Obesity-Related Cancer Deaths Surge in the U.S.
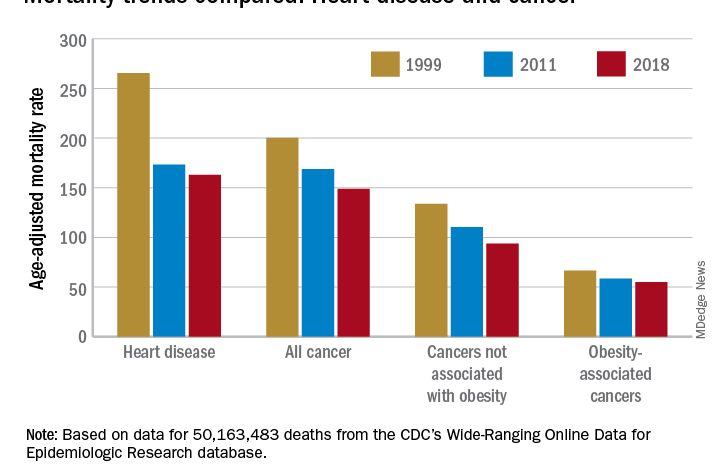
Obesity-related cancer deaths have increasingly become a serious public health concern in the United States, with the figure rising dramatically from 3.73 million to 13.52 million over the past two decades. This alarming trend underscores the profound connection between obesity and cancer, as excess body weight is now implicated in several chronic conditions, including hypertension, diabetes, and various forms of cancer that significantly contribute to cancer mortality rates. According to recent research presented at ENDO 2025, certain demographics, particularly older adults, females, and racial minorities, are at a heightened risk for these types of cancers. The Midwest experiences the highest rates of obesity-related cancer deaths, highlighting disparities that necessitate immediate public health strategies to combat this crisis. Weight loss and cancer prevention initiatives are essential components in addressing the explosion of obesity-related cancer cases, and comprehensive actions are required to improve health outcomes.
The rise in mortality associated with cancers linked to excess body weight is drawing attention to an urgent health issue that demands focused intervention. Terms like overweight-related malignancies and weight-induced cancer fatalities are gaining ground in discussions about chronic health conditions tied to obesity. As studies reveal the multifaceted nature of the relationship between obesity and various cancer types, it becomes increasingly evident that addressing lifestyle factors is crucial for effective cancer prevention strategies. Public health advocates emphasize the need for comprehensive approaches that not only target weight management but also promote healthier living. By integrating weight loss and cancer prevention efforts, the health community can tackle this formidable public health challenge.
The Rise of Obesity-Related Cancer Deaths in the U.S.
Obesity-related cancer deaths have seen a staggering increase in the United States, rising from just 3.73 million to 13.52 million in the span of two decades. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for awareness and intervention around the crisis of obesity and its direct correlation with increased cancer mortality rates. Research indicates that obesity not only amplifies the risk of certain cancers but also exacerbates chronic conditions such as hypertension and diabetes, which can further complicate treatment outcomes for cancer patients.
The findings presented by Dr. Mohamed Bakr and colleagues reveal that the burden of obesity-related cancer deaths is not evenly distributed. Older adults, racial minorities, and women are particularly at risk, indicating a need for targeted public health strategies. Notably, the Midwest has emerged as an area of concern, showcasing the highest rates of obesity-related cancer mortality. Efforts to combat this trend must be multifaceted, involving initiatives aimed at improving dietary habits, enhancing physical activity levels, and providing better access to health care.
Understanding the Link Between Obesity and Cancer
Extensive research indicates a strong link between obesity and the development of various cancers, including breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer, among others. Fat cells produce inflammatory cytokines that can lead to metabolic disruption and immune dysfunction, creating an environment conducive to cancer proliferation. This biological pathway underscores the importance of understanding how chronic conditions and obesity interconnect to affect not only individual health but also broader public health outcomes.
Given the alarming trends in cancer prevalence among obese individuals, it is crucial to focus on preventive strategies. Health experts advocate for lifestyle changes that include maintaining a healthy body weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise. These changes can drastically reduce the risk of developing obesity-related cancers, emphasizing that proactive measures are better than treatment interventions post-cancer diagnosis.
