Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy: New Stem Cell Breakthrough Unveiled
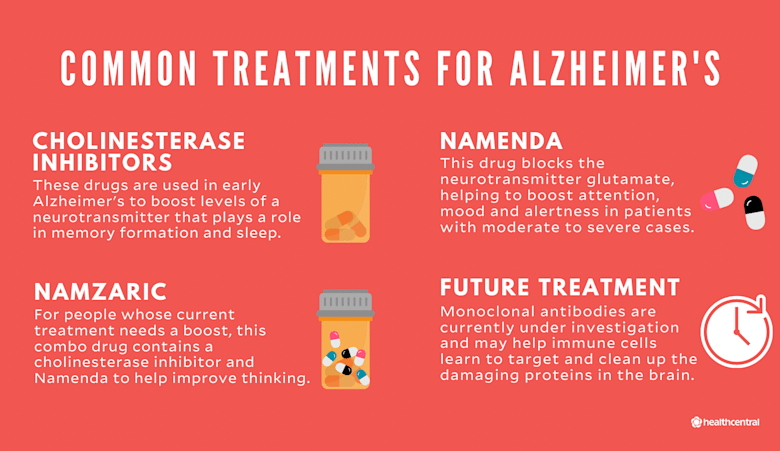
Alzheimer’s disease therapy is witnessing a revolutionary breakthrough with recent advancements in stem cell technology aimed at alleviating dementia symptoms. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine, have pioneered a new method that incorporates human immune microglia cells, re-engineered via CRISPR gene editing, to produce the neprilysin enzyme. This enzyme plays a critical role in breaking down the beta-amyloid plaques prevalent in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients, thereby addressing one of the disease’s core challenges. Early tests in mice showcased remarkable results, including neuron preservation and reduced neuroinflammation, igniting hope for effective Alzheimer’s treatment options. As over seven million Americans grapple with Alzheimer’s, these innovative therapies herald a new era in neurologic care, with potential implications extending to various central nervous system disorders.
The exploration of innovative therapies for Alzheimer’s disease, often referred to as dementia care solutions, is becoming increasingly important as the global population ages. Within this context, strategies involving cellular regeneration, particularly through the use of stem cell interventions and gene editing technologies, are gaining traction. Alternative treatments like those enhancing the function of microglia cells are at the forefront, facilitating the clearance of harmful proteins such as beta-amyloid through the action of the neprilysin enzyme. As the search for effective Alzheimer’s treatment intensifies, these advancements not only promise to revolutionize patient care but also open up potential avenues for addressing similar neurodegenerative conditions. The crucial need for fresh and diverse approaches underscores the urgency of research funding and innovation in this vital field.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy
Alzheimer’s disease therapy has long been a focal point for medical research, as the urgent need for effective treatments intensifies. Current therapeutic approaches often fall short in addressing the complexities of this neurodegenerative disorder. Recent advancements, particularly the use of stem cell therapy, bring renewed hope as researchers strive to unlock more effective strategies to combat Alzheimer’s-related symptoms.
The integration of innovative techniques such as CRISPR gene editing into Alzheimer’s disease therapy highlights a pivotal shift in treatment paradigms. By employing these advanced technologies, researchers aim to not only mitigate symptoms but also to tackle the root causes, such as the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques within the brain. This multifaceted approach signifies the potential for developing more comprehensive treatment modalities.
The Role of Stem Cell Therapy in Alzheimer’s Treatment
Stem cell therapy presents a transformative avenue in Alzheimer’s treatment, offering a chance to regenerate and repair neural tissues affected by the disease. The research conducted at the University of California, Irvine, illustrates how human immune cells, specifically engineered microglia, can be harnessed to combat neurodegeneration. This strategy not only addresses existing symptoms but aims to prevent further neuron loss, which is crucial for preserving cognitive function.
Moreover, the ability to customize stem cells from individual patients opens new doors for personalized medicine. By tailoring treatments to match the specific needs of patients, the risk of immune rejection can be minimized, enhancing the effectiveness of Alzheimer’s disease therapy. These developments underscore the importance of continued research into the therapeutic applications of stem cells, not only for Alzheimer’s disease but also for other central nervous system disorders.
CRISPR Gene Editing and its Impact on Alzheimer’s Research
CRISPR gene editing has revolutionized scientific research, particularly in the domain of genetic diseases like Alzheimer’s. By enabling precise modifications to DNA, researchers can improve the functionality of microglia cells, equipping them with the necessary tools to degrade harmful substances such as beta-amyloid plaques. The synergy between CRISPR technology and stem cell therapy amplifies the potential for innovative treatments in combating Alzheimer’s disease.
