Omega Fatty Acids: A Key to Protecting Women from Alzheimer’s
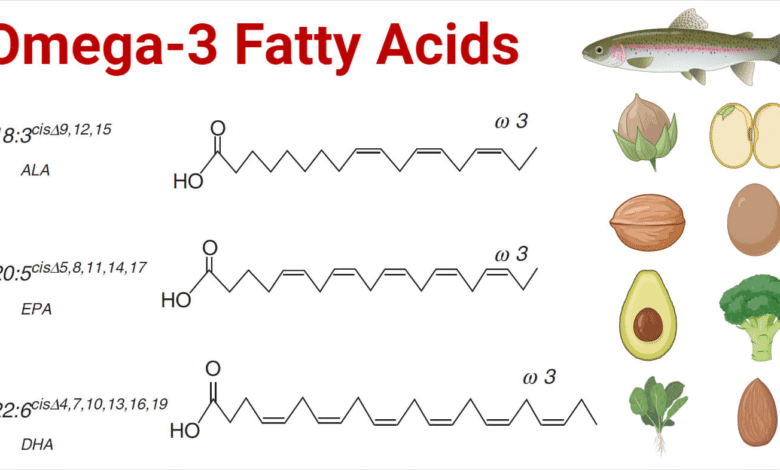
Omega fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in maintaining overall health, particularly for women. Recent studies have revealed a significant link between omega fatty acids and Alzheimer’s disease, indicating that these vital unsaturated fats could help protect women from this debilitating condition. Research conducted by King’s College London found that women diagnosed with Alzheimer’s exhibited lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids and other unsaturated fats when compared to their healthy counterparts. This finding sheds light on the importance of omega fatty acids in promoting brain health and understanding the gender disparities in Alzheimer’s prevalence. Incorporating sources rich in these fatty acids into the diet can be particularly beneficial not only for brain function but also for women’s health in general, paving the way for better nutritional strategies to combat neurological diseases.
Essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3 and omega-6, are gaining recognition for their potential contributions to cognitive health and disease prevention. These polyunsaturated fats are not only vital for brain function but are also implicated in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, which disproportionately affects women. Recent findings suggest that women may benefit significantly from incorporating sources of these healthful lipids, underscoring the importance of understanding how dietary fats influence physiological processes. Moreover, research surrounding lipid profiles in individuals with Alzheimer’s highlights the disparities in fat metabolism between genders, suggesting a need for further exploration into tailored dietary recommendations. Emphasizing the significance of healthy fats in our diets fosters a greater understanding of their role in enhancing brain health and possibly reducing the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
Understanding Omega Fatty Acids and Brain Health
Omega fatty acids, particularly omega-3, have been shown to play a crucial role in brain health. These essential fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which may help protect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Research has demonstrated that diets rich in omega-3s can support cognitive function and may even slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, particularly in women, who face a higher risk of developing the condition.
The connection between omega fatty acids and brain health is reinforced by evidence suggesting that women with Alzheimer’s often have lower levels of these beneficial fats. Unsaturated fats, including omega-3, are vital for maintaining neuronal integrity and promoting effective communication between brain cells. Therefore, ensuring an adequate intake of omega fatty acids through dietary sources like fatty fish can be a crucial strategy to bolster brain health in women.
The Impact of Unsaturated Fats on Women’s Health
Unsaturated fats, particularly omega fatty acids, are essential for maintaining overall women’s health, with significant implications for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. Studies have shown that these healthy fats help to regulate cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and improve heart health—all vital for women as they age. Incorporating foods high in unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can support not just cardiovascular well-being but also cognitive functions.
Moreover, the benefits of omega fatty acids go beyond general health. The lower concentrations of these fats found in women with Alzheimer’s suggest that dietary improvements may provide a preventative measure against cognitive decline. Educating women about the importance of omega-3s and encouraging dietary change is essential, as it may empower them to take charge of their brain health while decreasing the risk of Alzheimer’s.
Alzheimer’s Disease: Gender Differences in Fatty Acid Levels
The alarming data revealing that approximately two-thirds of Americans with Alzheimer’s disease are women underscores the need for a closer look at gender differences in fat metabolism. Recent studies have found that while both men and women can develop Alzheimer’s, women exhibit lower levels of protective unsaturated fats, which may explain their heightened vulnerability. Understanding the biological mechanisms behind these differences is crucial for developing tailored preventive strategies and treatments.
