Challenges Faced by Indigenous Peoples and Their Rights
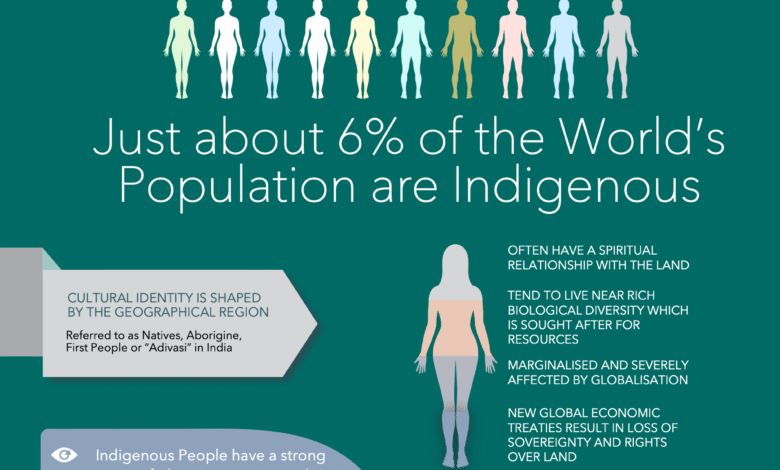
The challenges faced by Indigenous Peoples are profound and multifaceted, encompassing issues related to rights, governance, and social justice. With the ongoing exclusion from critical decision-making processes, Indigenous communities struggle to maintain their identity and self-determination. This situation has been highlighted in recent discussions surrounding the UN Declaration on Indigenous Peoples, which stresses the importance of recognizing Indigenous rights and participation in governance. As these communities confront barriers, especially Indigenous women challenges in accessing political and economic opportunities, their plight becomes a focal point for social equity and justice. Addressing these challenges is vital not just for the well-being of Indigenous Peoples, but for the integrity of our global human rights framework.
Indigenous communities worldwide are confronted with a myriad of systemic obstacles that hinder their rights and governance. These obstacles include social injustices that particularly impact Indigenous women, who often face discrimination and are deprived of basic services and representation. The United Nations forums are pivotal in shedding light on the essential need for incorporating Indigenous voices in decision-making processes, reflecting a growing acknowledgment of their unique governance systems. As discussions progress around the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, the emphasis on equity and justice remains at the forefront. It is imperative that we collectively advocate for the recognition and fulfillment of these rights to create a more inclusive society.
Understanding the Challenges Faced by Indigenous Peoples
Indigenous Peoples around the world face numerous challenges that stem from a long history of colonization and systemic marginalization. One of the foremost issues is their exclusion from decision-making processes related to their lands, territories, and cultural practices. The recent forum highlighted that without genuine participation, Indigenous communities struggle to assert their rights and protect their identities. This exclusion directly undermines their self-determination and the ability to sustain their ways of life, emphasizing the urgent need for reforms in governance that prioritize Indigenous Peoples’ rights.
Additionally, these challenges also extend to issues of food security and environmental sustainability. When Indigenous communities are bypassed in decisions regarding resource management and land use, the consequences ripple through their social fabric, affecting health and overall well-being. The call from leaders at the UN for inclusive governance underscores the inherent link between Indigenous rights and social justice, reinforcing the idea that justice for Indigenous Peoples is vital for a more equitable world.
The Role of UN Declaration on Indigenous Peoples in Empowering Governance
The UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples serves as a critical framework for advocating the rights and governance of Indigenous communities. Its implementation is paramount in empowering Indigenous leaders to engage effectively in political processes and make decisions about their own futures. This year’s theme at the UN forum emphasizes the necessity for member states to uphold the declaration, ensuring that Indigenous governance structures are respected and integrated into national policies. The recognition of Indigenous Peoples’ right to self-determination is not just a legal imperative but a moral one that aligns with the principles of justice and equality.
Fostering meaningful participation of Indigenous communities in governance can lead to better resource management and preservation of traditional knowledge. The challenges faced by Indigenous Peoples must be addressed through robust frameworks such as the UN Declaration, allowing Indigenous leaders to influence policies that affect their lives. As nations work towards implementing these principles, it becomes increasingly important to create win-win solutions that respect the rights of Indigenous Peoples while promoting social justice and sustainable development.
Indigenous Women: Advocating for Rights and Addressing Barriers
Indigenous women are at the forefront of advocating for their communities, yet they face unique challenges that exacerbate their marginalization. Barriers to political participation and access to essential services prevent them from fully engaging in governance processes. The recognition of Indigenous women’s roles as cultural leaders is crucial, as their voices are needed in discussions surrounding rights and resource management. They represent a vital link in the fight for social justice, advocating not only for their rights but also for the preservation of their cultures and the strength of their communities.
