
Symptoms of Pneumonia: What to Look For
Awareness of pneumonia symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms commonly include persistent coughing, fever, chills, shortness of breath, and chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing. In some cases, individuals may experience confusion or fatigue, which can be more pronounced in older adults. Understanding these signs can empower patients and caregivers to seek immediate medical advice, especially in high-risk groups.
Additionally, distinguishing between the severity of symptoms can aid in identifying the type of pneumonia. A severe cough accompanied by green, yellow, or bloody mucus often suggests bacterial pneumonia, while milder cases may indicate viral pneumonia. Recognizing the signs early can not only facilitate faster treatment but also potentially reduce the risk of complications, supporting better health outcomes.
How is Pneumonia Treated? Options and Approaches
Treatment for pneumonia varies significantly depending on whether it’s bacterial, viral, or fungal. Bacterial pneumonia typically necessitates antibiotic treatment, which can effectively target the infection. In moderate to severe cases, hospitalization may be required for intravenous antibiotics and supportive care. Dr. Siegel advises that early diagnosis is crucial, especially for those at high risk such as older adults, patients with COPD, or those with weakened immune systems.
On the other hand, viral pneumonia may not require antibiotics and often involves rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. In more severe instances, antiviral medications may be considered. It’s essential for patients to follow healthcare provider recommendations and undergo follow-up evaluations to ensure adequate recovery and prevent recurrence.
The Importance of Vaccination Against Pneumonia
Vaccination plays a pivotal role in prevention, particularly against bacterial pneumonia. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend pneumococcal vaccines for individuals over 60 to reduce their risk of severe infections. The pneumococcal vaccine, specifically the effective version known as Prevnar, protects against various strains of the disease that could lead to fatalities. With the elevated risk of pneumonia in vulnerable populations, including those with underlying health issues, vaccination should be a prioritized health strategy.
In addition to pneumococcal vaccines, seasonal flu vaccinations can reduce the incidence of viral pneumonia cases. By protecting oneself from the flu, individuals can potentially lower their risk of developing pneumonia as a secondary infection. Public health initiatives that emphasize vaccination can significantly impact overall community health by lowering hospitalization rates and mortality associated with pneumonia.
Role of Lifestyle in Pneumonia Prevention
Lifestyle choices significantly influence an individual’s risk of developing pneumonia. Smoking, for instance, can weaken lung function and the immune system, making a person more susceptible to respiratory infections. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can boost immune health, while regular physical activity strengthens the lungs. Simple habits such as handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can also play crucial preventive roles.
Moreover, it’s essential for individuals with chronic illnesses to adhere to treatment regimens and have regular medical check-ups. Healthcare providers often suggest tailored strategies to manage existing health conditions, ultimately reducing the risk of pneumonia and other complications. Being proactive about one’s health can significantly contribute to preventing the onset of this serious disease.
Pneumonia in Vulnerable Populations: A Closer Look
Certain populations are at increased risk of pneumonia due to physiological or medical conditions. Young children, the elderly, and people with chronic illnesses or weakened immune systems face higher susceptibility to both bacterial and viral types of pneumonia. For instance, older adults often exhibit atypical presentations of pneumonia, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment. Their age-related decline in immune function necessitates vigilant health monitoring and preventive measures, such as regular vaccinations.
Additionally, individuals with conditions like COPD or diabetes should be particularly aware of pneumonia warnings. Education about the risk factors and prompt recognition of early symptoms can empower patients to seek timely medical assistance, fostering better outcomes. Support from healthcare providers becomes crucial in guiding these vulnerable groups toward effective preventive strategies, ensuring they understand their heightened risk and the importance of protective measures.
Long-term Effects of Pneumonia: What Survivors Should Know
Survivors of pneumonia often encounter lingering effects that impact their quality of life. Common post-pneumonia challenges include chronic cough, fatigue, and reduced lung function. It’s important for individuals recovering from pneumonia to incorporate pulmonary rehabilitation exercises to restore lung capacity and improve overall stamina. Understanding that recovery can be a lengthy process helps set realistic expectations for both patients and their families.
Moreover, some individuals may be at risk for developing recurrent pneumonia or other respiratory conditions following initial pneumonia infections. Continued monitoring and medical follow-up are vital for these patients. Those who’ve had severe cases, particularly elderly individuals or those with underlying conditions, might benefit from regular assessments to track lung health and prevent future complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is pneumonia and how does it affect the lungs?
Pneumonia is an infection in the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It leads to inflammation of lung tissue, resulting in fluid or pus accumulation that can impair breathing and cause cough, fever, and chest pain.
What are the common symptoms of pneumonia?
Common pneumonia symptoms include cough, fever, chills, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. Some patients also experience fatigue and loss of appetite. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective pneumonia treatment.
What types of pneumonia are there?
Pneumonia can be categorized into bacterial pneumonia, which is more severe and caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, and viral pneumonia, which typically resolves on its own and can be triggered by viruses like influenza or COVID-19.
How is bacterial pneumonia different from viral pneumonia?
Bacterial pneumonia is generally more serious, often requiring antibiotics, while viral pneumonia usually occurs due to viruses and may not need medical treatment. Bacterial pneumonia tends to have more severe symptoms and can lead to complications if not treated.
What are the treatment options for pneumonia?
Pneumonia treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection. Bacterial pneumonia often requires antibiotics, whereas viral pneumonia may only require rest and supportive care. Vaccines, such as the pneumococcal vaccine, can help prevent certain types of pneumonia.
How can pneumonia be prevented, especially in high-risk groups?
Preventing pneumonia includes vaccination, practicing good hygiene, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The CDC recommends the pneumococcal vaccine for individuals over 60 and those with chronic illnesses to improve immunity against bacterial pneumonia.
What role did pneumonia play in Val Kilmer’s health struggles?
Pneumonia was reported as the cause of death for Val Kilmer, who had a history of throat cancer. His weakened immune system may have made him more susceptible to severe pneumonia, highlighting the risks for individuals with underlying health conditions.
Are there any long-term effects of pneumonia that I should be aware of?
Some individuals may experience long-term effects after pneumonia, such as decreased lung function and breathlessness, particularly if they had severe cases. Early and effective pneumonia treatment is important to minimize potential long-term health issues.
What should I do if I suspect I have pneumonia?
If you suspect you have pneumonia, seek medical attention promptly. Symptoms like a persistent cough, chest pain, or difficulty breathing warrant a visit to a healthcare provider for diagnosis and appropriate pneumonia treatment.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Val Kilmer’s death | Val Kilmer, renowned actor known for roles in “Top Gun” and “Batman Forever,” died at 65 from pneumonia. |
| What is pneumonia? | An infection in the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, leading to inflammation and fluid accumulation. |
| Types of pneumonia | Bacterial pneumonia is more severe and can result from pneumococcus bacteria. Viral pneumonia usually resolves on its own. Fungal pneumonia is rare but serious. |
| Risk factors | Risks increase with age, chronic illnesses, and a compromised immune system. |
| Treatment and prevention | Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial, especially for high-risk patients. Vaccination is recommended for those over 60. |
Summary
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can be life-threatening, particularly for individuals with existing health issues. The recent death of Val Kilmer due to pneumonia highlights the severity of this infection. Understanding the types, risks, and preventive measures can aid in safeguarding health, especially for vulnerable populations. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment remain key in the fight against pneumonia.




