Benefits of Eating Meat: New Study Reveals Health Insights
The benefits of eating meat have been a subject of research and discussion, especially highlighted by a recent study from Canada’s McMaster University. This study revealed that the consumption of animal protein is not associated with an increased risk of mortality, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. In fact, the findings suggest that animal proteins could even offer protective benefits against cancer-related mortality, challenging previous misconceptions about meat consumption. With nearly 16,000 adults analyzed, it was shown that higher intake of animal protein correlates with a modest reduction in cancer risks, while plant proteins do not yield the same protective effects. These insights contribute to the growing understanding of dietary protein sources and their crucial roles in maintaining health and longevity.
Exploring the advantages of meat consumption brings to light various aspects of dietary animal protein and its health implications. Recent findings underscore the significance of integrating red and white meat into our meals due to their high-quality protein content and essential nutrients. Studies examining dietary patterns have increasingly shown that the inclusion of animal proteins in the diet does not lead to higher mortality rates, particularly concerning chronic diseases like cancer. The balance between animal and plant-based proteins is crucial, as research indicates varying impacts on overall health outcomes from these dietary choices. By reevaluating the role of meat as a vital dietary component, individuals can make better-informed decisions leading to healthier lifestyles.
The Health Benefits of Eating Meat
Eating meat provides a variety of health benefits that are supported by numerous studies. According to recent findings from McMaster University, increased meat consumption has been linked to lower cancer-related mortality rates. This is vital because animal proteins offer essential amino acids that our bodies cannot produce on their own. The inclusion of these proteins in a regular diet can enhance muscle health and improve metabolic functions, making it an important dietary choice for many individuals.
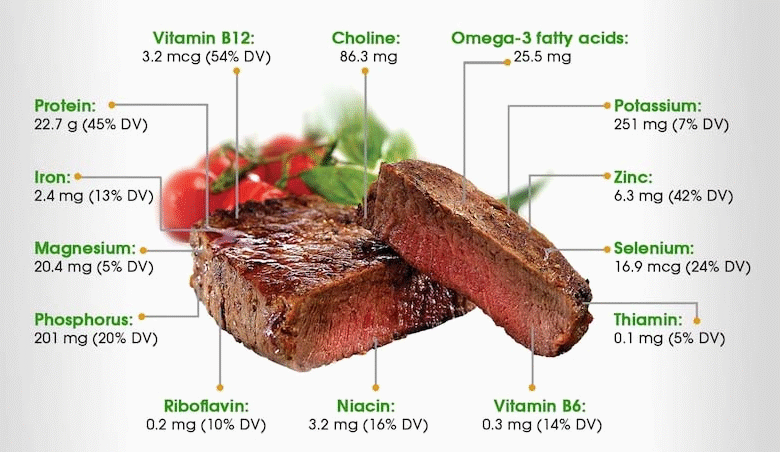
Moreover, meat is packed with vital nutrients including iron, zinc, and vitamin B12. Iron from animal sources is more easily absorbed by the body compared to plant-based iron, which is crucial for preventing anemia. As such, red meat can be a significant dietary source for those needing to boost their iron levels. When included in a balanced diet, these nutrients can contribute to overall health and longevity.
Understanding the Role of Animal Proteins in Diet
Animal proteins play a pivotal role in the diet, serving as a primary source of protein for many individuals worldwide. The recent study underscores the health benefits derived from these proteins, illustrating that they are not linked to a higher mortality risk as often perceived. In fact, participants who consumed higher amounts of meat showed no negative impact on their overall health status, supporting claims that a meat-inclusive diet can still be part of a healthy lifestyle.
Incorporating animal proteins into one’s diet goes beyond just cancer prevention; it also positively influences several other health facets. For instance, studies indicate that adequate protein intake is crucial for muscle synthesis and maintenance, particularly in aging populations. This highlights the necessity of animal proteins in dietary plans, especially in balancing with other protein sources such as legumes and nuts.
