Artificial Intelligence in Colonoscopy: Balancing Benefits and Risks
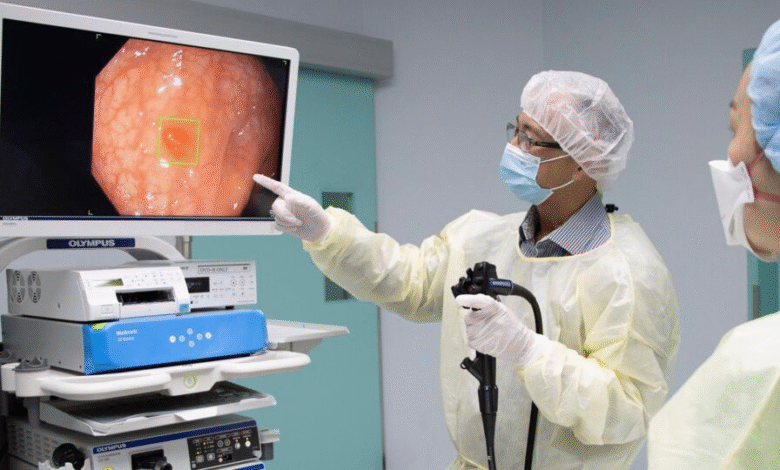
Artificial intelligence in colonoscopy is revolutionizing the way we approach cancer detection and screening. As AI in medicine becomes increasingly integrated into medical practices, its impact on colonoscopy technology cannot be overlooked. Recent research emphasizes the significant role that AI tools play in improving adenoma detection rates (ADR), a crucial metric in identifying early signs of colorectal cancer. However, this advancement brings to light potential AI healthcare risks, particularly concerning how endoscopist behavior may be affected when using these technologies. The balance between enhancing detection capabilities and maintaining clinician proficiency is vital for ensuring the effectiveness of colonoscopy procedures.
The utilization of technology-driven solutions in gastrointestinal examinations is opening new avenues for enhancing the accuracy of cancer screenings. The involvement of machine learning and algorithms in endoscopic procedures showcases a transformative shift in cancer detection protocols. By leveraging advanced imaging techniques, practitioners aim to improve the adenoma identification process, which is crucial for patient outcomes. Nevertheless, reliance on these sophisticated tools also raises questions regarding the human element, as variations in endoscopic performance may occur in the absence of such innovations. Striking a balance between technological assistance and the irreplaceable skills of healthcare professionals is essential for advancing patient care.
Understanding the Role of AI in Colonoscopy
Artificial intelligence in colonoscopy is transforming how endoscopists perform their procedures. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning, AI tools are capable of identifying polyps and other anomalies that the human eye might overlook. This technology enhances the overall effectiveness of colonoscopy procedures, contributing to earlier detection of colorectal cancer and potentially saving lives. In addition, AI tools are designed to assist doctors rather than replace them, promoting a collaborative environment where technology augments human expertise.
However, the introduction of AI in colonoscopy does not come without its challenges. A recent study highlighted that the reliance on AI could lead to a decline in endoscopist performance when these tools are not available. This raises important questions about how clinicians can maintain their skills and ensure patient safety in situations where they must operate without artificial intelligence assistance. As medical practitioners integrate AI into their routines, it’s essential to balance technological advancements with the need for human vigilance.
The Impact of AI on Adenoma Detection Rates
One of the critical metrics for evaluating the success of colonoscopy procedures is the adenoma detection rate (ADR). This rate indicates how effective endoscopists are at identifying adenomas, which are precursors to colorectal cancer. The study observed that the introduction of AI led to a notable decline in ADR; detection went from 28.4% to 22.4% following AI exposure, which is a significant drop. Such results highlight a paradoxical consequence of using AI; while it aids in polyp detection during procedures, it may create over-reliance on technology that could hinder doctors’ observational skills when AI is absent.
The findings underscore the importance of continuous training for endoscopists to maintain and improve their skills in adenoma detection. As Dr. Harvey Castro points out, even a minor decrease in detection can have substantial implications for patient survival rates. This emphasizes the critical need for a structured integration of AI tools in colonoscopy, ensuring that clinicians are equipped to perform effectively in a variety of circumstances, both with and without AI support. Training programs should focus on developing the clinician’s ability to recognize patterns and anomalies, thus reinforcing the importance of human observation in conjunction with AI advancements.
Balancing AI Benefits and Healthcare Risks
While artificial intelligence brings significant benefits to colonoscopy procedures, it also introduces various healthcare risks that need to be managed. The study demonstrated that, despite AI’s potential to enhance polyp detection, it may inadvertently lead to complacency among endoscopists when they rely too heavily on technology. This raises concerns about the significance of maintaining traditional scrutiny skills and the potential for diminished performance in its absence. Hence, healthcare providers must be aware of these risks and implement measures to ensure AI complements rather than diminishes clinical expertise.