The application of CRISPR in the context of Alzheimer’s therapy not only enhances the production of the neprilysin enzyme to clear amyloid deposits but also paves the way for understanding the genetic underpinnings of the disease. This deeper insight into molecular mechanisms ensures that future therapies can be more targeted and effective, ultimately leading to better outcomes for patients.
Microglia Cells: A Targeted Approach to Alzheimer’s Therapy
Microglia cells, the brain’s resident immune cells, play a pivotal role in maintaining neuronal health. Their dysfunction is often linked to neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. By focusing on microglia cells in therapy, researchers are innovating new ways to harness the body’s immune responses to address Alzheimer’s symptoms effectively. This targeted approach could lead to a significant shift in how therapies are formulated, aiming for improved patient outcomes.
Additionally, engineering microglia through advanced techniques like CRISPR has opened new avenues for therapeutic interventions. Enhancing the capability of these cells to manage inflammation and clear amyloid plaques holds promise for not just slowing the disease’s progression but potentially reversing some of its damaging effects. As studies continue to evolve, microglial therapy places a strong emphasis on the body’s ability to heal itself, facilitating a transformative step forward in neurodegenerative disease management.
The Importance of Neprilysin Enzyme in Alzheimer’s Treatment
The neprilysin enzyme plays a crucial role in the breakdown of amyloid-beta peptides, integral to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Research indicates that boosting neprilysin levels could mitigate plaque accumulation, one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s. The recent development of therapies that enable microglia cells to produce this enzyme showcases a novel strategy in Alzheimer’s treatment, potentially bridging a gap in existing therapeutic options.
Exploring ways to enhance neprilysin’s activity presents not just a target for Alzheimer’s treatment but also showcases the interplay between various biological systems in combating neurodegeneration. By understanding the mechanisms that regulate neprilysin, researchers can create more effective therapeutic interventions aimed at reducing cognitive decline, offering hope to millions affected by Alzheimer’s disease.
Future Directions for Alzheimer’s Disease Research
The ongoing exploration into Alzheimer’s disease treatment is more crucial than ever, especially considering the increasing prevalence of the condition among the aging population. With innovative therapies like stem cell intervention and CRISPR gene editing showing promise, the landscape of Alzheimer’s disease research is evolving rapidly. The future of Alzheimer’s disease therapy may revolve around personalized medicine, where treatments are specifically tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup and disease progression.
Furthermore, collaborations between research institutions and funding bodies, such as the National Institutes of Health, play a significant role in catalyzing advancements in Alzheimer’s research. Encouraging diverse research funding can help expand treatment options and foster innovation, paving the way for breakthroughs that not only address Alzheimer’s disease but also enhance our understanding of related central nervous system disorders.
Personalized Medicine in Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
Personalized medicine is emerging as a revolutionary approach to treating Alzheimer’s disease. By leveraging individual genetic profiles and disease characteristics, therapies can be tailored to optimize effectiveness and minimize side effects. The potential of customizing therapies using patients’ own stem cells, as indicated in recent studies, signifies a major leap toward personalizing Alzheimer’s disease treatment.
In this context, therapies designed to enhance the function of microglia and increase neprilysin production can be tailored to match each patient’s unique disease pathology. This approach not only holds promise for more effective interventions but also empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on the best available data, ultimately fostering a more proactive stance toward managing Alzheimer’s disease.
Implications of New Therapies for Alzheimer’s and Other Disorders
The implications of new therapies developed for Alzheimer’s extend far beyond this singular condition. Findings from recent research illuminate pathways that may be applicable to other central nervous system disorders, such as brain cancer and multiple sclerosis. The use of engineered microglia and strategic gene editing not only offers hope for Alzheimer’s patients but also opens avenues for broader neurological therapies.
As scientists refine these innovative approaches, the potential applications could greatly enhance the manpower of our medical arsenal against complex diseases. Highlighting the interconnectedness of central nervous system disorders informs a comprehensive strategy to tackle neurodegeneration, possibly creating multi-targeted therapies that address a spectrum of symptoms and conditions.
The Role of Research Funding in Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy Advancements
Research funding is paramount in advancing therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. The critical support from organizations like the National Institutes of Health helps propel groundbreaking studies, such as those focusing on stem cell therapy and CRISPR gene editing. Adequate funding ensures that innovative ideas have the resources necessary to transition from the laboratory to clinical trials—an essential step in making effective treatments available to patients in need.
