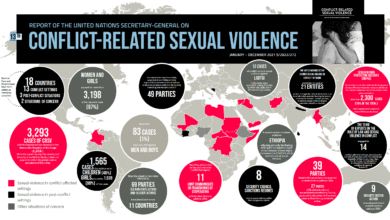
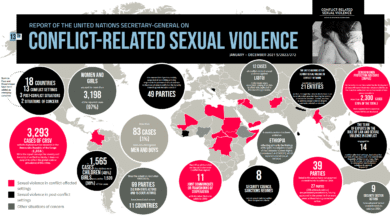
Gender Equality Funding Shortfall: $420 Billion Gap Exposed
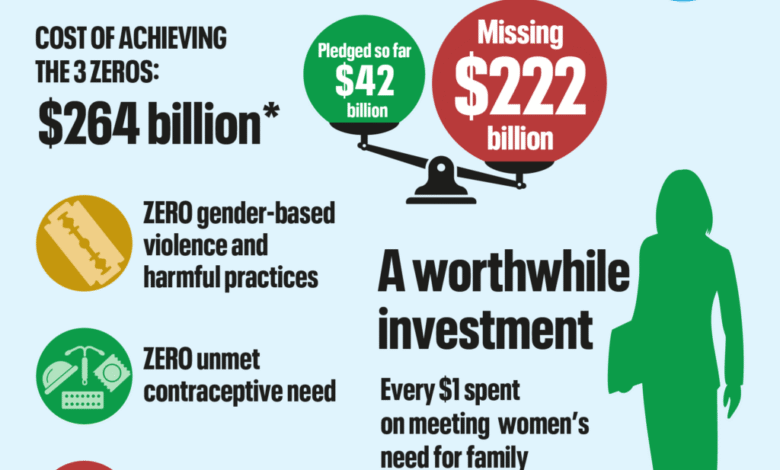
Gender equality funding shortfall remains a critical barrier to achieving equitable growth and development, particularly in developing countries where the deficit reaches an alarming $420 billion annually, according to UN Women. This financial gap hampers essential programs and services that are vital for women and girls, preventing them from accessing opportunities for advancement. As discussions intensify at the Fourth International Conference on Financing for Development in Sevilla, global leaders are urged to prioritize funding for gender equality to support the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Without adequate investment in gender-responsive budgeting and public care systems, many nations will continue to struggle in closing the gender gap. Urgent action is needed to ensure that these funds reach the communities that need them most, transforming gender equality from a marginal issue into a cornerstone of public policy.
The persistent underfunding of initiatives aimed at achieving gender equity, often referred to as the gender equality funding shortfall, highlights a significant challenge in global development. This funding deficiency undermines the potential for women in developing regions to thrive, exacerbating existing disparities. Recent estimates emphasize the need for substantial financial commitments to address gender equality in developing countries, particularly through enhancing public investment and reforming budgetary practices. Key strategies, such as gender-responsive budgeting and support for public care systems, are crucial for fostering a more inclusive economic environment. As global attention shifts towards effective financing methods, it’s imperative that gender equality becomes an integral component of policy discussions.
Understanding the Gender Equality Funding Shortfall
The pressing issue of gender equality funding shortfall highlights a critical gap of $420 billion annually in financial resources necessary to empower women and girls in developing countries. This shortfall, underscored by UN Women, indicates that existing efforts are insufficient in addressing the needs of marginalized populations effectively. Programs aimed at enhancing women’s educational opportunities, healthcare access, and economic participation are often undervalued and underfunded, leading to a perpetuation of gender disparity.
To tackle this funding gap, world leaders must recognize the importance of prioritizing gender equality in financial planning and public policy. A strategic shift towards allocating sufficient resources for women’s empowerment can transform socio-economic outcomes. By understanding the gravity of the funding crisis and its implications, stakeholders can initiate robust advocacy for increased investments that directly support gender-responsive initiatives.
The Importance of Gender-Responsive Budgeting
Gender-responsive budgeting serves as a vital mechanism to ensure that public funds are directed towards addressing the unique needs of women and girls. This budgeting approach enables governments to assess their spending through a gender lens, facilitating a clearer understanding of where financial resources can be most impactful. When effectively implemented, gender-responsive budgeting can enhance accountability and transparency regarding how funds are allocated towards achieving gender equality.