Furthermore, the dialogue surrounding AI in medicine needs to include active discussions about the ethics of technological dependency. As AI continues to evolve within healthcare, understanding its limitations and potential drawbacks is crucial. Clinicians must engage in ongoing training and education that foster both technical skills and critical thinking, ensuring that they do not become overly reliant on AI systems. By finding a balance between leveraging AI capabilities and preserving essential medical judgment, the healthcare sector can optimize patient outcomes while safeguarding against emerging risks.
Enhancing Endoscopist Behavior Through AI Training
In light of the recent findings regarding the role of AI in influencing endoscopist behavior, training programs must evolve to address these changes. Understanding how AI affects clinical performance is vital for developing curricula that enhance both technical skills and personal judgment. Proper training should not only familiarize endoscopists with AI tools, but also encourage them to maintain their analytical capabilities when performing colonoscopies without AI support. This dual focus on technology and clinician insight can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Implementing hands-on workshops combining AI technology and live practice can prepare endoscopists to navigate challenges effectively. This training can emphasize the importance of adapting to various scenarios, including instances where AI may not be available. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between AI tools and endoscopist behavior, medical institutions can ensure their staff remains proficient in detecting adenomas and other abnormalities, ultimately improving the quality of patient care across the board.
The Future of AI in Colonoscopy: Collaboration or Replacement?
The future of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy hinges on understanding its role as a collaborative tool rather than a replacement for human clinicians. As highlighted in the study, while AI can provide critical assistance in polyp detection, it is equally essential to acknowledge the irreplaceable skills that physicians bring to the table, such as intuition and judgment. The goal should be to create an environment where AI augments the capabilities of endoscopists, allowing for improved detection rates and enhanced patient outcomes.
Healthcare institutions need to foster a culture of collaboration between AI and human practitioners. This involves rigorous training that stresses the symbiotic relationship between technology and human expertise. As Dr. Castro indicates, effective integration of AI requires careful consideration of how these tools are implemented, ensuring they maximize physician performance without creating dependency. Ultimately, the best outcomes will emerge from a system where technology and healthcare professionals work in concert, guiding patients through safe and efficient care pathways.
Addressing Concerns about AI in Healthcare
As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly integrated into the healthcare infrastructure, it is crucial to address the overarching concerns related to its use. One major issue revolves around the fear of de-skilling among healthcare professionals, particularly in fields such as gastroenterology where technology plays a significant role in clinical decision-making. The noted decrease in adenoma detection rates after AI exposure suggests a need for vigilance in maintaining clinician skills, ensuring that medical professionals remain adept at diagnosing and interpreting findings without the aid of AI.
In addition to skill degradation, ethical considerations arise as AI struggles with transparency in decision-making processes. Clinicians must be trained not only to utilize AI effectively but also to understand the limitations of these systems. By fostering critical thinking and emphasizing personal expertise, the healthcare sector can empower professionals to make informed decisions when it comes to patient care, ultimately enhancing the overall standard of health services while addressing potential AI healthcare risks.
Ethical Implications of AI in Colonoscopy
The ethical implications of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy are significant and require ongoing discourse among practitioners and policymakers. Questions regarding patient consent, data privacy, and the influence of AI on clinical judgment are paramount, especially given that reliance on technology may alter physician behavior. One of the ethical concerns highlighted in the study is the risk of over-reliance on AI tools, which might inhibit the clinician’s ability to make autonomous decisions. As healthcare continues to evolve, it is vital to ensure that AI serves to enhance, rather than compromise, the clinician-patient relationship.
Moreover, policies must be established to govern the use of AI in clinical settings, safeguarding patient rights while promoting equitable access to the benefits of technology. Healthcare systems should prioritize transparency regarding how AI tools analyze data and make recommendations, fostering trust between patients and medical professionals. By aligning ethical practices with the integration of AI, the medical community can work towards maximizing the advantages of technology in colonoscopy while addressing its inherent challenges.
Staying Informed: The Evolving Landscape of AI in Medicine
Keeping abreast of developments in artificial intelligence within the medical field is crucial for both practitioners and patients. As AI technology continues to evolve and permeate various specialties, it becomes imperative for healthcare professionals to understand its capabilities and limitations. This not only involves staying updated on new tools and innovations in colonoscopy but also comprehending the broader implications of AI in medicine, such as its potential risks and benefits. A proactive approach to education and training ensures that professionals can adapt to changing environments and leverage AI to improve patient outcomes.
