Hantavirus: Understanding Its Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Hantavirus has emerged as a significant health threat in recent months, especially following the tragic deaths associated with Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) in California. This deadly virus, primarily transmitted by rodents, has caused alarm amongst health officials, particularly in Mammoth Lakes, where three fatalities have been reported. Symptoms of hantavirus can start subtly but rapidly progress into severe respiratory issues, making this illness particularly dangerous if not caught early. As communities take strides towards Hantavirus prevention, understanding how the virus spreads and implementing effective rodent control measures becomes crucial in averting further cases. With growing concerns over hantavirus transmission, it’s essential to raise awareness about the risks and necessary precautions to protect public health.
The current emergence of a virulent rodent-borne illness has reignited discussions about the dangers posed by Hantavirus. Often linked to severe respiratory conditions, this zoonotic virus is spread primarily through contact with infected rodent excretions, raising awareness about the importance of preventative measures. Recognizing the symptoms associated with this pathogen is vital for timely intervention, as the progression can lead to life-threatening conditions like hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Public health efforts are now focusing on effective strategies for rodent control to safeguard communities, emphasizing the necessity of educating individuals on how to limit their exposure to potential carriers. Given the recent increase in reported cases, it’s crucial to stay informed and proactive in combating this serious health threat.
Understanding Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is a serious disease caused by hantaviruses that primarily spread through contact with rodents, especially deer mice. This condition can escalate quickly, often presenting with initial symptoms that resemble the flu, such as fever, muscle aches, and fatigue. If left untreated, these symptoms can progress to severe respiratory issues, including coughing and shortness of breath, which ultimately may lead to respiratory failure and death. The mortality rate for HPS cases can reach nearly 40%, highlighting the urgent need for awareness and prompt medical attention when symptoms arise.
Recent cases in California, including the unfortunate deaths connected to HPS, underline the alarming nature of this virus. Health officials stress the importance of recognizing the risk factors and symptoms associated with hantavirus. Understanding HPS is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, particularly in areas where rodent populations are high, as the disease is usually noted during late spring and summer. With three fatalities in Mono County, the seriousness of this disease cannot be understated, as awareness and quick response are vital to prevent further incidents.
How Hantavirus is Transmitted
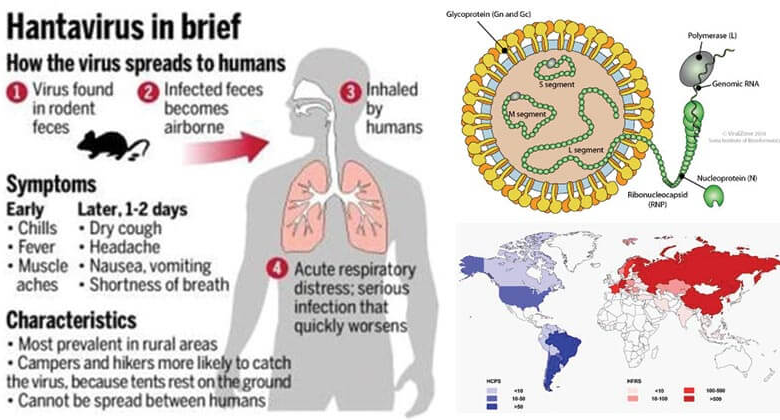
The transmission of hantavirus occurs primarily through the inhalation of virus-laden particles from rodent droppings, urine, or saliva. Activities such as cleaning areas where rodents have been present can disturb these materials, leading to aerosolization of the virus into the air. This means individuals can unknowingly breathe in the virus, which poses a significant health risk, especially in homes or workplaces with rodent infestations. It’s especially vital to exercise caution during the early months of the year when mouse populations may surge.
In addition to respiratory transmission, hantavirus may spread through direct contact with rodent waste or bites from infected animals. People need to understand that hantavirus is not transmitted from person to person, which is a common misconception. Preventing hantavirus transmission involves implementing effective rodent control measures and maintaining a clean environment free from rodent waste.