Research, including that from King’s College London, indicates that the lipid profiles of women with Alzheimer’s exhibit significantly diminished omega fatty acid concentrations, compared to their male counterparts. This insight emphasizes the importance of incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into the diet early in life, particularly for women, to mitigate the risks associated with cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
Dietary Recommendations for Increasing Omega-3 Intake
To combat the alarming trends regarding Alzheimer’s disease in women, it is recommended that women prioritize their diet to include sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources and should be included at least twice a week. Additionally, plant-based omega-3 sources, such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, can be beneficial for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Incorporating omega-3 supplements could also provide an essential boost, especially for those who struggle to consume sufficient quantities from food sources. By being proactive about their dietary choices, women can potentially enhance their brain health and reduce the risk factors associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Moreover, blending these dietary habits with regular physical activity and cognitive exercises can yield an overall healthier lifestyle.
The Role of Omega-3s in Alzheimer’s Research
Ongoing research into omega-3 fatty acids continues to shed light on their potential protective effects against Alzheimer’s disease. Studies are increasingly focused on understanding the specific mechanisms through which omega-3s impact neuroprotection and cognitive health. The correlation between lower levels of these unsaturated fats and the prevalence of Alzheimer’s in women strengthens the case for omega-3s as a focal point in Alzheimer’s research moving forward.
Efforts are underway to investigate how early interventions involving omega-3 supplementation may alter disease trajectories for at-risk populations. Future clinical trials will likely explore not only the effectiveness of omega-3s in improving cognitive function but also their potential role in reducing the onset of Alzheimer’s. This research could provide invaluable insights into how dietary fats influence brain health and the importance of nutrition in mitigating the risks of neurodegenerative diseases.
Fatty Acids and Inflammation: A Connection to Alzheimer’s
Inflammation has long been recognized as a contributing factor in Alzheimer’s disease progression. Omega fatty acids possess anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce neuroinflammation associated with brain health deterioration. By lowering inflammation levels, omega-3s may improve neuronal survival and function, underscoring the potential of these fats in Alzheimer’s treatment protocols.
The research from King’s College London highlights the dysregulation of fatty acids in women with Alzheimer’s, showing a prevalence of saturated fats—often considered ‘bad’ fats—compared to the protective effects of omega fatty acids. This underscores the importance of reducing inflammation through a balanced intake of healthy fats in one’s diet, thereby presenting a natural strategy to combat cognitive decline in women.
Clinical Implications of Omega Fatty Acids in Alzheimer’s Treatment
The clinical implications of understanding omega fatty acids in the context of Alzheimer’s disease extend into personalized medicine. By recognizing that women present distinct lipid profiles in relation to Alzheimer’s, healthcare providers can tailor nutrition and treatment plans aimed at increasing the intake of beneficial fats. This approach could significantly enhance the overall management of Alzheimer’s disease.
As evidence builds around the protective effects of fatty acids, clinicians are called to integrate dietary counseling focused on omega-3 intake within their therapeutic frameworks. Creating awareness about the importance of omega fatty acids and encouraging routine monitoring of lipid profiles in women could empower patients to manage their risks more effectively while enhancing their cognitive health.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Brain Health in Women
Modifying one’s lifestyle to support brain health can be a crucial step in reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, particularly among women. In addition to dietary changes that include omega-3 fatty acids, incorporating regular exercise, mental stimulation, and social engagement can significantly enhance cognitive resilience. These lifestyle changes not only promote overall well-being but also specifically target the risk factors associated with neurodegeneration.
Women are encouraged to embrace a holistic approach to their health by weaving together a nutrient-rich diet, regular physical activity, and practices that foster mental acuity. Activities such as reading, puzzles, creative arts, and social interaction can engage the brain, protect cognitive function, and support mental health. Together, these strategies offer a comprehensive framework for enhancing brain health and potentially warding off Alzheimer’s disease.
Future Directions in Omega Fatty Acids Research
Looking ahead, future research is poised to explore deeper insights into the relationship between omega fatty acids and Alzheimer’s disease. Scientists are particularly interested in deciphering how these essential fats influence neurotransmitter function, neuronal health, and systemic inflammation in the context of gender disparities. Understanding these dynamics will be crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies tailored to both men and women.
