Choline and Alzheimer’s Risk: Boost Brain Health Today
Choline and Alzheimer’s risk are increasingly linked through emerging research, suggesting that dietary changes may play a crucial role in cognitive health. Recent findings from a group of researchers highlight that individuals who consume foods rich in dietary choline may experience a significantly lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, a common form of dementia. This essential micronutrient is found in various foods such as eggs, poultry, cruciferous vegetables, and fish, all of which support optimal brain health. With a focus on nutrition and Alzheimer’s prevention, enhancing one’s diet to include adequate choline intake can be a simple yet effective strategy for boosting cognitive function. As more studies reveal the protective benefits of choline, prioritizing this nutrient may become a vital aspect of dementia prevention strategies.
The relationship between dietary habits and cognitive decline has gained attention, particularly concerning the role of choline in promoting brain health. This essential nutrient, which can be predominantly found in foods such as eggs, meats, and certain vegetables, is believed to support cognitive function and may mitigate the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. As experts explore the implications of nutrition on brain wellness, understanding how adequate intake of sources rich in choline can aid in dementia prevention becomes essential. By fostering a diet that emphasizes nutrients critical for maintaining cognitive vigor, individuals can take proactive steps towards bolstering their mental acuity as they age. The conversation surrounding nutrition and Alzheimer’s is evolving, paving the way for more informed choices that prioritize brain health.
The Vital Role of Choline in Brain Health
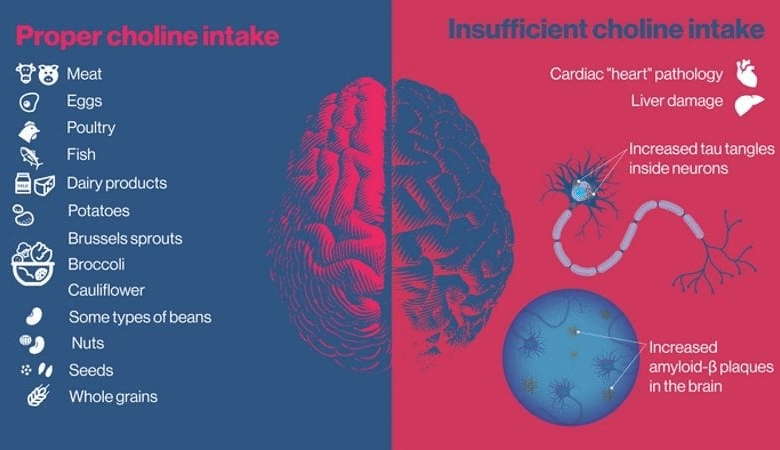
Choline, a water-soluble nutrient, plays a critical role in brain health and cognitive processes. This essential micronutrient is involved in synthesizing acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is crucial for memory and muscle control. Foods rich in dietary choline, such as eggs, poultry, and fish, not only enhance cognitive function but also work synergistically with other nutrients to support overall brain health. Recent research emphasizes that inadequate choline intake can lead to cognitive decline and heightened risk of neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Studies indicate that choline consumption is not merely beneficial; it’s vital for maintaining optimal brain function as we age. Regular intake of choline-rich foods has been linked to improved memory capabilities and protection against cognitive decline. Furthermore, its anti-inflammatory properties contribute to enhancing brain resilience, potentially staving off conditions such as dementia. By making proactive choices in nutrition, particularly by including dietary choline, individuals can significantly support their brain health and mitigate risks associated with cognitive impairment.
How Dietary Choline Lowers Alzheimer’s Risk
Emerging studies reveal a strong correlation between dietary choline and a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease among older adults. According to a recent investigation, participants who consumed around 350 milligrams of choline daily exhibited the lowest rates of Alzheimer’s diagnoses after an eight-year follow-up. This suggests that incorporating sufficient choline in the diet could play a preventative role in the onset of common dementias, shedding light on an accessible method for risk reduction.
The benefits of choline extend beyond mere prevention; they also encompass the enhancement of cognitive function. For instance, research led by nutrition experts indicates that higher choline intake not only supports memory improvement but also contributes to overall brain health stability. Moreover, the multifaceted nature of dietary choline—found in foods such as eggs, salmon, and walnuts—allows individuals to integrate these findings easily into their daily meals, making them proactive agents in their own health destiny.