Hantavirus Prevention and Control Measures: Effective Strategies for Safety and Health
Preventing hantavirus transmission requires proactive measures, particularly in areas like Mammoth Lakes, where recent cases have provoked health alerts. Public health officials recommend sealing potential entry points in and around homes to keep rodents out. This includes patching up holes, removing food sources, and utilizing rodent-proof containers for storing food. Regular maintenance and monitoring of your property can significantly reduce the risk of hantavirus exposure.
Another crucial prevention strategy is to avoid actions that disturb rodent droppings or nests, such as vacuuming or sweeping these materials. Instead, contaminated areas should first be sprayed with disinfectant, allowing them to be properly cleaned safely. These measures limit aerosolization and minimize the risk of inhalation. For instance, in homes where rodent activity is suspected, airing out spaces for at least 30 minutes can help ensure the reduction of any virus particles present in the air.
Recognizing Symptoms of Hantavirus Infection
The symptoms of hantavirus infection often develop subtly within one to eight weeks following exposure. Initially, individuals may experience mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, and general fatigue. However, as the virus progresses, these symptoms can escalate, leading to severe respiratory distress characterized by shortness of breath and fluid accumulation in the lungs. It is imperative for anyone experiencing these symptoms to seek immediate medical attention, especially if they have had exposure to environments infected by rodents.
Understanding the timeline and progression of symptoms is crucial in combating hantavirus. Healthcare professionals emphasize that early identification and support can be lifesaving, as those affected could require intensive medical care, including oxygen therapy. With a high fatality rate associated with HPS, recognizing the signs and obtaining treatment quickly is essential to improving outcomes for those infected.
Effective Hantavirus Prevention Strategies
Effective hantavirus prevention strategies include a combination of environmental control measures and public education. Health officials frequently advise residents to stay vigilant about rodent activity, particularly in rural areas or places with known outbreaks. Simple actions, such as cleaning up food waste and maintaining a tidy living space, can prevent rodent invasions and subsequently decrease hantavirus risks. Additionally, community awareness programs about hantavirus transmission can significantly contribute to overall public health safety.
Another important strategy is educating individuals on proper cleanup techniques. Rather than sweeping or vacuuming up rodent droppings, which can aerosolize the virus, health authorities recommend dampening the area with disinfectant or bleach solution first. This reduces the chances of inhaling virulent particles, thereby protecting residents and workers involved in cleanup efforts. These preventive strategies collectively contribute to minimizing hantavirus incidents and enhancing community health.
Understanding Rodent Control Measures
Controlling rodent populations is a fundamental aspect of preventing hantavirus transmission. Rodent control measures involve identifying and eliminating potential entry points for rodents around homes and workplaces. This may include sealing gaps in walls, using traps, and employing appropriate bait in infested areas. Regular property inspections aid in early detection and remediation before infestations escalate, thus limiting the risk of hantavirus.
Community-level initiatives can also play a significant role in effective rodent control. Neighborhood awareness and collaborative cleanup efforts can significantly impact reducing nearby rodent habitats. Encouraging local education about the importance of rodent control can foster a culture of vigilance and collective responsibility for minimizing hantavirus risks. By employing these measures, communities can work together to create safer environments free from rodent-related health threats.
The Importance of Community Awareness in Hantavirus Prevention
Community awareness is vital in preventing hantavirus infections, particularly in areas like Mono County, where recent case spikes have raised alarms. Public health campaigns aimed at educating residents about hantavirus risks, transmission methods, and preventive strategies can foster a proactive attitude toward rodent control. Engaging community members in discussions, distributing informational materials, and hosting workshops can significantly enhance the knowledge and preparedness of the population.
By creating a well-informed community, individuals are empowered to take necessary actions to protect themselves and their families from hantavirus. It is important to emphasize collective efforts as a means to combat rodent infestations and reduce hantavirus exposure effectively. Such initiatives not only protect individual households but also contribute to the overall health security of the entire community.
Responding to Hantavirus Outbreaks: What You Should Know
In the wake of detecting hantavirus cases in the community, it is essential for residents to know how to respond appropriately. Alerting public health officials to suspected hantavirus activity within their area is vital, as it allows authorities to monitor and control potential outbreaks. Moreover, individuals who demonstrate symptoms associated with hantavirus should seek immediate medical care and inform healthcare providers of potential exposure to rodents.