Public Health Strategies to Tackle Obesity and Cancer
The rising incidence of obesity-related cancer deaths necessitates the implementation of robust public health strategies. Experts suggest that early screenings and increased access to care are fundamental in high-risk areas. Additionally, educational initiatives around nutrition and physical activity can foster healthier lifestyle choices among populations at risk. Public health campaigns must aim to create supportive environments that promote active living, especially in rural and underserved regions.
Furthermore, health authorities should consider policies that address the availability of healthier food options and ensure that communities have the resources they need to make informed choices. By integrating these strategies into community health programs, we can work towards effectively reducing obesity rates and, consequently, the associated cancer mortality rates.
Chronic Conditions and Their Impact on Cancer Risk
Chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease are often found alongside obesity, compounding the risks associated with cancer. Recent studies have drawn a direct correlation between these chronic illnesses and increased cancer mortality rates, highlighting the necessity for integrated care approaches that address obesity as a critical factor in overall health. Managing these conditions not only improves quality of life but also potentially curtails the risk of developing obesity-linked cancers.
Health professionals continue to emphasize the importance of holistic treatment plans that consider the interplay between weight management, chronic conditions, and cancer prevention. Offering support for lifestyle changes can empower individuals to take charge of their health, ultimately reducing both obesity rates and the burden of chronic diseases that contribute to cancer risk.
Weight Loss as a Strategy for Cancer Prevention
Weight loss has been identified as a pivotal strategy in reducing cancer risk, particularly for those at high risk of obesity-related cancers. Studies show that shedding excess weight can lower levels of inflammatory markers in the body, which are linked to cancer development. By promoting healthy eating and regular physical activity, we can combat obesity while simultaneously reducing cancer risk factors.
Medical advancements, such as weight loss medications like GLP-1 drugs, have also emerged as promising tools in the fight against obesity and related cancers. These medications can assist individuals in achieving sustainable weight loss, thereby minimizing inflammation and potentially decreasing the likelihood of cancer onset. It’s crucial for individuals at risk to consult healthcare professionals to explore effective weight loss strategies tailored to their unique health conditions.
The Role of Preventive Healthcare in Reducing Cancer Risks
Preventive healthcare plays an indispensable role in decreasing the incidence of cancer associated with obesity. Regular check-ups and screenings can aid in early detection of health issues before they evolve into serious complications. The importance of routine cancer screenings cannot be overstated, as they can identify potential cancers at an earlier, more treatable stage, especially in individuals with higher obesity-related risks.
Additionally, engaging patients in preventive discussions about the link between obesity and cancer can empower them to make informed decisions regarding their health. Healthcare providers should prioritize preventative care strategies, fostering a culture that values early intervention and lifestyle modifications to lower the cancer burden associated with obesity.
Emerging Research on Obesity, Diabetes, and Cancer Linkages
New research continues to unveil the complex relationship between obesity, diabetes, and cancer. Recent findings suggest that the inflammatory pathways activated by excess fat can lead to insulin resistance, which is a crucial factor in the progression of several malignancies. Understanding these mechanisms allows researchers and healthcare professionals to develop more targeted interventions that not only address weight management but also aim to improve metabolic health.
As more studies emerge to elucidate this connection, it becomes increasingly important for healthcare providers to incorporate this knowledge into treatment and prevention strategies. Promoting metabolic health through effective weight loss techniques and diabetes management can contribute significantly to reducing cancer risk in obese patients.
The Importance of Nutritional Education in Cancer Prevention
Nutritional education is a cornerstone of effective public health strategies aimed at preventing obesity and, subsequently, obesity-related cancers. By equipping individuals with knowledge about healthy eating habits, portion control, and nutrient-rich foods, we can foster healthier lifestyles that can mitigate cancer risks. Educational campaigns targeted at both schools and communities can help instill these principles from a young age.
Moreover, integrating nutrition education into healthcare practices can enhance patient engagement and reinforce the importance of healthy living. Healthcare professionals should advocate for comprehensive nutritional guidance as part of routine care, enabling patients to make informed dietary choices that can significantly impact their weight and cancer risk.
Advocating for Healthier Food Environments
Creating healthier food environments is essential for combating obesity and reducing cancer risks. Improving access to nutritious foods and ensuring that healthy choices are readily available in all communities can help individuals make better dietary decisions. Public policies that seek to limit the availability of highly processed, unhealthy foods—especially in schools and low-income neighborhoods—are crucial in this fight.