Nutrition and Alzheimer’s: The Connection
Nutrition is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in Alzheimer’s risk management. Diets low in essential nutrients such as choline may hasten cognitive decline and contribute to neurodegenerative diseases. By prioritizing nutrient-dense foods, including those high in choline, individuals can create a supportive environment for cognitive longevity. The relationship between nutrition and brain health highlights the need for comprehensive dietary strategies aimed at preventing dementia.
Incorporating brain-healthy foods into everyday meals can be a delightful way to foster cognitive well-being. Salad mixes that feature leafy greens, walnuts, and blueberries not only offer vibrant flavors but also supply essential nutrients. Additionally, regular consumption of omega-3-heavy fish like salmon complements choline sources, creating a nutritional powerhouse that caters specifically to brain health. Ultimately, a diet rich in these elements has the potential to fortify one’s defense against Alzheimer’s and dementia.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet for Cognitive Function
Maintaining a balanced diet is paramount for optimal cognitive function, particularly as we advance in age. A well-rounded dietary approach that incorporates both macronutrients and micronutrients, such as choline, is essential for sustaining robust brain health. By ensuring that your diet is filled with brain-boosting foods, you not only support memory retention but also improve overall cognitive capabilities.
Healthy fats, such as those found in walnuts or fish, contribute significantly to brain health by enhancing neurotransmitter functions and reducing inflammation. Additionally, the strategic inclusion of fruits and vegetables can further bolster cognitive function due to their high antioxidant content. Ensuring a nutrient-dense diet tailored to individual needs, particularly one rich in choline, is a foundational step toward enhancing cognitive resilience and preventing diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
Choline Sources: Discovering Nutritional Powerhouses
The journey to enhancing brain health begins with understanding where to find reliable sources of dietary choline. Foods such as egg yolks, poultry, and fish are exceptional sources. While many people may lean towards egg whites for a lighter option, it’s essential to note that choline is primarily concentrated in the yolk, making it a worthwhile addition to your meals. Additionally, incorporating broccoli and Brussels sprouts not only diversifies your diet but also taps into the power of choline-rich vegetables.
For those who find it challenging to meet their choline requirements through food alone, choline supplementation may be an effective strategy. Personalized guidance from a healthcare professional can ensure that supplementation aligns with individual dietary needs while enhancing cognitive function and overall brain health. By being proactive about choline intake, individuals can make significant strides toward protecting themselves against cognitive decline.
Brain Health and the Impact of Aging
As we age, the importance of maintaining brain health becomes increasingly evident due to the correlation between aging and increased risk of cognitive decline. Age-related changes in brain structure and function necessitate a nutritional approach that is both preventive and restorative. Ensuring that diets are rich in nutrients that support cognitive function, such as choline, can significantly impact the trajectory of brain health.
Research has shown that engaging in preventive measures—such as consuming a diet rich in choline—can protect against age-related memory decline. Strategies that prioritize nutrition, coupled with mental exercises and regular physical activity, can create a robust framework for nurturing brain health as one ages. The interconnectedness of diet and cognitive longevity underscores the necessity for prioritized nutrient intake in older adults.
Alzheimer’s Prevention Through Lifestyle Choices
Alzheimer’s prevention is increasingly recognized as not just a genetic or age-related concern but also heavily influenced by lifestyle choices, including nutrition. The integration of foods rich in choline into daily meals offers a viable path towards mitigating risk factors associated with cognitive decline. This holistic approach towards brain health encompasses not only what we eat but how we choose to live, promoting a well-rounded lifestyle.
Moreover, the synergistic effect of a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and cognitive challenging activities creates a comprehensive strategy for preventing Alzheimer’s. The conscious choice to prioritize foods that enhance brain function, combined with an active lifestyle, can have profound implications for mental clarity and cognitive longevity. As research continues to evolve, understanding Alzheimer’s risk factors will empower individuals with the knowledge to make informed dietary and lifestyle decisions to safeguard their brain health.
Cognitive Function: The Role of Diet and Nutrition
Nutrition and cognitive function are deeply intertwined, with dietary habits substantially affecting brain health. A diet rich in essential nutrients, including choline, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants, has been shown to significantly support cognitive function and slow down the aging process of the brain. Foods such as fatty fish, nuts, and green leafy vegetables play prominent roles in nurturing our cognitive faculties.
Incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into daily diets ensures that the brain receives the necessary support to function optimally. Furthermore, understanding the science behind how certain foods influence cognitive abilities can lead to better food choices. With the goal of fostering long-term brain health, individuals are encouraged to embrace a diet that not only satisfies hunger but also promotes cognitive well-being.
Expert Nutritionist Insights on Choline Intake
Nutritionists and healthcare experts continue to emphasize the significance of adequate choline intake for supporting brain health and cognitive function. Registered dietitian nutritionists highlight the need for dietary assessments to tailor choline requirements based on individual needs, revealing that certain demographics may lag in their choline consumption. The insights of nutrition experts point to a collective need to raise awareness about the importance of incorporating choline-rich foods into our diets.
Experts recommend a variety of food sources for choline, ensuring inclusivity for different dietary practices. Recognizing the role of artificial barriers, such as dietary restrictions, is essential in making choline intake accessible to all. Increasing education around this vital nutrient could empower individuals to consciously focus on nutrition, thus minimizing the risk of Alzheimer’s and supporting overall brain health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does dietary choline affect Alzheimer’s risk?
Research indicates that a higher intake of dietary choline may lower the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Foods rich in choline, such as poultry, eggs, and certain vegetables, contribute to better cognitive health and may help prevent dementia.
What role does choline play in brain health and cognitive function?
Choline is essential for brain health because it supports the structure of cell membranes and is a precursor to neurotransmitters, which are crucial for brain function. Optimal choline intake has been linked to improved cognitive function and may be particularly beneficial in reducing Alzheimer’s risk.
Can eating foods high in choline prevent dementia?
Studies suggest that consuming foods rich in choline, such as eggs, dairy, and certain vegetables, may help reduce the risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease. Regular consumption of these foods can contribute to maintaining cognitive function as you age.
What are some common sources of dietary choline?
Dietary choline can be found in a variety of foods, including eggs (especially the yolk), chicken, fish, beans, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts. Incorporating these foods into your diet may support brain health and help mitigate Alzheimer’s risk.
How much choline do older adults need to reduce Alzheimer’s risk?
Research has shown that older adults who consume approximately 350 milligrams of choline daily may experience a lower risk of clinical Alzheimer’s diagnoses. It’s important for individuals to assess their dietary intake and consider supplements if their choline needs aren’t being met through food.
Is choline supplementation necessary for brain health?
While many can meet their choline needs through a balanced diet, those who limit high-choline foods, such as egg whites, may benefit from choline supplements. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine individual choline needs for optimal brain health and Alzheimer’s risk reduction.
How does estrogen influence choline requirements for women?
Estrogen levels can affect choline metabolism; premenopausal women may require less dietary choline as higher estrogen stimulates the body’s own production of choline. Understanding individual needs can help in tailoring dietary habits to support brain health.
What other nutrients support brain health alongside choline?
In addition to choline, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants from fruits and vegetables are vital for promoting brain health. Foods like wild salmon, walnuts, and blueberries can complement a choline-rich diet to further reduce Alzheimer’s risk.
What advice do experts give about choline and brain health?
Experts recommend including choline-rich foods in your diet and considering the overall nutritional balance for brain health. Regular consumption of nutrient-dense foods, alongside adequate choline intake, can help prevent cognitive decline and support long-term brain function.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase Alzheimer’s Risk Awareness | Research indicates that dietary choices can influence the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Role of Choline | Choline is a vital micronutrient linked to improved brain health and reduced Alzheimer’s risk. |
| Recommended Choline Intake | About 350 mg per day is associated with lowered clinical Alzheimer’s risk in older adults. |
| Sources of Choline | Found in eggs (mostly yolk), poultry, dairy, broccoli, beans, and fish. |
| Expert Recommendations | Nutritionists emphasize a balanced diet including brain-healthy foods like walnuts and salmon. |
| Supplements Consideration | Potential for supplements such as choline, vitamin D, or omega-3s to enhance brain health. |
Summary
Choline and Alzheimer’s risk is a growing area of research, highlighting that a nutritious diet rich in choline can play a crucial role in lowering the chances of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Studies show that older adults who consume sufficient choline may experience improved cognitive function, as this nutrient supports brain health. By incorporating choline-rich foods into your diet, such as eggs, poultry, and leafy vegetables, you may take proactive steps to protect your brain as you age. Additionally, consulting with nutritionists and considering supplements may further enhance your dietary approach to reducing Alzheimer’s risk.