Furthermore, as highlighted by experts in the field, comprehensive funding initiatives can encourage a wider array of research projects. Such diversification may lead to unexpected discoveries that could reshape our approach to treating Alzheimer’s and other related disorders. The commitment to investing in Alzheimer’s research is not just about finding a cure; it’s about improving the quality of life for millions affected by this devastating disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of stem cell therapy in Alzheimer’s disease therapy?
Stem cell therapy plays a crucial role in Alzheimer’s disease therapy by utilizing human immune cells, particularly microglia, to target and alleviate symptoms associated with the condition. Recent studies have developed techniques that leverage these stem cells to enhance the brain’s ability to clear harmful beta-amyloid plaques, which are linked to neurodegeneration.
How does CRISPR gene editing contribute to Alzheimer’s treatment?
CRISPR gene editing contributes significantly to Alzheimer’s treatment by enabling the modification of microglia cells, allowing them to produce neprilysin, an enzyme that helps break down beta-amyloid plaques. This innovative approach shows promise in reversing neurodegeneration and protecting neurons in the context of Alzheimer’s disease.
What is the significance of the neprilysin enzyme in Alzheimer’s disease therapy?
The neprilysin enzyme is highly significant in Alzheimer’s disease therapy as it plays a vital role in breaking down beta-amyloid plaques, which are detrimental to brain health. By enhancing neprilysin production through engineered microglia, researchers aim to improve neuronal preservation and reduce inflammation, which could lead to more effective treatment strategies.
Can microglia cells be effectively used in therapies for Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, microglia cells can be effectively used in therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Recent research indicates that engineered microglia cells, when modified using CRISPR gene editing, can reduce beta-amyloid buildup and support neuron health, offering a targeted approach to treatment that may address the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s.
What implications does this research have for future Alzheimer’s disease treatments?
This research has profound implications for future Alzheimer’s disease treatments as it lays the groundwork for innovative therapies that utilize stem cells and gene editing. The positive outcomes observed in mice suggest that these methods could potentially be adapted for human trials, providing new avenues for personalized treatment options and addressing the urgent need for effective Alzheimer’s therapies.
How might the findings on stem cell therapy impact other central nervous system disorders?
The findings on stem cell therapy may significantly impact other central nervous system disorders by establishing a successful framework that could be adapted for conditions like brain cancer and multiple sclerosis. The techniques developed for manipulating microglia and enhancing neprilysin production could offer new therapeutic strategies beyond Alzheimer’s disease.
What is the current state of Alzheimer’s disease therapy research?
The current state of Alzheimer’s disease therapy research is rapidly evolving, with a strong focus on innovative approaches such as stem cell therapy and CRISPR gene editing. With the growing number of Alzheimer’s patients, recent advancements underscore the urgent need to explore diverse treatment options, as highlighted by ongoing studies and funding efforts aimed at broadening the scope of effective therapies.
How does the research funded by the National Institutes of Health support Alzheimer’s treatment?
The research funded by the National Institutes of Health supports Alzheimer’s treatment by facilitating groundbreaking studies aimed at exploring novel therapies. This financial backing emphasizes the importance of advancing knowledge in stem cell therapy and gene editing as potential solutions for Alzheimer’s, contributing to the overall development of effective treatment strategies.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Promising Therapy | Utilizes stem cells and microglia to combat Alzheimer’s symptoms. |
| CRISPR Gene Editing | Enhances microglia to produce neprilysin, which breaks down beta-amyloid plaques. |
| Test Results | Engineered cells preserved neurons, reduced inflammation, and decreased beta-amyloid buildup in mice. |
| Potential Applications | Therapy could also benefit other CNS disorders such as brain cancer and multiple sclerosis. |
| Research Significance | Highlights the urgent need for effective Alzheimer’s treatments as cases rise to seven million in the U.S. |
| Future Trials | The success in mice paves the way for future human trials using patient-customized stem cells. |
| Funding and Publication | Research funded by NIH and published in *Cell Stem Cell* indicating its significance. |
| Call for Further Research | Emphasis on diverse funding for broader treatment options as the population ages. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s disease therapy is entering a new era with innovative approaches that leverage stem cells and gene editing technologies. A recent study indicates that harnessing microglia through CRISPR gene editing can significantly combat the debilitating symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. This groundbreaking research not only demonstrates the potential for effective treatment but also calls for increased funding and diverse research strategies to address the rising number of Alzheimer’s patients. As we advance, the therapeutic possibilities for this condition and other related CNS disorders seem promising, ushering in hope for those affected by these challenging ailments.




