High Blood Pressure: New Guidelines for Prevention and Care
High blood pressure, often referred to as hypertension, is a pervasive health issue affecting nearly half of U.S. adults. Recognized as a silent killer, it poses serious risks to heart health and can lead to severe complications if left unchecked. Recent high blood pressure guidelines from the American Heart Association recommend proactive measures to prevent high blood pressure and ensure early treatment for those already affected. Individuals are encouraged to adopt a healthy lifestyle for blood pressure management, which can significantly minimize the adverse effects of high blood pressure on overall health. By understanding and implementing these new recommendations, patients can take charge of their well-being and reduce their risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Hypertension is a critical health concern that often goes unnoticed until serious complications arise. This condition is frequently described as elevated arterial pressure, which can lead to heart disease or stroke if not adequately managed. The latest recommendations focus not only on the adjustment of treatment strategies but also on lifestyle changes that are essential for maintaining optimal health. Individuals are urged to follow established guidelines, which include diet modifications and regular physical activity, to mitigate the risks associated with elevated pressure levels. By prioritizing a holistic approach to cardiovascular health, experts hope to undo the increasing trend of hypertension among adults.
Understanding High Blood Pressure and Its Risks
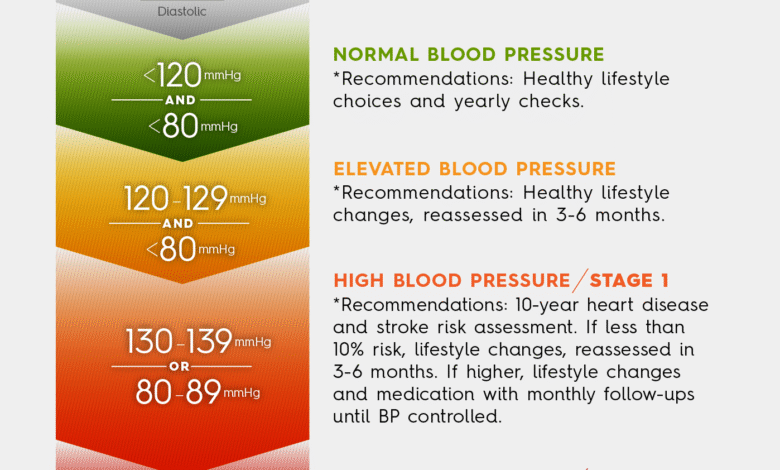
High blood pressure, often dubbed the ‘silent killer,’ affects nearly half of U.S. adults today, significantly increasing their risk of developing heart disease and stroke. This condition develops gradually and may go unnoticed for years, leading to severe health complications if left unmanaged. According to the latest guidelines from reputable organizations such as the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American College of Cardiology (ACC), addressing high blood pressure early is crucial in minimizing potential damage. Implementing preventative measures, such as regular screening and lifestyle modifications, is essential for maintaining heart and brain health.
The effects of high blood pressure extend beyond just physical health; they can also influence mental well-being. Recent studies suggest a strong link between uncontrolled blood pressure and cognitive decline, including dementia. This connection underscores the need for effective high blood pressure treatment and the importance of adhering to blood pressure guidelines, as these are not only pivotal for physical health but also for preserving cognitive function as we age.
New Guidelines for Managing High Blood Pressure
The updated high blood pressure guidelines represent a significant shift in the medical approach to this condition. No longer is there a one-size-fits-all strategy. Instead, the introduction of the PREVENT tool allows healthcare professionals to assess an individual’s long-term cardiovascular risk by considering various factors beyond just blood pressure. These factors include cholesterol levels, metabolic health, and even geographic location. Such a comprehensive assessment paves the way for tailored interventions that are more likely to yield effective results in managing high blood pressure and preventing future heart-related events.
