Birth Rates in Women Over 40 Surpass Teens for First Time
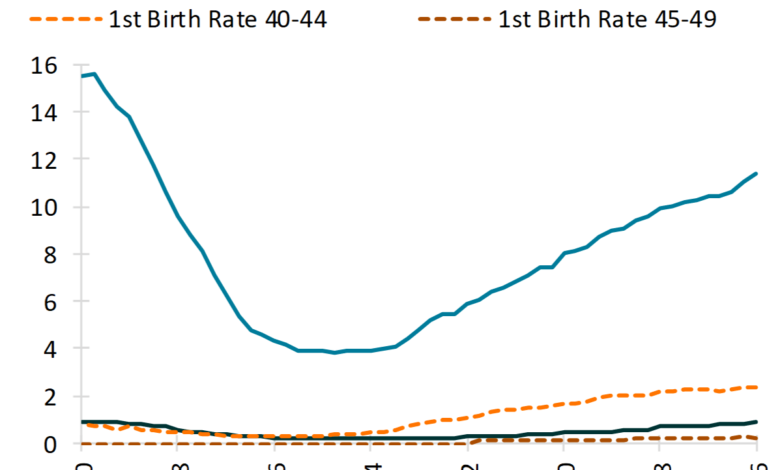
Birth rates in women over 40 are witnessing a remarkable surge, having increased 193% since 1990, according to recent CDC birth data. This striking trend marks a pivotal shift in fertility patterns, as for the first time in U.S. history, more babies are now born to women over 40 than to teenagers. While statistics indicate that teen pregnancy rates are declining, the rise in births among older women reflects a broader socio-cultural trend of women delaying childbirth. As advances in reproductive technologies continue to evolve, women are increasingly empowered to make informed choices about when to start their families. By 2025, these fertility trends not only showcase changing demographics but also highlight the growing influence of reproductive technology on motherhood choices.
The demographic landscape of motherhood is shifting, with more women choosing to embrace parenthood later in life. This phenomenon, characterized by an increase in birth rates among women aged 40 and above, contrasts sharply with the significant decline in births among younger mothers. Various factors contribute to this shift, including the decreased incidence of adolescent pregnancy and the increasing popularity of assisted reproductive technologies. As societal norms evolve and healthcare advancements flourish, the landscape of childbearing continues to be redefined, allowing women to pursue their personal and professional aspirations before starting families. In essence, the trend of older maternal ages signifies a transformative period in reproductive patterns and choices.
The Rise in Birth Rates Among Women Over 40
Recent statistics reveal a significant trend in U.S. birth rates: for the first time, more babies are being born to women over 40 than to teenagers. According to the CDC, the birth rates for women aged 40 and older have surged by an astounding 193% between 1990 and 2023. This change is noteworthy, indicating a cultural shift in how women are approaching motherhood, with many opting to start families later in life. Factors such as better career prospects, educational opportunities, and evolving societal norms have contributed to this trend, allowing women to delay childbirth until they feel more prepared for the responsibilities of parenting.
Additionally, this rise in births among older mothers contrasts sharply with a dramatic decline in teen pregnancies. Data from the CDC shows that birth rates among women under 20 have plummeted by 73% during the same period. This stark contrast highlights changing reproductive patterns and societal expectations, leading many to speculate about the long-term implications for family structures and support systems in the United States.
Understanding the Decline in Teen Pregnancy Rates
The decline in teen pregnancy rates over recent decades is evidenced by the CDC’s findings, showing a decrease from one in eight births to one in 25 births among teenagers. This downward trend has been attributed to multiple factors, including enhanced access to contraception and sex education. Public health programs focused on educating young people about reproductive health have made significant strides in reducing unplanned pregnancies, showcasing a proactive approach to adolescent sexual health.
Moreover, cultural shifts have altered how teens perceive pregnancy and parenthood. With a growing focus on education and career development, many young people are choosing to prioritize personal growth over early parenthood. These changes reflect an essential movement towards promoting informed choices regarding family planning, ultimately leading to a generation that is better prepared and more responsible.
