Heart Disease Risk Women: Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits
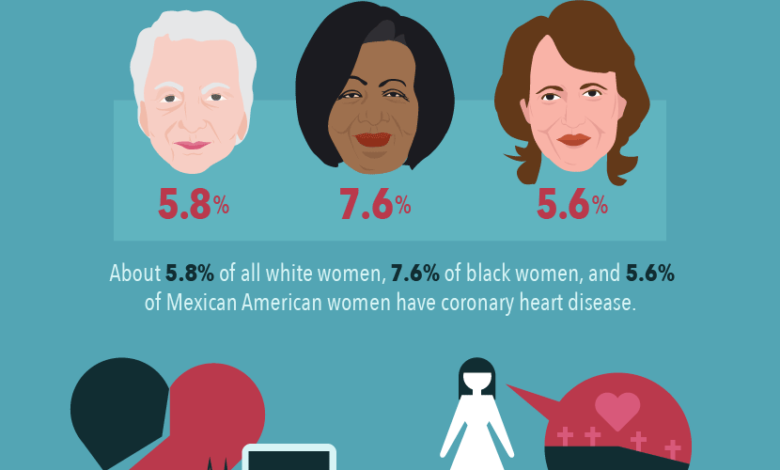
Heart disease risk women face is increasingly becoming a critical focus in the realm of cardiovascular health, as recent studies reveal alarming trends. Effective heart disease prevention strategies tailored for women are essential, especially since unhealthy lifestyle habits may disproportionately affect their heart health compared to men. Researchers have found that diet, exercise, and overall health markers such as body mass index and blood pressure have a more significant impact on women’s risk of cardiovascular disease. This growing awareness underscores the importance of prioritizing women’s health, so they can make informed decisions about their wellness. By understanding these risks, women can work towards reducing heart disease through mindful lifestyle choices and preventative health measures.
The threat posed by cardiac issues to women’s health has garnered considerable attention, with recent studies shedding light on the elevated vulnerabilities experienced by females. A critical examination of cardiovascular health among women shows that certain detrimental lifestyle factors can amplify their chances of developing heart conditions more than those seen in men. As we delve into heart disease prevention, it is vital to observe the nuanced differences in risk factors and outcomes between genders. Women must become vigilant about their health and consider how their unique biological and lifestyle challenges affect their cardiovascular well-being. Understanding these variations opens the door to better tailored health strategies aimed at reducing heart disease risk in women.
Understanding Heart Disease Risk in Women
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of mortality among women, with research highlighting how various lifestyle habits can significantly affect their cardiovascular health. Women often experience greater adverse effects from specific unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and high stress levels. As noted in recent studies, these adverse impacts lead to a heightened risk of cardiovascular complications, emphasizing the need for tailored heart disease prevention strategies that cater to women’s unique health profiles.
Additionally, conditions unique to women, including pregnancy and menopause, contribute to changes in cardiovascular health that may not be adequately addressed in conventional models. Hormonal fluctuations associated with these milestones may exacerbate the risks of high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, both of which are crucial risk factors for heart disease. Therefore, understanding heart disease risk in women requires a more nuanced approach that considers these hormonal influences and encourages preventative measures tailored to women’s health.
Identifying Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits
The discovery of particular habits that escalate heart disease risk in women serves as a wake-up call for many individuals. Key lifestyle factors include a diet high in saturated fats, physical inactivity, and smoking, all of which can lead to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Research indicates that these habits, while detrimental for both men and women, disproportionately affect women’s heart health, signaling the urgent need for awareness and behavioral change.
Furthermore, other lifestyle factors, such as sleep quality and stress management, play critical roles in shaping cardiac outcomes. Women often juggle multiple responsibilities, which can lead to poor sleep hygiene and increased stress levels. Such factors can contribute to the risk of heart disease, necessitating proactive approaches that encourage healthier living, such as regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and consistent sleep patterns. This multifaceted approach is essential for lowering heart disease risk among women.
Cardiac Health: The Gender Divide
Emerging data underscores a significant gender divide when it comes to heart disease, revealing that women’s responses to similar risk factors differ markedly from men’s. For instance, women with intermediate health assessments face greater risks compared to their male counterparts. This difference highlights the need for healthcare professionals to adopt a gender-specific lens when evaluating heart disease risk and potential interventions.
Women are often found to maintain healthier lifestyle choices than men, yet their overall cardiovascular health can be impacted severely by factors like hormonal changes involved in menopause. These unique circumstances necessitate specialized preventive care that addresses the distinct vulnerabilities women face concerning heart disease, facilitating better patient education around heart disease prevention.
The Importance of Hormonal Health
Hormonal shifts throughout a woman’s life significantly influence her cardiovascular health. Events such as pregnancy and menopause lead to changes in estrogen levels, which have protective effects against heart disease. As these hormonal levels fluctuate or decline, the risk of various cardiovascular issues tends to increase, necessitating closer monitoring and tailored interventions.
Healthcare providers must recognize these hormonal influences on women’s health to offer effective preventative strategies and treatment options post-menopause. As studies indicate, after menopause, the age-adjusted cardiovascular risks for women rise sharply, aligning closer to those of men. By understanding and addressing hormonal health, women can take proactive steps to mitigate their heart disease risk.
Lifestyle Modifications to Mitigate Heart Disease Risk
Adopting healthier lifestyle habits is crucial for women seeking to lower their heart disease risk. Key recommendations include maintaining a balanced diet low in saturated fats and sugars, engaging in regular aerobic exercise, and managing stress effectively through mindfulness or other relaxation techniques. These modifications not only improve cardiovascular health but also have positive effects on overall well-being.