Additionally, engaging in dialogues about the future of medicine, particularly the role of AI, fosters a well-informed community that can navigate this transformative landscape. Collaborative efforts among clinicians, researchers, and technologists will be essential to refine AI applications, ensuring they enhance clinical practice rather than detract from it. By embracing lifelong learning, healthcare providers can lead the charge in integrating artificial intelligence in a manner that ultimately prioritizes patient safety and health as the foremost goal.
Conclusion: Embracing AI with Vigilance and Purpose
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy represents a double-edged sword. While it offers remarkable potential for enhancing the detection of polyps and improving patient outcomes, it also presents unique challenges, particularly concerning the behavior and skills of endoscopists. As indicated by recent research, fostering a balanced approach to AI utilization is crucial to mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on technology. The collaboration between AI tools and human intuition must be carefully managed to uphold the standards of care.
Moving forward, the healthcare community must commit to continuous training and development for clinicians, ensuring they remain adept regardless of the technological landscape. By thoughtfully integrating AI into clinical practice, healthcare providers can harness the benefits of innovation while preserving the essential human elements of medicine that are vital for effective patient care. The path to a successful future in medicine lies in collaboration—where technology enhances human capabilities, leading to safer and more effective healthcare for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does artificial intelligence in colonoscopy play in adenoma detection rates?
Artificial intelligence in colonoscopy significantly enhances adenoma detection rates (ADR) by improving polyp identification during the procedure. Studies have shown that AI tools can assist endoscopists in detecting tumors more effectively, although there is a concern that reliance on AI may reduce the clinician’s ability to detect issues independently.
Are there risks associated with AI in colonoscopy technology?
Yes, AI in colonoscopy technology presents certain healthcare risks. Research indicates that while AI can aid in detecting cancer, it may also diminish the endoscopist’s ability to recognize critical issues when not using AI tools, as evidenced by a decline in adenoma detection rates when clinicians performed colonoscopies without AI assistance.
How does AI impact endoscopist behavior during colonoscopy procedures?
The incorporation of AI in colonoscopy has shown to alter endoscopist behavior. A study found that continuous exposure to AI might lower the adenoma detection rate of standard non-AI-assisted colonoscopies, suggesting that clinicians may become reliant on AI tools, potentially affecting their performance in AI-absent situations.
What was the outcome of the ACCEPT trial regarding AI in colonoscopy?
The ACCEPT trial, which focused on artificial intelligence in colonoscopy for cancer prevention, revealed a significant drop in tumor detection rates following the introduction of AI tools. Specifically, the adenoma detection rate decreased from 28.4% prior to AI introduction to 22.4% afterward, raising concerns about the effects of AI on endoscopist performance.
How should healthcare integrate AI in colonoscopy effectively?
To effectively integrate AI in colonoscopy, healthcare providers must ensure a balanced approach that enhances clinician capabilities rather than undermining them. This involves proper training, ongoing oversight, and purposeful design of AI systems to support endoscopists while maintaining their critical diagnostic skills.
Is AI in healthcare likely to replace human doctors in colonoscopy procedures?
AI in healthcare, including colonoscopy, is not expected to replace human doctors but rather to assist them. The optimal scenario involves a collaborative effort where AI enhances detection capabilities, while the clinician’s experience, judgment, and insight remain essential for patient care.
What implications does the decline in adenoma detection due to AI suggest for cancer patient outcomes?
Even a minor decline in adenoma detection rates due to AI can have significant implications for cancer patient outcomes. Research indicates that reductions in ADR can impact colon cancer survival rates, emphasizing the need for a cautious approach to AI integration in colonoscopy procedures.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Background | Examined AI influence on endoscopist behavior during colonoscopies; part of ACCEPT trial in Poland. |
| Research Period | September 2021 to March 2022; included both AI-assisted and non-AI-assisted procedures. |
| Patient Count | 1,443 patients underwent colonoscopies before and after AI implementation. |
| Key Findings | Detected tumor rate dropped from 28.4% before AI exposure to 22.4% after. |
| Contributors to Decline | Exposure to AI, and factors like patient gender and age influenced detection rates. |
| Expert Opinion | Dr. Harvey Castro: AI may assist but could reduce doctors’ detection ability. |
| Future Recommendations | AI should be integrated thoughtfully in medicine to enhance, not overshadow, clinician skills. |
Summary
Artificial intelligence in colonoscopy presents both remarkable opportunities and significant challenges. While AI can enhance the detection of tumors during procedures, recent findings indicate that its presence might inadvertently degrade the performance of endoscopists when AI is unavailable. This paradox emphasizes the need for a balanced approach in integrating AI within the medical field, ensuring that human expertise remains central to patient care. The goal should be to design AI systems that complement physicians, improving overall outcomes for patients.