The Impact of Advancements in Reproductive Technology
Advancements in reproductive technology have played a crucial role in the growing trend of women over 40 becoming mothers. Techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), egg freezing, and embryo banking have revolutionized how women view their fertility options, ultimately empowering them to make choices about when to start a family. Dr. Ashley Wiltshire from Columbia University notes that these technologies provide women with enhanced reproductive autonomy, allowing them to delay childbirth without sacrificing their desire to become mothers.
Additionally, the utilization of donor eggs has also significantly impacted birth rates in older women, improving their chances of successful pregnancies and live births. As a result of these technological advancements, many women in their 40s are experiencing successful pregnancies, signifying a shift in reproductive trends as they embrace motherhood at a stage once considered unconventional.
Comparative Analysis: Fertility Trends of the Future
Looking forward, fertility trends indicate continuing changes in age distribution among new mothers, particularly as women increasingly choose to have children later in life. Projections for 2025 suggest that birth rates among women over 30 will continue to rise, while rates among women under 30 will remain stagnant or potentially decrease further. This shift will have profound implications for various social and economic factors, including workforce demographics and healthcare services catered to older mothers.
Moreover, as societal views continue to evolve, the notion of family structures is being redefined. Women delaying childbirth may lead to unique family dynamics that prioritize flexibility and individual choice. With continued advancements in reproductive technologies, the scope for family planning will broaden even further, ensuring that women have support to pursue their reproductive goals regardless of age.
The Societal Implications of Delayed Childbirth
Delaying childbirth carries significant societal implications, with potential influences on population growth, economic stability, and healthcare systems. With an increasing number of women over 40 having children, there are questions about how this trend will affect overall birth rates and demographic shifts in society. As older mothers become more common, it may lead to changes in family structures, child-rearing practices, and demands for resources, particularly in the education and health sectors.
Moreover, the trend of women opting to have children later may contribute to a movement towards more inclusive workplace policies that support parents of all ages. As businesses recognize the need for flexibility for older parents who may also be navigating career advancements, policies may evolve to accommodate new family dynamics, promoting a more supportive environment for all workers.
Statistics and Data: The Pulse of Birth Trends
The pulse of birth trends can be accurately captured through statistics and data analysis provided by reputable sources like the CDC. As reported, there has been a 14% decline in total U.S. births from 1990 to 2023, with the most striking decrease observed among women under 30. Meanwhile, the significant increase in births among older women illustrates shifting reproductive norms, making statistical analysis key to understanding these changes.
Moreover, data revealing that women aged 30 and older accounted for more than half (51.4%) of all births in 2023 signals a transformation in maternal age distributions. This quantitative approach allows for informed discussions about the health, social, and economic implications of these trends within society, highlighting the urgent need for policies that adapt to shifting demographics.
The Role of Education in Family Planning
Education plays a pivotal role in shaping perceptions and decisions regarding family planning among women. Increasing access to comprehensive sex education and reproductive health resources is critical in equipping young women with the knowledge they need to make informed choices about when to become mothers. With diminishing teen pregnancy rates, it’s evident that education focused on reproductive health significantly influences women’s decisions surrounding childbirth.
Furthermore, educational initiatives promoting awareness about reproductive technology advancements equip women of all ages with the tools to plan effectively. By understanding the options available—such as egg freezing or the use of donor eggs—women can align their family planning with their personal and professional aspirations, ensuring they have the support and information necessary for their unique journeys.
Exploring the Future of Reproductive Health Policies
As birth trends continue to evolve, there is a pressing need to reassess reproductive health policies. Policymakers are called to consider the implications of rising birth rates among older women and declining rates among teenagers while addressing access to reproductive healthcare and technologies. These changes signal the necessity for a responsive healthcare system that supports diverse reproductive choices across varying demographics.
In addition, improving access to information about assisted reproductive technologies (ART) will empower more women to explore their options, potentially contributing to healthier pregnancies and families. Comprehensive reproductive health policies should foster an environment that facilitates informed decisions, ultimately reducing barriers for all women, regardless of age, who wish to realize their family planning goals.
Cultural Shifts Towards Parenthood
Cultural attitudes towards parenthood are shifting dramatically, particularly as more women prioritize education and career aspirations over early childbirth. This cultural shift is leading to new norms surrounding family formation, as societal acceptance of older maternity grows. Stories of successful older mothers have become more prevalent, reshaping how society views age in the context of parenthood.
