Aspergillus Infections: Rising Threat from Climate Change
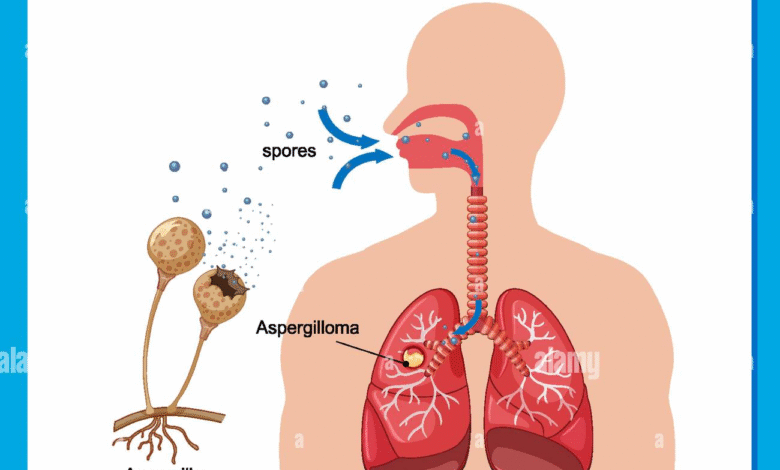
Aspergillus infections are becoming an urgent concern as climate change influences the spread of this notorious fungal mold. Research indicates that rising global temperatures will enhance the growth of Aspergillus, leading to increased instances of a related disease known as Aspergillosis. While many healthy individuals might not exhibit symptoms upon exposure, those who are immunocompromised could face severe health risks, including invasive lung infections. Additionally, it’s crucial to recognize Aspergillosis symptoms early to manage these potentially life-threatening fungal infections effectively. Preventing Aspergillus from causing harm requires vigilance, especially in light of the predicted rise in environmental prevalence due to climate change effects.
In the realm of fungal diseases, Aspergillus represents a challenging group of pathogens that thrive in varied climates and environments. Commonly, the term “Aspergillosis” refers to the infections caused by these ubiquitous molds, which affect a range of hosts from plants to animals and humans. Both environmental factors and compromised immune systems play pivotal roles in the emergence of these infections. As climate-related changes continue to reshape ecosystems, understanding and addressing potential risks to health becomes vital for vulnerable populations. Enhanced awareness of the impact of climate fluctuations on fungal proliferation is essential to develop effective preventive strategies against these infections.
Understanding Aspergillus Infections
Aspergillus infections, commonly referred to as Aspergillosis, are caused by a type of mold often found in the environment. For most healthy individuals, exposure to Aspergillus spores generally doesn’t lead to serious health problems, as their immune systems can usually handle the small amounts of spores inhaled daily. However, for immunocompromised individuals—such as those on chemotherapy or with pre-existing respiratory conditions—the spores can lead to severe respiratory infections, including Aspergillus pneumonia. The recent studies suggest that climate change could exacerbate the prevalence of these infections, making understanding them even more critical.
The symptoms of Aspergillus infections can vary widely, ranging from mild allergic reactions, including wheezing and fever, to severe respiratory distress in those with weakened immune systems. Given the environmental persistence of Aspergillus spores, as climates warm, more people may unknowingly breathe in these spores without realizing the associated risks. This makes it crucial for the healthcare community to not only recognize Aspergillus infections early but also improve awareness among vulnerable populations about the potential threats posed by this ubiquitous fungus.
The Impact of Climate Change on Aspergillus Spread
Researchers have indicated that rising global temperatures can significantly influence the growth and spread of Aspergillus. As warm, damp climates become more prevalent due to climate change, the conditions become increasingly favorable for the proliferation of this mold. Predictions suggest a potential rise of up to 77% in Aspergillus infections by 2100 if current climate trends continue. This alarming forecast highlights how changes in our environment can have direct consequences on public health, especially concerning fungal infections.
The shift in climate not only supports the growth of Aspergillus but also facilitates its migration to new areas. As certain geographical locations start to experience warmer conditions, the risk of fungal infections such as Aspergillosis could spill over into populations that previously had little exposure. This underscores the necessity for increased surveillance and understanding of how climate change may influence the dynamics of fungal infections, which can have far-reaching effects on both human health and agriculture.