Additionally, smoking cessation is vital for both immediate and long-term cardiovascular benefits. Women who quit smoking significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall health outlook. Therefore, targeted health education initiatives focusing on encouraging positive lifestyle changes among women can pave the way for reduced heart disease risk and improved health outcomes.
The Role of Screening and Regular Check-ups
Regular health screenings and check-ups are essential components in the early detection and prevention of heart disease in women. Given that women may experience differing symptoms and risks compared to men, it is paramount for healthcare providers to conduct comprehensive assessments tailored to women’s unique health profiles. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and body mass index can aid in identifying risk factors early on and guide appropriate lifestyle modifications.
Additionally, implementing sex-specific guidelines in cardiovascular risk assessments can enhance the accuracy of predicting heart disease risk. Routine screenings enable women to understand their cardiovascular health better and engage in preventive measures well before any potential heart issues arise. Such proactive care strategies are critical in the fight against heart disease.
Educating Women on Heart Disease Risks
In order to combat the rising rates of heart disease among women, comprehensive education on associated risks and prevention strategies is crucial. Outreach programs focused on women’s health can facilitate awareness regarding the significant ways an unhealthy lifestyle impacts heart disease risk. Initiatives should aim to educate women about recognizing symptoms of heart disease, the importance of lifestyle choices, and the role of regular health screenings in prevention.
Moreover, healthcare providers should emphasize the uniqueness of heart disease risk for women compared to men, ensuring that patients are fully informed of their individual vulnerabilities. By cultivating an educated and aware population, women can take affirmative steps toward heart health and reduce their risk of developing heart-related health issues.
Men vs Women: Understanding Heart Risk Differences
While both men and women face risks associated with heart disease, recent studies reveal that women experience these risks differently. For example, women with poor health status generally exhibit a higher risk of heart disease compared to men. This disparity underscores the complexities involved and indicates that prevention and management strategies need to be tailored to women, acknowledging the varying impact of both lifestyle and biological factors.
Research shows that men are often diagnosed with heart disease earlier than women, highlighting an essential gap in awareness and treatment. Women are more likely to develop heart disease after menopause, making awareness and preventive care crucial in postmenopausal women. By bridging this gender gap in understanding heart risks, healthcare systems can better address women’s cardiovascular health needs.
Heart Disease Prevention Strategies for Women
Effective heart disease prevention strategies must include lifestyle changes tailored specifically for women. Promoting healthy eating practices rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can significantly decrease heart disease risk. Additionally, encouraging women to partake in regular physical exercise can help manage weight, reduce stress levels, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Moreover, women need to be aware of the significance of mental health in relation to heart disease. Integrating stress management techniques, such as yoga and meditation, can greatly benefit women’s heart health. By understanding the multifactorial aspects of heart disease prevention, women can adopt a holistic approach to maintaining cardiovascular wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What unhealthy lifestyle habits increase heart disease risk in women?
Women’s heart disease risk is significantly impacted by unhealthy lifestyle habits, including poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, high body mass index (BMI), and unmanaged blood pressure and blood sugar levels. A recent study shows that these factors have a more pronounced effect on women’s cardiovascular health compared to men.
How do men’s and women’s heart disease risks compare?
Research indicates that while men and women may have similar unhealthy lifestyle habits, women experience a greater heart disease risk from these behaviors. For instance, women with poor health face nearly five times the higher risk of heart disease compared to their healthier counterparts, in contrast to a 2.5 times greater risk observed in men.
What role does menopause play in women’s heart disease risk?
Menopause significantly affects women’s heart disease risk, as hormonal changes during this period lead to a decrease in estrogen levels, which have protective cardiovascular effects. This hormonal shift, coupled with potential weight gain, can increase the susceptibility of women to heart disease.
Why is sex-specific screening important in assessing heart disease risk?
Sex-specific screening is crucial in assessing heart disease risk because the impact of health factors varies between genders. Studies suggest that women display a greater increase in heart disease risk for similar health profiles compared to men, highlighting the need for tailored risk assessment approaches.
What cardiovascular health issues do women face more prominently?
Women face distinct cardiovascular health issues, including a significant risk of heart problems after menopause and complications related to pregnancy and childbirth. Conditions like unstable angina and heart failure can also manifest differently in women, underscoring the importance of understanding sex-specific risks in cardiovascular health.
How can women improve their heart health and reduce disease risk?
To enhance cardiovascular health and mitigate heart disease risk, women should adopt healthier lifestyle habits, including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoking, managing weight, and controlling blood pressure and blood sugar levels. Regular health check-ups can also help monitor these factors effectively.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease Risk Factors | The risk factors like diet, sleep, physical activity, and others affect women more than men. |
| Impact of Lifestyle Habits | Eight specific unhealthy habits have double the risk effect on women as compared to men. |
| Health Outcomes | Women showed a higher percentage in ideal health compared to men, but poorer health significantly elevates heart disease risk. |
| Hormonal Influence | Significant hormonal changes in women, especially around milestones like menopause, can affect heart health. |
| Need for Gender-Specific Studies | There is a growing necessity for studies focused on women’s cardiovascular risks and their unique health challenges. |
Summary
Heart disease risk in women is highlighted by new research showcasing how unhealthy lifestyle habits can affect them more severely than men. While women generally exhibit better overall health, factors like diet and hormonal changes can significantly elevate their risk for heart disease. It’s crucial for women to be aware of these risks, particularly as they age and experience key life milestones like menopause, which can exacerbate these factors. Understanding these nuances in heart health can lead to better prevention strategies that are tailored specifically for women.