Additionally, community programs that promote local agriculture, such as farmers’ markets and community gardens, can empower individuals to choose healthier options. By fostering environments where nutritious foods are accessible and affordable, we can significantly impact obesity rates and, consequently, obesity-related cancer mortality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of obesity-related cancer deaths on public health?
Obesity-related cancer deaths pose a significant public health challenge, with mortality rates increasing dramatically from 3.73 million to 13.52 million between 1999 and 2020. This surge underscores the urgent need for public health strategies aimed at reducing obesity and its correlation with cancer mortality rates.
How does obesity increase the risk of cancer mortality?
Obesity has been associated with a higher risk of developing 13 types of cancer, including breast, colon, and pancreas cancer. Individuals with obesity experience chronic inflammation, leading to immune disruption, which can significantly elevate cancer mortality rates.
What steps can be taken to prevent obesity-related cancer deaths?
Preventive strategies include maintaining a healthy body weight through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and early cancer screenings. Public health initiatives should focus on improving access to nutritious foods and promoting active lifestyles to combat obesity-related cancer deaths.
What are the statistics surrounding obesity and cancer in the U.S.?
Recent studies show that obesity-related cancer deaths in the U.S. have quadrupled in the past two decades, with particular increases among older adults, women, and racial minorities. These statistics highlight the pressing correlation between obesity and increasing cancer mortality rates in the population.
What public health strategies are effective in reducing obesity-related cancer deaths?
Effective public health strategies entail implementing early screenings, enhancing access to care, and providing nutritional education. These strategies aim to address obesity comprehensively, thereby reducing obesity-related cancer deaths and chronic conditions associated with it.
What types of cancer are most commonly linked to obesity?
Obesity is linked to several cancers, including breast cancer (post-menopausal), colon and rectal cancers, and pancreatic cancer. Recognizing these associations can help in developing targeted prevention strategies for obesity-related cancer deaths.
How can weight loss impact cancer prevention?
Weight loss plays a critical role in cancer prevention by reducing inflammation caused by excess fat. This can lower the risk of developing obesity-related cancers and ultimately reduce cancer mortality rates associated with obesity.
What role do new therapies play in combating obesity-related cancer risks?
New therapies, including GLP-1 medications, have shown promise in reducing cancer risk among obese individuals. Such advancements represent significant medical progress in managing obesity and mitigating obesity-related cancer mortality.
How do demographic factors influence obesity-related cancer death rates?
Demographic factors such as age, gender, and race significantly influence obesity-related cancer death rates. Older adults, women, and certain racial minorities exhibit higher risks, which necessitates tailored public health interventions to adequately address these disparities.
Why is obesity considered a serious public health threat in relation to cancer?
Obesity is viewed as a serious public health threat due to its profound link to increased cancer mortality rates. The rising prevalence of obesity and its association with numerous chronic conditions further amplify the urgency to address this crisis.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Surge in Obesity-related Cancer Deaths | Obesity-related cancer deaths in the U.S. increased from 3.73 million to 13.52 million between 1999 and 2020. |
| Research Background | Study conducted by researchers at Jersey Shore University Medical Center and presented at ENDO 2025. |
| At-Risk Populations | Older adults, females, and racial minorities have a higher risk of obesity-related cancer deaths. |
| Geographic Disparities | Midwest has the highest rates of obesity-related cancer deaths; Northeast has the lowest. |
| Types of Cancer Associated with Obesity | Includes 13 types, like breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer. |
| Recent Trends | Obesity-related cancer mortality tripled in the U.S. with the most significant increase between 2018 and 2020. |
| Preventive Strategies | Encouraging healthy weight through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and access to care. |
| Medical Advancements | GLP-1 drugs linked to reduced cancer risk, according to some medical professionals. |
Summary
Obesity-related cancer deaths have reached alarming numbers in the U.S., increasing significantly over the past two decades. The data highlights the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to combat this public health crisis, emphasizing the importance of targeted screenings, healthcare access for at-risk populations, and lifestyle modifications to reduce obesity rates. It’s imperative that we address obesity not only as a condition but as a critical risk factor for various cancers, ensuring that future public health initiatives prioritize education and preventive measures.