Symptoms and Consequences of Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis can manifest in various forms, with symptoms ranging from mild allergic responses to severe pneumonia that can be fatal, particularly in vulnerable groups. Common symptoms include cough, fever, and shortness of breath, which can escalate quickly in patients with compromised immune systems. The complexity in diagnosing Aspergillosis lies in its presentation, often resembling other respiratory diseases, making it crucial for healthcare providers to be vigilant and consider a fungal origin in underlying cases.
The consequences of untreated Aspergillus infections can be dire, especially among the elderly and those with existing respiratory issues. In immunocompromised individuals, the progression from simple infection to systemic illness can occur rapidly, leading to complications affecting multiple organs through the bloodstream. As Aspergillus spores spread, physicians must possess a keen awareness of symptoms to avoid misdiagnosis and ensure timely intervention, highlighting the need for improved diagnostic practices in recognizing fungal infections.
Preventing Aspergillus Infections in Vulnerable Populations
Preventative measures are paramount for individuals at heightened risk of developing Aspergillus infections. Immunocompromised patients must take additional precautions by avoiding exposure to environments where Aspergillus thrives, such as damp, decaying vegetation or construction sites. It is also essential for these individuals to consult healthcare providers to discuss possible protective strategies and medications that can minimize their risk. Moreover, public health initiatives must focus on educating at-risk populations about the signs and symptoms of Aspergillosis.
In addition to personal precautions, healthcare systems must enhance their training for medical professionals to recognize and treat Aspergillus infections promptly. Improved awareness among clinicians can lead to quicker diagnoses and better treatment outcomes. The development of new antifungal agents is also critical, as current treatment options can be ineffective, especially with the rising incidence of drug-resistant fungal strains. This dual approach of education and medical advancement is necessary for effectively combating the threats posed by Aspergillus.
The Role of Research in Combating Aspergillus Infections
Ongoing research plays a crucial role in understanding and combatting Aspergillus infections. With the predicted increase in prevalence due to climate change, studies focusing on the biology of Aspergillus and its interaction with human hosts are essential. Understanding how Aspergillus causes disease can lead to more effective therapies and preventative measures. Investigations into new medications and improved diagnostic methods are urgently needed to prepare for challenges stemming from rising Aspergillus cases.
Furthermore, funding and supporting research initiatives focused on Aspergillus can yield significant benefits in public health. By investing in scientific inquiries that explore the interactions between environmental factors and fungal infections, healthcare systems can better develop resilient strategies to protect vulnerable populations. Collaboration among researchers, healthcare professionals, and public health organizations will be key to reducing the risk of Aspergillus infections in future generations.
Aspergillus Infections and Agricultural Risks
Aspergillus not only poses risks to human health but also significantly impacts agriculture. The presence of this mold in fields can lead to crop diseases that affect food supply and economic stability for farmers. Conditions conducive to Aspergillus growth can facilitate the spread of infections in plants, resulting in reduced yields and quality. This interconnectedness between human health and agriculture highlights the need for a multi-faceted approach to addressing the challenges posed by Aspergillus.
As agriculture adapts to climate change, new measures must be implemented to manage the risks associated with Aspergillus infections in plants. Strategies such as crop rotation, improved soil health, and monitoring environmental conditions can help mitigate potential outbreaks. Collaborating with agricultural researchers to develop fungal-resistant crop strains can also be beneficial in reducing the impact of Aspergillus on food production. Awareness and proactive measures in the agricultural sector can help ensure food security while addressing public health concerns.
The Global Outlook on Aspergillus Infection Trends
The global outlook for Aspergillus infections suggests a troubling trend influenced by climate change and the increasing vulnerability of populations. Studies project that rising temperatures will not only expand the habitat range of Aspergillus but also increase the incidence of infections, particularly in regions previously less affected. Understanding these trends is critical for public health planning and resource allocation, especially in areas seeing changes in climate that favor fungal growth.
As a result, global health agencies must prepare for a potentially rising tide of Aspergillus infections. Increased monitoring of environmental conditions, coupled with public health interventions aimed at educating populations at risk, is essential. These strategies should also include international collaborations to share data and best practices, ensuring that all countries can effectively respond to the threats posed by Aspergillus and similar pathogens in a warming world.