One of the most transformative recommendations in the new guidelines emphasizes early intervention; this may involve starting patients on blood pressure medications sooner than in the past. The shift away from merely suggesting limited alcohol consumption to advocating for abstinence reflects a deeper understanding of how alcohol impacts individual blood pressure levels. This approach not only aims to lower hypertension but also to educate patients on making informed lifestyle choices that align with their cardiovascular health objectives.
Leading a Healthy Lifestyle to Prevent High Blood Pressure
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is a proven method for preventing high blood pressure and maintaining overall well-being. Key components of this lifestyle include eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. The guidelines recommend a dietary intake emphasizing low-fat dairy and plenty of nuts and seeds, which are beneficial for heart health. Regular physical activity, alongside these dietary changes, is critical in preventing hypertension and enhancing cardiovascular function.
Moreover, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise not only helps prevent high blood pressure but also alleviates stress on the heart. Lifestyle modifications such as reducing sodium intake from 2300 mg to 1500 mg per day are essential facets of the updated guidelines aimed at curbing hypertension. By integrating these practices into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of high blood pressure and its associated health complications.
The Role of Nutrition in Blood Pressure Control
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in managing high blood pressure and preventing its onset. Recent guidelines stress the importance of a heart-healthy diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Incorporating more vegetables, fruits, and legumes into meals, along with whole grains and fish, not only promotes overall health but also directly influences blood pressure levels. Such dietary habits are linked with improved cardiovascular health and can significantly reduce the need for medication.
Additionally, moderation in food choices—like opting for non-tropical oils and limiting saturated fats from animal products—can further support blood pressure management. The emphasis on nutrient-rich, low-sodium diets is a central theme in the latest blood pressure guidelines, illustrating how nutrition fortifies the body’s defense against hypertension and its damaging effects.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection of high blood pressure is critical in thwarting long-term health complications. Regular blood pressure screenings are recommended as part of preventive healthcare, ensuring that individuals are aware of their levels and can take actionable steps to address any concerns. The new guidelines advocate for timely medical interventions, allowing for prompt treatment before serious conditions arise. Awareness of personal health metrics can empower individuals to embrace preventative measures, ultimately reducing the burden of hypertension-related diseases.
Incorporating lifestyle modifications, along with early medical treatment, is essential in successfully managing blood pressure. New advancements in treatment options, including newer medications and prevention strategies, illustrate the evolving nature of high blood pressure management. As clinicians are urged to act sooner, patients must also recognize the importance of being proactive in their health journey, focusing on early detection to mitigate risks associated with high blood pressure.
The Impact of Alcohol on Blood Pressure
Recent guidelines have shifted the perspective on alcohol consumption in relation to high blood pressure. Instead of merely recommending limited intake, experts now advocate for complete abstinence, particularly for those at risk of hypertension. This significant change underscores the need for individuals to understand the intricate ways in which alcohol can impact their blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health. Educational initiatives are crucial in helping patients navigate their relationship with alcohol, encouraging them to make healthier choices.
Furthermore, for those who do choose to drink, the guidelines suggest moderation: less than one drink per day for women and less than two drinks for men. Understanding the unique effects that alcohol can have on blood pressure is critical for informed decision-making. Such focused recommendations aim to not only prevent high blood pressure but also to promote a more holistic approach to heart health.
Blood Pressure Management During Pregnancy
Managing blood pressure during pregnancy is critical for the health of both mother and child. The updated guidelines highlight the unique challenges that expectant mothers face, as hypertension during pregnancy can lead to serious complications such as preeclampsia. Thus, it is vital for pregnant women to prioritize regular monitoring and maintain healthy lifestyle choices to mitigate risks. Emphasizing a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and routine check-ups are essential elements of effective blood pressure management in pregnancy.
Moreover, healthcare providers are encouraged to implement tailored strategies that account for the physical changes and heightened risks associated with pregnancy. Adopting holistic approaches that incorporate medical monitoring alongside lifestyle advice can help manage blood pressure effectively during this critical period. This proactive approach not only protects the mother’s health but also fosters optimal development for the baby.