Protein Sources and Nutritional Balance
When planning a diet, it is essential to consider all available protein sources, both animal and plant-based. While the recent research emphasizes the protective effects of animal protein against cancer-related mortality, it does not diminish the importance of plant proteins. Combining diverse proteins can offer a more rounded nutrient profile, ensuring that individuals receive all essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals necessary for robust health.
For those seeking to adopt a healthier diet, balancing animal proteins with plant proteins can provide benefits from both groups. Research found that while animal proteins may offer greater protection against health risks, each protein source contributes uniquely to dietary needs. Moreover, understanding the implications of various protein sources can help individuals craft a more informed approach towards their nutrition, leading to better health outcomes.
Meat Consumption Study: Key Findings and Implications
The meat consumption study from McMaster University revealed significant insights into how animal proteins contribute to overall health. Wrapping around the findings, the research demonstrated that those consuming higher levels of animal protein reported a modest reduction in cancer mortality. These results could reshape health conversations revolving around diet and protein sources by challenging the long-standing stigma associated with meat consumption.
Moreover, the study collected robust data from nearly 16,000 adults, providing a comprehensive perspective on dietary habits. This depth of data adds credibility to the findings and reinforces the argument for including healthy animal proteins in daily diets. Such evidence is pivotal for health professionals and dietary guidelines, promoting a balanced and evidence-based view on the role of meat in nutrition.
Animal Protein vs. Plant Protein: A Comparative Analysis
A critical aspect of the recent research involves comparing animal protein consumption to that of plant proteins. Although both protein types play beneficial roles in health, the study indicated that while plant protein contributes minimally to reducing cancer mortality, animal proteins demonstrated a protective effect. This distinction is vital for those discerning the most effective dietary sources for health and longevity.
Understanding these differences can help guide dietary choices according to individual health goals. For instance, individuals focusing on muscle preservation may benefit more from animal sources due to their complete amino acid profiles. Conversely, those aiming for lower cholesterol or trying to incorporate more plant-based foods may prioritize legumes and grains while still considering the health benefits of animal proteins in moderation.
The Importance of Protein in Everyday Diet
Protein plays an indispensable role in our daily diets, acting as a building block for bones, muscles, and tissues. Given the energy demands of modern living, understanding the importance of diverse protein sources, including animal proteins, is crucial for maintaining health. The latest findings from McMaster University support the inclusion of meat in a balanced diet, reinforcing its role as a nutrient-dense food.
Furthermore, with the increasing trend of plant-based diets, it’s important to ensure that all nutritional needs are met. Animal proteins can provide essential nutrients that may be harder to obtain solely from plant sources. Incorporating a mix of both food groups can offer comprehensive nutritional support and may prevent potential deficiencies, especially in essential vitamins like B12 that are predominantly found in animal products.
Making Informed Dietary Choices
With varying opinions on dietary protein sources, making informed choices is more important than ever. The findings from the Canadian study empower consumers by suggesting that higher meat consumption is not detrimental to health as commonly thought. By considering evidence-based research, individuals can make better dietary choices that align with their health needs.
Moreover, the insights gathered from this research can also enlighten healthcare professionals as they provide nutritional advice to clients. By embracing a balanced perspective on protein consumption — valuing both animal and plant sources — professionals can guide individuals to achieve their health goals effectively and sustainably.
The Nutritional Value of Red Meat in Diets
Red meat has long been a staple in many diets around the world, and its nutritional value should not be overlooked. The recent study highlighted how moderate consumption of red meat is associated with various health benefits, supporting the notion that red meat can indeed be part of a healthy lifestyle. It is an excellent source of heme iron, which is more bioavailable than non-heme iron found in plant sources, making it essential for maintaining iron levels and preventing anemia.
Additionally, red meat is rich in vital nutrients such as B vitamins and protein, contributing to energy levels and muscle repair. These nutrients are critical for active individuals and those engaged in regular physical activity. Understanding the benefits of red meat can help counteract myths surrounding its consumption and guide individuals in making balanced dietary choices that reflect both personal preferences and health recommendations.
