Sexual Violence in Conflict: UN Reports Alarming Rise
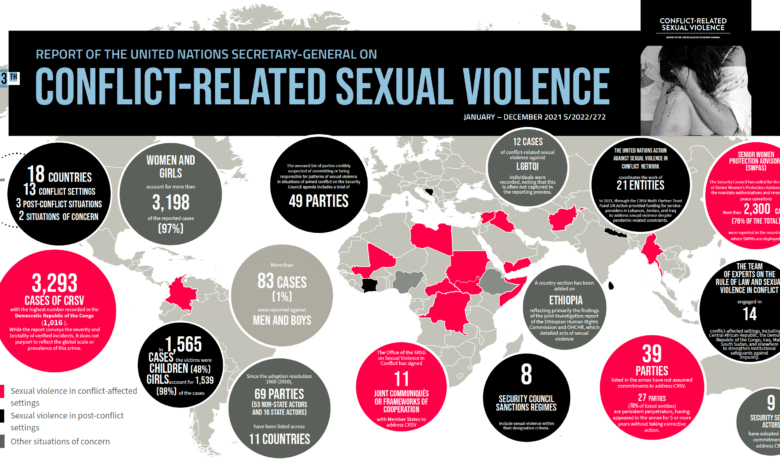
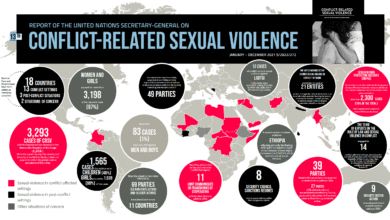
Sexual violence in conflict remains one of the most harrowing aspects of modern warfare, with the UN reporting a staggering rise of 25% in such incidents last year. This increase includes over 4,600 individual cases, many of which involved systematic abuses inflicted by both State and non-State actors across 21 countries, including the Central African Republic and South Sudan. The 2024 UN report on sexual violence highlights that women and girls accounted for 92 percent of the victims, but men and marginalized groups were also tragically affected. Such violence is not merely a byproduct of war; it is weaponized to devastate communities, instill fear, and exert control. As survivors of sexual violence grapple with stigma and societal rejection, the urgent need for accountability and support becomes ever clearer.
In the context of armed conflicts, the term “gender-based violence in conflict” encompasses a wide array of heinous acts, including sexual violence used as a weapon of war. The alarming statistics reported in the latest UN documentation point towards an escalation of conflict-related sexual violence, revealing a grim reality that transcends mere numbers; it embodies the struggles of countless survivors. These acts not only violate fundamental human rights but also serve as strategic tools for oppression and terror. As we delve into the intricacies of war crimes and sexual violence, it becomes evident that the urgent call for international action and support for affected individuals is not just necessary but non-negotiable. The global community must recognize these crimes for what they are: serious violations that demand stringent legal and humanitarian responses.
The Alarming Rise of Sexual Violence in Conflict Zones
In 2024, the United Nations reported a staggering increase of 25% in incidents of sexual violence in conflict zones compared to the previous year. This dramatic surge resulted in over 4,600 identified survivors who suffered abuses that were tragically utilized as weapons of war and tools of political oppression. The report highlighted that both State and non-State actors were implicated in these horrific acts across 21 nations, with the Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and South Sudan being amongst the most affected countries. This rise in sexual violence underscores the urgent need for global attention towards conflict-related sexual violence and for the international community to take decisive action to support survivors and hold perpetrators accountable.
The statistics reveal that women and girls represent a staggering 92% of all victims, but it is essential to recognize that other marginalized groups, including men, boys, and individuals from diverse gender identities, are also tragically affected. Such violence not only inflicts immediate physical and psychological harm but leaves lasting scars on communities. The UN’s findings indicate that these crimes reflect wider patterns of gender-based violence in conflict, necessitating a comprehensive approach to address the systemic issues that allow such atrocities to continue unchecked. Without adequate prevention measures and support systems, the cycle of violence against survivors is perpetuated, thereby undermining peace-building efforts.
Violent Dynamics in Detention Centers
The latest UN report highlights a deeply concerning trend regarding the rise of sexual violence in detention, where violations have increasingly become tools for intimidation, torture, and forced information extraction. Predominantly affecting men and boys, this violence also encompasses women and girls, illustrating the pervasive nature of sexual abuse in conflict settings. Non-State armed groups use these tactics to exert control over territories and propagate extremist ideologies. Unfortunately, factors such as widespread weapon availability, mass displacements, and food insecurity exacerbate vulnerabilities, making survivors even more susceptible to violence.
Moreover, the lack of access to humanitarian aid compounds the suffering of those imprisoned and abused. Many survivors face not only the trauma of violence but also the systemic barriers preventing them from seeking help. The UN warns that the obstruction of aid is a deliberate strategy employed by conflicting parties to maintain power dynamics and suppress potential uprisings. It is imperative for the international community to confront these violations, ensuring that humanitarian access is granted unreservedly, allowing for crucial support and rehabilitation services for survivors.
Challenges in Legal Compliance Concerning Sexual Violence
According to the report, there are currently 63 State and non-State actors suspected of committing sexual violence within conflict zones, yet compliance with international humanitarian law remains alarmingly low. Although some groups have made commitments to confront these crimes, the backlog of impunity and lack of accountability for perpetrators continues to hinder justice for victims. The UN emphasizes the need for Security Council sanctions against those who perpetuate these egregious acts, noting that sexual and gender-based violence has now become sanctionable under counter-terrorism frameworks. Such measures are vital in addressing war crimes and fostering a culture of accountability.