Long-Term Health Benefits of Controlling Blood Pressure
Aggressively managing high blood pressure can yield significant long-term health benefits. Studies demonstrate that individuals who effectively control their hypertension can greatly reduce their risks of developing cardiovascular diseases, strokes, and cognitive decline associated with aging. The updated guidelines stress the importance of maintaining vigilance against high blood pressure throughout one’s life, emphasizing that early intervention can help prevent serious health issues later.
Additionally, research suggests that individuals who take steps to lower their blood pressure early in life may better preserve their cognitive abilities as they age. This connection between blood pressure management and mental sharpness highlights the intertwined nature of cardiovascular and cognitive health, reinforcing the need for comprehensive strategies that focus on both physical and mental well-being.
Regular Monitoring and Its Role in Blood Pressure Control
Regular monitoring of blood pressure is a cornerstone of effective hypertension management. Keeping track of blood pressure levels allows individuals and healthcare providers to identify any concerning trends early on, facilitating timely interventions that can make a significant difference in health outcomes. The guidelines encourage patients to adopt a proactive stance by regularly measuring their blood pressure at home and attending routine check-ups with their physicians.
Moreover, fostering open communication between patients and healthcare providers regarding monitoring results can enhance treatment strategies and ensure that personal health goals are aligned with evidence-based guidelines. This collaborative approach empowers patients, giving them greater control over their health and reinforcing the importance of adhering to prescribed management plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the new high blood pressure guidelines for 2025?
The new high blood pressure guidelines for 2025, released by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology, focus on a personalized approach to managing high blood pressure. They recommend using the PREVENT tool to assess individual risk factors for heart disease, starting medication earlier for high blood pressure treatment, and promoting complete abstinence from alcohol or limiting intake.
How can I prevent high blood pressure effectively?
To prevent high blood pressure, it is essential to adopt a healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, reducing sodium intake to 1500 mg per day, exercising regularly, and eliminating alcohol consumption. These practices can significantly lower the risk of developing high blood pressure.
What are the effects of high blood pressure on health?
The effects of high blood pressure can be severe, including an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney damage, and even dementia. Managing high blood pressure is crucial to protecting both heart and brain health, as well as prolonging life expectancy.
What treatments are available for high blood pressure?
High blood pressure treatment options include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, along with medications. New guidelines suggest starting treatments earlier for those diagnosed with high blood pressure, including options like GLP-1 drugs for specific patients.
What lifestyle changes are recommended for healthy blood pressure?
To maintain healthy blood pressure, individuals should focus on consuming a nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, avoiding alcohol, and reducing sodium intake. Following these tips can help stabilize and lower blood pressure effectively.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure Awareness | High blood pressure is a prevalent risk, affecting nearly half of U.S. adults and categorized as a silent killer. |
| New Guidelines | New guidelines from AHA and ACC focus on individual risk assessment for heart attacks and strokes using the PREVENT tool. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Recommendations include abstaining from alcohol or limiting intake: less than one drink for women, less than two for men. |
| Sodium Intake | The recommended sodium intake has been reduced from 2300 mg to 1500 mg per day. |
| Dietary Recommendations | Adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to manage blood pressure. |
| Importance of Early Intervention | The updated guidelines advocate for earlier prescription of medications for high blood pressure. |
| Impact on Pregnancy | Managing blood pressure during pregnancy is crucial for maternal and infant health. |
| Cognitive Health | Controlling blood pressure early can help prevent dementia and preserve cognitive function. |
Summary
High blood pressure is a widespread health concern that requires immediate attention to prevent severe complications. The updated guidelines from health organizations emphasize the importance of managing blood pressure through various lifestyle changes and early medical interventions. It is crucial to understand individual risk factors, limit alcohol intake, reduce sodium consumption, and maintain a balanced diet. By acting promptly and adhering to these recommendations, individuals can significantly reduce the risks associated with high blood pressure, thereby safeguarding their cardiovascular and cognitive health.