The Impact of Dietary Proteins on Longevity
Dietary protein has been extensively studied in relation to its impact on longevity. The findings from McMaster University indicate that higher consumption of animal proteins may offer certain health advantages, particularly in reducing cancer-related mortality. This is an important finding for individuals who prioritize longevity and healthy aging in their dietary choices.
Furthermore, a well-rounded diet that includes both animal and plant proteins can provide a broader spectrum of nutrients essential for a longer, healthier life. The complex relationship between protein consumption and health outcomes underscores the need for ongoing research. Emphasizing the importance of diverse protein sources will help individuals make better dietary decisions for enhanced quality of life.
Moving Forward: The Future of Protein Research
As research on dietary proteins continues to evolve, the future promises to deliver more nuanced findings regarding the roles of different protein sources in health. The McMaster University study contributes valuable knowledge to this area, highlighting the potential benefits of including animal proteins in a healthy diet. This information is critical not only for individuals but also for shaping dietary guidelines and nutritional policies.
Looking ahead, it is clear that further studies exploring the long-term health outcomes of various protein sources will be essential. With a growing focus on plant-based diets, researchers must balance their findings to include the advantages of both animal and plant proteins. This balanced perspective will ultimately support the health of diverse populations, acknowledging individual dietary needs while promoting overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the health benefits of eating meat and animal protein?
Eating meat and animal protein has several health benefits, including providing essential nutrients that support muscle health and overall well-being. According to recent studies, such as the one from McMaster University, higher consumption of animal protein is not linked to increased mortality rates and may even reduce the risk of cancer-related deaths.
Is there a link between meat consumption and cancer mortality?
Research indicates that there may be a link between meat consumption and reduced cancer mortality. The study from McMaster University found that while plant protein had a minimal effect on cancer mortality, animal protein was associated with a modest reduction in cancer-related death rates, suggesting potential protective benefits from including meat in a healthy diet.
How does animal protein compare to plant protein in dietary benefits?
Animal protein differs from plant protein in its impact on health. Studies show that animal proteins may provide superior benefits concerning protein and cancer mortality. While both dietary protein sources contribute positively to health and longevity, animal proteins might offer additional protective effects against certain conditions, including cancer.
Can eating meat be part of a healthy diet?
Yes, incorporating meat into a healthy diet can enhance nutrient intake and offer various health benefits. The findings from studies, including those from McMaster University, suggest that animal proteins contribute positively to health outcomes, and their inclusion can help individuals make informed dietary choices.
What does the recent meat consumption study reveal about dietary protein sources?
The recent study conducted by McMaster University reveals that dietary protein sources, especially animal proteins, contribute to improved health markers. It indicates that higher meat consumption does not correlate with increased mortality risk, and may reduce the chances of dying from cancer, highlighting the role of animal protein in a balanced diet.
| Key Points | ||
|---|---|---|
| Study Source: McMaster University, Canada | Study Population: Nearly 16,000 adults aged 19 and older | Research Findings: Higher consumption of animal protein linked to reduced cancer mortality |
| Key Focusing Areas: Effects of animal vs. plant protein on mortality risk | No increased risk of death from animal protein consumption | Plant protein shows minimal impact on cancer mortality |
| Conclusion: Animal proteins may offer protective benefits for health | Study published in Applied Physiology, Nutrition and Metabolism | Supported by National Cattlemen’s Beef Association, ensuring independent research |
Summary
The benefits of eating meat are highlighted by recent research from McMaster University, which suggests that increased consumption of animal protein may enhance health outcomes and reduce cancer-related mortality. The study, which examined a diverse group of adults, found no significant risk of death associated with animal proteins, instead suggesting these foods can play a protective role in health. This shift in understanding can help individuals make more informed dietary choices that promote longevity and well-being.