Being informed about hantavirus and its implications is critical for public safety. Communities must come together to share information swiftly and support one another during such outbreaks. Strengthening communication between public health departments and community members can significantly enhance awareness, preparedness, and response, ultimately limiting the impact of future hantavirus transmission.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in Hantavirus Cases
Healthcare professionals play a critical role in identifying and managing hantavirus cases effectively. With their training, medical staff can recognize symptoms indicative of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome and initiate appropriate treatment protocols. This includes not only supportive care but also educating patients about the potential sources of exposure and preventive measures.
Collaboration among healthcare providers, public health officials, and the community is essential for managing hantavirus. By staying up-to-date with the latest research and trends associated with hantavirus infections, healthcare professionals can contribute valuable knowledge to public health efforts, facilitating quicker responses to outbreaks and improving patient outcomes.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions in Hantavirus Studies
Ongoing research plays a pivotal role in confronting the challenges posed by hantavirus infections. Scientists and public health experts continue to explore the epidemiology, transmission mechanisms, and potential vaccines or treatment options for hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Investments in scientific inquiries enhance our understanding of how hantaviruses operate and provide insights into effective prevention strategies.
Future directions in hantavirus studies include advancements in monitoring rodent populations and vector control methods. By applying innovative approaches, researchers aim to reduce the incidence of hantavirus while identifying strategies to minimize risks for populations at risk. Continued research and collaboration among scientists, health officials, and community organizations are essential for devising sustainable solutions against the threat of hantavirus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome and how can it be prevented?
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) is a severe respiratory disease caused by hantaviruses, primarily transmitted through contact with infected rodents. To prevent HPS, it is crucial to implement rodent control measures such as sealing cracks and openings in homes, storing food in rodent-proof containers, and maintaining a clean environment to deter rodents.
What are the symptoms of Hantavirus after exposure?
Symptoms of Hantavirus can appear one to eight weeks after exposure and typically start with fever, muscle aches, and fatigue. These initial symptoms can progress to serious respiratory issues, including coughing and shortness of breath, within four to ten days.
How does Hantavirus transmission occur in humans?
Hantavirus transmission occurs primarily when humans inhale dust contaminated with rodent urine, droppings, or saliva. Other routes of transmission include touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face, or being bitten by an infected rodent. Effective hantavirus prevention strategies focus on minimizing contact with rodent waste.
What rodent control measures are effective against Hantavirus?
Effective rodent control measures include sealing holes and gaps in homes to prevent rodent entry, using traps to reduce rodent populations, and ensuring food is stored in airtight containers. It is also essential to avoid vacuuming or sweeping areas contaminated with rodent droppings, as this can aerosolize the virus.
What should you do if you suspect exposure to Hantavirus?
If you suspect exposure to Hantavirus or experience symptoms such as fever and respiratory issues, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and supportive care, including oxygen therapy, can be critical in managing hantavirus pulmonary syndrome.
Is there a treatment for Hantavirus infection?
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for Hantavirus infection. However, early detection and intensive care can improve outcomes for patients with Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, emphasizing the importance of symptom awareness and seeking prompt medical care.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Disease Name | Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) |
| Recent Cases | Three fatalities in Mammoth Lakes, California |
| Transmission | Primarily from rodent urine, feces, or nesting materials |
| Symptoms | Fever, muscle aches, fatigue, gastrointestinal problems; progresses to respiratory issues |
| Fatality Rate | Approximately 38%-40% for those infected |
| Prevention Measures | Seal homes, use rodent-proof containers, avoid vacuuming droppings, disinfect contaminated areas |
| Expert Advisories | Increased vigilance around rodent presence and waste is crucial |
Summary
Hantavirus has become a significant public health concern, particularly highlighted by the recent fatalities in California due to Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS). This viral infection, primarily transmitted by rodents, poses serious respiratory threats to humans and carries a high fatality rate. The alarming increase in cases underscores the need for awareness and preventive measures against rodent exposure. Experts urge the importance of maintaining rodent control in homes and workplaces to mitigate the risks associated with hantavirus.