However, a staggering three-fourths of countries worldwide fail to have the necessary systems in place to track and allocate public funds with a gender perspective. This lack of infrastructure not only undermines efforts for gender equality but also hinders overall economic growth and stability in developing regions. By investing in gender-responsive budgeting, policymakers can ensure that resources are equitably distributed, therefore fostering an environment conducive to women’s progression in various sectors.
Investing in Public Care Systems
Investment in public care systems is crucial to achieving gender equality, as it enables women to participate fully in the workforce. By establishing comprehensive child and elder care programs, governments can provide women with the necessary support to balance work and family responsibilities effectively. This investment not only benefits individual families but also strengthens the overall economy by maximizing women’s potential contributions in the labor market.
Furthermore, public care systems create a support network that alleviates the burden placed on women, who disproportionately shoulder caregiving responsibilities. By recognizing the importance of these systems and committing resources to expand them, countries can promote a more equitable society. As highlighted by UN Women, such initiatives are fundamental for fostering an inclusive workforce where women can thrive both personally and professionally.
Urgent Need for Debt Relief to Boost Gender Budgeting
Many developing countries grapple with excessive debt burdens that severely limit their capacity to invest in gender equality initiatives. UN Women’s recent call for urgent debt relief sheds light on this obstacle, stressing that without financial leeway, nations cannot allocate vital funds for advancing gender equality. As a consequence, programs geared towards women’s empowerment and gender-responsive budgeting suffer significant underfunding.
To combat this issue effectively, collaborative efforts between international financial institutions and governments are required to alleviate unsustainable debt levels. Implementing actionable debt relief measures will create an environment where investments in gender equality can flourish, enabling the establishment of policies that truly uplift women and support sustainable development goals.
Global Commitment to Gender Equality Funding
The Compromiso de Sevilla, adopted during the International Conference on Financing for Development, serves as a pivotal step towards global commitments in advancing gender equality. This agreement outlines critical strategies for nations to adopt, including the promotion of gender-responsive budgeting and the allocation of resources aimed at closing the gender gap. Such a commitment, if executed diligently, can significantly alter the landscape of gender equality funding.
Success in achieving gender equality relies heavily on leadership that prioritizes investment in women not merely as an expense, but as a transformative opportunity for societal growth. Continuous advocacy and accountability are required to uphold these commitments, ensuring tangible progress is made in funding gender equality initiatives across nations. The global community must rally together to reinforce these goals and embed gender equality at the core of public policy.
The Role of UN Women in Closing the Gender Gap
UN Women plays a crucial role in mobilizing resources and providing guidance to governments for implementing gender equality initiatives effectively. Through its advocacy efforts, UN Women emphasizes the importance of targeted funding to close the existing $420 billion shortfall. By working with member states, UN Women aims to create frameworks that encourage investment in gender-responsive programs that prioritize women’s needs and long-term empowerment.
Moreover, UN Women supports capacity-building initiatives that educate policymakers on the significance of integrating gender considerations into budgeting processes. This approach fosters a more inclusive environment where women’s rights are recognized and upheld, ultimately leading to sustainable development outcomes. As international dialogue continues on financing options, UN Women remains a key player in pushing for enhanced funding commitments towards gender equality.
Public Policy and Gender Equality: A Call to Action
To achieve true gender equality, public policies must be reformulated to prioritize women’s needs across all sectors. This necessitates a reevaluation of budget allocations to ensure that gender equality is not sidelined but is at the forefront of developmental priorities. Policymakers must recognize that gender equality funding shortfall impacts not just women, but the overall health of the economy and society.
Investment in women’s empowerment should be seen as a critical component of national development strategies. By implementing policies that embed gender equality into the heart of public funding decisions, governments can create an effective structure for equitable growth. This transformative change requires a concerted effort from all sectors of society to advocate for policies that enhance the lives of women and girls globally.