Innovative Treatment Approaches for Aspergillus Infections
Innovation in treatment options for Aspergillus infections is urgently needed in light of the rising prevalence and the emergence of drug-resistant strains. Current antifungal medications often fall short, leaving healthcare providers searching for more effective alternatives. Research focused on developing novel antifungal therapies that can target Aspergillus specifically has the potential to revolutionize treatment protocols and improve patient outcomes.
In addition to new medications, enhancing existing treatments through combination therapies may offer better efficacy against Aspergillus infections. The application of immunotherapy to bolster the immune response in at-risk populations could also serve as a preventive measure. Investing in cutting-edge research and clinical trials will be essential not only for combating current cases but also for preparing for Aspergillus infections as a public health concern in the future.
Raising Awareness about Aspergillus Infections
Raising public awareness about Aspergillus infections is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with this pervasive fungus. Initiatives that educate individuals about the potential dangers of exposure, especially for those with weakened immune systems, can empower communities to take preventive measures. Public health campaigns should highlight safe practices, early recognition of symptoms, and when to seek medical attention.
Moreover, integrating awareness programs within healthcare settings can greatly improve the recognition and management of Aspergillus infections. Training healthcare providers to identify symptoms and understand patient histories related to Aspergillus exposure can lead to quicker diagnoses and better treatment outcomes. By fostering a culture of awareness, we can significantly reduce the incidence of severe Aspergyrus infections and improve overall public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common Aspergillosis symptoms to watch for?
Common Aspergillosis symptoms can include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Individuals may also experience allergic reactions, such as asthma exacerbations, especially those with pre-existing respiratory conditions or weakened immune systems.
How can climate change effects increase the risk of Aspergillus infections?
Climate change effects, particularly rising temperatures and increased humidity, create favorable conditions for Aspergillus to flourish. This increased prevalence can lead to a higher risk of Aspergillus infections in vulnerable populations, especially in warmer regions.
What measures can be taken for preventing Aspergillus infections?
Preventing Aspergillus infections involves minimizing exposure, especially for immunocompromised individuals. It’s crucial to consult healthcare providers about protective measures, such as avoiding soil work and managing environmental exposure.
Why are immunocompromised individuals at a higher risk for Aspergillus infections?
Immunocompromised individuals are at a higher risk for Aspergillus infections because their immune systems are weakened, making it difficult to clear inhaled spores. This can lead to serious conditions like Aspergillus pneumonia and systemic infections.
What should I know about the treatment of Aspergillosis?
Treatment for Aspergillosis may include antifungal medications; however, these infections can be challenging to diagnose and treat effectively due to potential drug resistance. Early recognition and medical training are crucial for improving outcomes.
How is Aspergillus exposure common in everyday life?
Aspergillus is commonly found in the environment, particularly in soil and decaying organic matter, making it difficult to avoid exposure. Most healthy individuals can usually tolerate minimal exposure without adverse effects.
What role does Aspergillus play in agricultural diseases?
Aspergillus is associated with various agricultural diseases, impacting crops and livestock health. Climate change may exacerbate these risks, leading to increased prevalence and potential economic implications for farming.
Are there any advancements in diagnosing Aspergillus infections?
Current research emphasizes the need for better diagnostic methods for Aspergillus infections. Advances in this area are necessary to enhance disease recognition, which is critical for effective treatment and management.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Fungus Overview | Aspergillus is a fungal mold that thrives in warm, damp climates. It can affect humans, livestock, and plants. |
| Projected Increase | The prevalence of Aspergillus could rise by 77% by 2100 due to climate change. |
| Health Risks | Infections can range from mild allergy-like symptoms to severe invasive diseases, especially in immunocompromised individuals. |
| Current Treatment Challenges | Diagnosis is difficult, and treatment options for invasive fungal infections are limited. |
| Prevention Recommendations | Immunocompromised individuals should avoid soil exposure and consult healthcare providers for protective measures. |
Summary
Aspergillus infections pose a significant health threat, especially as climate change may lead to increased prevalence. Researchers warn that rising temperatures could allow Aspergillus to thrive, putting millions at risk of infections such as Aspergillosis. For immunocompromised individuals, exposure can lead to severe lung infections and systemic diseases. While there are antifungal treatments available, the challenge lies in accurate diagnosis and the development of new therapies. Proactive measures are essential to mitigate the risks associated with this concerning fungal pathogen.