As these cultural changes unfold, discussions about the evolving expectations for women in both personal and professional realms emerge. Future generations will likely benefit from the groundwork laid by women today, who are navigating these complex choices and advocating for broader acceptance of varied family structures and parenting paths.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current birth rates in women over 40 compared to teens?
According to recent CDC birth data, for the first time in U.S. history, women over 40 are having more babies than teens. Birth rates in women over 40 have surged by 193% since 1990, while teen pregnancy rates have dropped significantly, decreasing by 73% during the same period.
How is the trend of women delaying childbirth affecting birth rates?
The trend of women delaying childbirth is positively impacting birth rates in women over 40. As more women choose to wait for various personal and professional reasons, advancements in reproductive technology have made it possible for them to conceive later in life, contributing to the increase in birth rates among older mothers.
What role do reproductive technology advancements play in increasing birth rates in women over 40?
Advancements in reproductive technology, including assisted reproductive technology (ART) and methods such as egg freezing, have dramatically improved the odds of conception for women over 40. These technologies allow women to delay childbirth while maintaining their fertility options, leading to an increase in birth rates in this age group.
How do fertility trends in 2025 reflect the shift in childbirth age demographics?
Fertility trends in 2025 showcase a significant shift where women over 40 are having more babies than those under 30. This reflects a societal change whereby younger women are either postponing childbirth or opting not to have children at all, resulting in a decrease in overall birth rates while women aged 30 and older, including those over 40, see increases in childbirth.
What is the impact of CDC birth data on understanding fertility trends?
CDC birth data highlight crucial fertility trends, particularly the increase in births among women over 40 paired with a decline in teen births. This shift underscores changing societal norms regarding motherhood and the growing influence of reproductive technology, shaping our understanding of current fertility patterns.
Why are more women over 40 giving birth now than ever before?
More women over 40 are giving birth now due to comprehensive reproductive advancements, greater access to fertility treatments, and increased societal acceptance of later-in-life motherhood. Many women are also focusing on their careers and personal development before starting a family, leading to this historic rise in birth rates for this age group.
What factors contribute to the increase in births among women aged 35 and older?
Factors contributing to the rise in births among women aged 35 and older include improvements in reproductive healthcare and technology, increased educational and career opportunities for women, and changing societal norms that support later motherhood. All of these factors combine to create a conducive environment for women to have children later in life.
How does the rise in births among women over 40 impact overall fertility rates?
Despite the rise in births among women over 40, overall fertility rates are declining due to significant decreases in birth rates among younger women. The increase in older mothers does not fully offset the decline in births in younger age groups, suggesting a broader trend of delayed childbirth.
What implications do these birth rate trends have for public health policy?
The increasing birth rates in women over 40 and decreasing rates among younger women imply a need for public health policies to address the unique healthcare needs of older pregnant women, including prenatal care and maternal health services, as well as continued support for reproductive health options for all women.
How do societal attitudes toward motherhood impact birth rates in women over 40?
Societal attitudes toward motherhood have evolved, with greater acceptance of women pursuing late motherhood for personal or career reasons. This shift in perspective has empowered many women to prioritize their life goals before starting a family, consequently increasing birth rates among women over 40.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Birth rates in women over 40 have increased by 193% since 1990, as reported by the CDC. |
| For the first time in U.S. history, more babies are born to women over 40 than to teenagers. |
| Birth rates among women under 20 have decreased by 73% from 1990 to 2023. |
| Women aged 30 to 34 have seen a 24% increase in births, while women aged 35 to 39 have seen a 90% increase. |
| In 1990, women over 40 represented 1.2% of total births, rising to 4.1% by 2023. |
| Advancements in contraception and assisted reproductive technology contribute to women having children later in life. |
Summary
Birth rates in women over 40 have seen a significant increase, marking a pivotal shift in demographic trends. For the first time in U.S. history, more babies are born to women in this age category than to teenagers. This dramatic change, as evidenced by the CDC’s report, indicates that societal norms regarding motherhood are evolving, with many women opting to postpone childbearing. Factors such as advanced contraception and reproductive technologies like egg freezing are empowering women to make informed decisions about their family planning. As a result, women over 30 accounted for over half of births in 2023, compared to a much smaller percentage in 1990, illustrating a transformation in maternal age distribution in the U.S.