Challenges in Implementing Gender Equality Initiatives
Despite widespread recognition of the importance of gender equality, challenges remain in the implementation of effective initiatives. One significant barrier is the lack of adequate funding and resources to support programs designed for women. As discussed, UN Women highlights a staggering annual funding gap, which reflects a broader systemic issue of prioritizing gender equality in policy agendas.
Additionally, institutional norms and societal attitudes continue to hinder progress towards true gender equality. Many governments face political pressure or cultural resistance that prevents the adequate mobilization of resources. Overcoming these challenges requires collaborative efforts across sectors to foster an environment where gender equality can be advanced and celebrated as a societal necessity.
The Future of Gender Equality Funding
Looking ahead, the future of gender equality funding hinges on the commitment of global leaders to prioritize this critical issue. As the conversation around financing for development evolves, it is crucial that gender equality becomes an integral part of this dialogue. Reinforcing the need for funding directed at women’s initiatives will create the foundation for sustained progress towards closing the gender gap.
In conclusion, addressing gender equality funding shortfall and its broader implications requires persistent advocacy and action from all stakeholders. By embedding gender-responsive practices into budgeting processes and supporting initiatives that target the specific needs of women and girls, the international community can foster a future where gender equality is not just an aim but a reality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the gender equality funding shortfall in developing countries?
The gender equality funding shortfall in developing countries amounts to a staggering $420 billion annually. This deficit highlights the urgent need for investment in gender equality initiatives, as many essential programs and services aimed at supporting women and girls remain underfunded.
How does UN Women address the funding for gender equality?
UN Women plays a crucial role in addressing the funding shortfall for gender equality by advocating for increased financial commitments from governments and international bodies. They emphasize the importance of integrating gender-responsive budgeting to ensure that funds effectively reach programs that support women and girls.
Why is investment in public care systems important for achieving gender equality?
Investment in public care systems, such as child and elder care programs, is vital for achieving gender equality because it enables women to participate fully in the workforce. By decreasing the burden of unpaid care work, these investments help to ensure that women can access equal employment opportunities.
What is gender-responsive budgeting and why is it important?
Gender-responsive budgeting is an approach that allocates funds in a way that addresses the specific needs of different genders. It is crucial for closing the gender equality funding shortfall, as it helps track and allocate resources effectively, ensuring that programs targeting gender equality receive the necessary financial support.
How can countries overcome the gender equality funding shortfall?
Countries can overcome the gender equality funding shortfall by prioritizing gender equality in their budgets, adopting gender-responsive budgeting practices, and committing to debt relief. Additionally, governments should create targeted funding programs and reallocate resources to ensure that the needs of women and girls are adequately met.
What commitments have been made at the Fourth International Conference on Financing for Development regarding gender equality?
At the Fourth International Conference on Financing for Development, member states adopted the Compromiso de Sevilla, which includes commitments to enhance development financing with a focus on promoting gender equality. This initiative aims to mobilize more funds and encourage effective allocation to support gender equality efforts globally.
Why is gender equality viewed as an investment rather than a cost?
Gender equality is viewed as an investment rather than a cost because empowering women leads to significant economic growth and social progress. By investing in gender equality initiatives, governments can harness the full potential of their population, which benefits society as a whole and contributes to sustainable development.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Women in developing countries face a $420 billion annual funding shortfall for gender equality efforts. |
| Funding gaps mean essential programs for women and girls are consistently underfunded. |
| The current international financing structure needs revitalization to support gender equality as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. |
| Only 25% of countries have systems to track public funds related to gender equality. |
| Investment in public care systems is crucial to allow women to participate in the workforce. |
| Debt relief is necessary for many nations to allocate funds towards gender equality initiatives. |
| Governments must back commitments for gender equality with actions, seeing women as an investment. |
Summary
The gender equality funding shortfall is a critical issue, with women in developing countries missing out on $420 billion annually for necessary programs and services. This underfunding persists despite the urgent need for targeted investments and structural reforms aimed at integrating gender equality into public policy. Closing this gap requires a collective commitment from global leaders to improve financial tracking and prioritize women’s contributions in the economy, ensuring that investments are made to foster inclusive development.