In addition to clarifying the mechanisms of omega-3 action in the brain, research will likely expand to include long-term studies to monitor dietary intake and its impact on cognitive health over time. As research continues to evolve, integrating findings on omega fatty acids can be instrumental in defining dietary guidelines and clinical practices aimed at reducing the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease among women.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are omega fatty acids and their role in brain health?
Omega fatty acids, particularly omega-3s, are essential unsaturated fats known to support brain health. They play a crucial role in maintaining cellular structure and function, potentially lowering the risk of cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
How do omega fatty acids impact women’s health specifically in relation to Alzheimer’s disease?
Research indicates that omega fatty acids may protect women from Alzheimer’s disease, addressing the higher prevalence of the disorder among women. Women with Alzheimer’s had significantly lower levels of these healthy fats, suggesting that they are vital to brain health and preventing neurodegeneration.
What foods are good sources of omega fatty acids for supporting brain health?
Healthy sources of omega fatty acids include fatty fish like salmon, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and various supplements. Incorporating these foods into the diet can help improve brain health and potentially reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Why are women more affected by Alzheimer’s disease in relation to omega fatty acids?
Studies show that women diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease tend to have lower levels of omega fatty acids, which are essential for brain health. Understanding the biological differences in lipid profiles between men and women is crucial for developing targeted strategies against Alzheimer’s.
Can omega-3 benefits extend to improving overall brain function?
Yes, omega-3 fatty acids are linked to several omega-3 benefits, including enhancing cognitive function, memory, and concentration. These healthy fats support brain structure and may contribute to overall mental well-being.
What is the connection between unsaturated fats like omega fatty acids and brain inflammation?
Omega fatty acids are classified as unsaturated fats that can be anti-inflammatory. Research suggests that a lack of these beneficial fats may increase brain inflammation, which is a contributing factor in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Should women consider omega fatty acid supplements for Alzheimer’s prevention?
Given the findings linking lower levels of omega fatty acids to Alzheimer’s in women, considering supplements could be beneficial. However, it is advisable to consult healthcare providers for personalized recommendations.
How can lifestyle changes related to diet influence Alzheimer’s disease outcomes in women?
Adopting a diet rich in omega fatty acids, along with other healthy lifestyle changes, may potentially reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease in women. This highlights the importance of nutrition in long-term cognitive health.
What ongoing research is being conducted around omega fatty acids and Alzheimer’s disease?
Current research aims to explore how early in life omega fatty acid deficiencies may occur in women and their relationship to Alzheimer’s disease, as scientists work to better understand the mechanisms at play.
Are there any specific studies highlighting the role of omega fatty acids in Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, a significant study from King’s College London highlighted the biological differences in lipid levels, including omega fatty acids, between female Alzheimer’s patients and those without the disease, emphasizing the need for further exploration.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Connection between Omega Fatty Acids and Alzheimer’s | A study found women with Alzheimer’s have lower levels of omega fatty acids compared to healthy women. |
| Research Institutions | The study was conducted by King’s College London and Queen Mary University of London. |
| Lipid Study Details | Researchers analyzed plasma samples from 841 Alzheimer’s patients using mass spectrometry. |
| Difference in Lipid Levels | Findings suggest a significant increase in saturated lipids (unhealthy) among female Alzheimer’s patients. |
| Statistical Context | Approximately two-thirds of Alzheimer’s patients in the U.S. are women, with about 4.2 million women aged 65+ affected. |
| Health Recommendations | Experts recommend women include omega fatty acids in their diet through foods like fatty fish or supplements. |
| Future Research Directions | Further studies are needed to understand the mechanisms behind the differences in lipid levels and its impact on Alzheimer’s. |
Summary
Omega fatty acids play a crucial role in protecting against Alzheimer’s disease, particularly for women who are disproportionately affected by the condition. A recent study highlighted a direct link between lower levels of omega fatty acids and the prevalence of Alzheimer’s in women. This research emphasizes the importance of incorporating omega fatty acids into the diet to potentially mitigate the risk of developing neurological conditions. Understanding the biological differences and dietary needs of women regarding omega fatty acids could pave the way for more tailored treatments in the future.