Moreover, the intersection between gender-based discrimination and the rights of Indigenous Peoples cannot be overlooked. Indigenous women often bear the brunt of systemic inequalities, experiencing both gender and ethnic discrimination. Their struggle for recognition, equity, and access to resources must be central to any discussions about Indigenous rights. Empowering Indigenous women by addressing these barriers is essential not only for their communities but for the broader quest for social justice for Indigenous Peoples as a whole.
The Need for Social Justice for Indigenous Peoples
Social justice for Indigenous Peoples encompasses a broad range of issues, including land rights, cultural preservation, and access to education and healthcare. The systemic inequities faced by Indigenous communities reflect historical injustices that have been perpetuated over centuries. Addressing these disparities requires a comprehensive approach that aligns policies with the principles enshrined in the UN Declaration on Indigenous Peoples. By fostering equity in social institutions, respect for Indigenous cultures can flourish, leading to sustainable development that benefits both Indigenous and non-Indigenous populations.
Furthermore, achieving social justice necessitates collaborative efforts from governments, civil society, and Indigenous leaders. Initiatives focused on inclusion and participation can create pathways toward resolving longstanding grievances and fostering healing. Social justice is not merely a political agenda; it is an imperative that recognizes the dignity of Indigenous Peoples and honors their rights. Only through concerted actions can the vision of a just and equitable society be realized, one where Indigenous Peoples can thrive in harmony with their lands and cultures.
Indigenous Governance: A Path Forward
Indigenous governance is essential for ensuring that Indigenous Peoples have a say in the management of their lands and resources. By reviving traditional governance systems and integrating them into modern practices, Indigenous communities can foster resilience and sustainability. The UN forum underscored the importance of respecting these governance systems, as they provide a framework for self-determination and cultural preservation. Empowering Indigenous governance enables communities to address their unique challenges and defend their rights against external threats.
Establishing a dialogue between Indigenous leaders and governmental bodies can also enhance mutual understanding and cooperation. This collaboration can lead to policies that are reflective of Indigenous knowledge and practices, further reinforcing the social justice framework outlined in international agreements. By prioritizing Indigenous governance, a more inclusive approach to decision-making can emerge, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for Indigenous Peoples in various aspects of life.
Addressing Environmental Issues through Indigenous Knowledge
Indigenous Peoples possess a wealth of traditional knowledge that has been honed over centuries, particularly related to environmental stewardship and resource management. Their deep connection to the land equips them with unique insights into sustainable practices that can combat climate change and biodiversity loss. The participation of Indigenous leaders in ecological discussions is vital for integrating their perspectives into broader environmental policy. Recognizing the rights of Indigenous Peoples is crucial for fostering the stewardship of their ancestral lands, ensuring both protection and restoration of ecosystems.
The UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples emphasizes the necessity of incorporating Indigenous knowledge into contemporary sustainability efforts. By validating and respecting Indigenous governance, not only do we honor their rights but also enhance our global strategies for environmental management. Empowering Indigenous voices can lead to innovative solutions to current ecological challenges, fostering a collaborative approach that respects both traditional practices and modern science.
Confronting Systemic Discrimination against Indigenous Peoples
Historically, systemic discrimination has marginalized Indigenous Peoples in many societies, denying them equal access to resources, education, and political representation. Addressing these injustices requires holistic reforms in societal structures that perpetuate inequality. At the recent UN forum, leaders called for urgent actions to dismantle systemic barriers that prevent Indigenous Peoples from realizing their rights and potential. Understanding the link between discrimination and social justice is critical in formulating effective policies that promote inclusivity and equality.
Combating systemic discrimination also involves raising awareness and educating broader society about the rights and contributions of Indigenous Peoples. It is essential for non-Indigenous communities to engage in dialogue and support initiatives that uplift Indigenous voices. Collaborative efforts must challenge the status quo and highlight Indigenous experiences, fostering a climate of mutual respect and understanding that promotes healing and justice.
The Importance of International Support for Indigenous Rights
International support plays a crucial role in advancing the rights of Indigenous Peoples globally. Institutions like the UN offer platforms where Indigenous leaders can advocate for their rights and influence policy decisions. This support creates opportunities for more equitable partnerships, fostering collaborative efforts between Indigenous communities and states to uphold the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples. The engagement of international organizations can also provide the resources needed to implement effective practices that respect Indigenous governance and social justice.
Moreover, global attention to Indigenous issues can drive national governments to prioritize the rights of Indigenous Peoples in domestic agendas. Advocating for recognition and protection of Indigenous rights on a global scale supports localized efforts and elevates issues that may otherwise be overlooked at the national level. This collective international commitment is essential for promoting social justice and ensuring that Indigenous Peoples can thrive in their communities.
Promoting Education and Empowerment among Indigenous Communities
Education is a key factor in empowering Indigenous Peoples and equipping them with the tools necessary to advocate for their rights. Access to quality education that is culturally relevant can help Indigenous communities reclaim their identity and traditions while preparing future generations for the challenges ahead. It is important that educational frameworks respect Indigenous knowledge systems and incorporate traditional practices to foster a sense of belonging and pride. Empowering Indigenous youth through education can significantly enhance their capacity to contribute to governance and social justice movements.
Furthermore, promoting vocational training and economic development initiatives tailored to Indigenous communities is vital. By providing skills training and resources, Indigenous Peoples can create sustainable livelihoods that honor their cultural identities. These initiatives should be designed in consultation with Indigenous leaders to ensure that they align with the needs and aspirations of the community. Ultimately, fostering education and economic opportunities is essential for building self-determination and resilience among Indigenous Peoples.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary challenges faced by Indigenous Peoples regarding their rights?
Indigenous Peoples face numerous challenges in asserting their rights, including legal recognition of land titles, political representation, and cultural preservation. These challenges stem from historical injustices and ongoing marginalization, which impede their self-determination and participation in decision-making processes that affect their communities.
How does the UN Declaration on Indigenous Peoples address challenges faced by Indigenous communities?
The UN Declaration on Indigenous Peoples provides a framework aimed at promoting the rights of Indigenous communities, emphasizing their right to self-determination, land ownership, and participation in governance. It calls for states to respect Indigenous rights and includes provisions to ensure their voices are heard in decisions affecting their lands and cultures.
In what ways do Indigenous governance systems contribute to social justice for Indigenous Peoples?
Indigenous governance systems play a critical role in achieving social justice by empowering Indigenous leaders to make decisions on issues affecting their communities. These systems promote cultural heritage and community autonomy, which are essential for overcoming the challenges faced by Indigenous Peoples and ensuring their rights are upheld.
What specific challenges do Indigenous women face compared to their male counterparts?
Indigenous women encounter unique challenges, including heightened barriers to political participation, access to economic opportunities, and essential healthcare services. They often deal with gender-based violence and systemic inequalities, which complicate their roles as leaders within their communities and hinder their capacity to advocate for rights and justice.
Why is it important to include Indigenous Peoples in decision-making processes?
Including Indigenous Peoples in decision-making processes is vital for ensuring their rights and addressing the historic exclusions they face. Their participation leads to more equitable governance, respectful handling of natural resources, and recognition of their cultural values, ultimately fostering sustainable development and social justice.
How do Indigenous leaders advocate for their rights on the international stage?
Indigenous leaders advocate for their rights on the international stage through participation in forums like the UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues, where they bring attention to their struggles and seek support for the implementation of the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples. They also collaborate with civil society and ally organizations to amplify their voices.
What impact does the non-regulated extraction of resources have on Indigenous communities?
The non-regulated extraction of resources on Indigenous lands disrupts their social, economic, and environmental conditions, leading to food insecurity, loss of traditional livelihoods, and environmental degradation. This exploitation undermines Indigenous Peoples’ rights and poses severe threats to their cultural identity and connection to their land.
What measures are being taken to address the disparities faced by Indigenous Peoples?
Efforts to address disparities faced by Indigenous Peoples include the promotion of their rights through international declarations and local policies, initiatives aimed at enhancing their economic opportunities, and mechanisms to ensure their involvement in governance. Advocacy from both Indigenous leaders and supportive organizations plays a crucial role in these measures.
How does systemic marginalization affect Indigenous Peoples’ access to services?
Systemic marginalization restricts Indigenous Peoples’ access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and economic opportunities. This exclusion from necessary resources results in persistent health disparities, lower educational attainment, and limited job prospects, perpetuating cycles of poverty and inequality.
What role does the UN play in supporting Indigenous Peoples’ rights and challenges?
The UN plays a pivotal role in supporting Indigenous Peoples’ rights by facilitating discussions on their challenges, promoting international legal frameworks like the UN Declaration on Indigenous Rights, and urging Member States to uphold these rights through policy reforms and inclusive governance practices.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Exclusion from Decision-Making | Indigenous Peoples are often excluded from decisions affecting their lands and cultures. |
| Impact on Identity and Survival | UNPFII emphasizes the impact of governance on Indigenous identity and self-determination. |
| Indigenous Women Challenges | Indigenous women face unique barriers to participation and access to resources. |
| Call for Empowerment | Governments are urged to empower Indigenous governance and ensure rights are upheld. |
| Global Leadership Awareness | International forums aim to recognize and act on the needs of Indigenous Peoples. |
Summary
Challenges faced by Indigenous Peoples are deeply rooted in systemic exclusion and oppression that affects their rights, identity, and sovereignty. Despite ongoing efforts to address these issues through initiatives such as the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, many Indigenous communities continue to struggle for representation in decision-making processes that influence their lives and lands. From the persistent barriers faced by Indigenous women to the urgent need for equitable governance, these challenges are not merely injustices but affronts to dignity and justice that demand immediate attention and action.