The persistence of legal loopholes and the reluctance of some nations to take definitive action against their forces only emboldens violators. Reports indicate that while there is a growing acknowledgment of these crimes, the political will to implement effective measures against key perpetrators remains lacking. For the international community to ensure a significant reduction in conflict-related sexual violence, there must be an unwavering commitment to uphold and enforce international norms, accentuating the roles of justice and reparative processes in supporting survivors’ recovery and rights.
Addressing New Patterns in Conflict-Related Sexual Violence
The UN’s continued efforts to monitor sexual violence in conflict have recently revealed new patterns, notably the emergence of groups like the Résistance pour un Etat de Droit and various Libyan State actors using sexual violence as part of their operational strategies. These findings underscore the need for adaptive responses from the international community to not only address existing groups but to stay ahead of emerging risks. Enhanced information sharing and targeted interventions are necessary to combat the rise of sexual violence as a weapon utilized in conflicts, demonstrating that the fight against such atrocities must be proactive.
Furthermore, the alarming reports of sexual violence against hostages taken during conflicts highlight the multi-faceted nature of this issue. Cross-border crises, especially those involving complex geopolitical dynamics, necessitate robust collaboration among nations to curtail the operations of these groups. By holding violators accountable and introducing stricter international laws governing conflict conduct, the global community can set a precedent to deter future instances of sexual violence in warfare, thereby ensuring that the rights of all individuals, regardless of their identity, are protected during times of conflict.
Raising Awareness: The Role of the International Community
The UN has continuously urged the international community to recognize the profound consequences of sexual violence in conflict and confront it with a unified approach. Heightened awareness campaigns and educational initiatives are crucial in mitigating stigma associated with survivors of sexual violence. These measures not only facilitate a more supportive atmosphere for victims but also empower communities to challenge the societal norms that support such violence. Encouraging community involvement and survivor stories can galvanize advocates who work tirelessly to dismantle oppressive systems and support healing efforts.
Moreover, the international community must maintain pressure on state actors to uphold their responsibilities regarding the prevention of sexual violence. Public accountability measures, including global campaigns and media scrutiny, can prove effective in pushing governments to take the necessary actions against perpetrators. Advocacy groups should work in tandem with UN bodies to establish reporting mechanisms for survivors, ensuring their voices are heard and prioritized in policy discussions. This collaborative approach positions sexual violence against conflict as a global priority, necessitating parallel actions at local, national, and international levels for meaningful change.
The Call for Accountability and Support for Survivors
The 2024 report serves as a poignant reminder that survivors of sexual violence in conflict demand more than just acknowledgment; they require actionable steps towards their recovery and justice. UN officials emphasize the importance of engaging conflict parties in adopting clear policies that prohibit sexual violence and ensuring accountability for perpetrators. The recognition that sexual violence can be sanctioned under international law represents a critical step toward dismantling the culture of impunity that commonly pervades conflict zones. Without stringent legal frameworks and enforcement, the cycle of violence is likely to persist, endangering future generations.
In tandem with accountability efforts, there is a pressing need for robust support systems for survivors. Access to healthcare, psychological support, and legal assistance is paramount for survivors as they navigate the aftermath of their trauma. Community-based programs that promote reintegration and provide resources can help restore normalcy in the lives of survivors. The UN’s call for effective and decisive action speaks to the responsibility of the global community to not only support victims but to strive toward eradicating these crimes altogether. It is time for the international community to translate urged commitments into tangible acts of support and reform.
The Impact of War Crimes on Communities
War crimes, particularly those involving sexual violence, leave profound scars on the social fabric of affected communities. Beyond the individual trauma experienced by survivors, these atrocities can lead to long-term socio-economic repercussions that hinder development and peace-building efforts. Communities grappling with the aftermath of conflict often find themselves facing disrupted social networks, increased poverty rates, and eroded trust among members. Gender-based violence and exploitation become pervasive, fueling cycles of violence that can persist for generations. Understanding these broader impacts emphasizes the need for comprehensive approaches to address the root causes of violence and support community healing.
Moreover, the repercussions of sexual violence extend into the political realm, as victims often face marginalization and discrimination, making it challenging to advocate for their rights. Efforts to restore justice and promote accountability must therefore encompass not only legal remedies but also community-level interventions that focus on rebuilding relationships and trust. Investing in community-led healing programs can foster resilience and empower survivors to reclaim their lives. By focusing on comprehensive justice that includes socio-economic recovery, the international community can contribute towards creating a more stable and just post-conflict environment.
The Role of Women and Girls in Peacebuilding
Women and girls play a critical role in peacebuilding efforts, particularly following periods of intense conflict marked by sexual violence. Their experiences and perspectives are invaluable in crafting inclusive policies that address the needs of affected populations. Recognizing the integral role of women in recovery and reconstruction processes is essential not only for their empowerment but also for fostering sustainable peace. Programs that promote women’s participation in decision-making positions can help challenge existing power dynamics and bring about transformative change in conflict-affected societies.
Moreover, involving women and girls in peace processes enhances the likelihood of achieving lasting solutions to conflicts. Research shows that when female participation is prioritized, the resulting agreements are more comprehensive and have greater longevity. The UN continues to advocate for the integration of gender perspectives in peace negotiations and post-conflict lawmaking to address the root causes of sexual violence in conflict. By uplifting women’s roles in these processes, the international community acknowledges their resilience while simultaneously breaking the cycles of violence and promoting a more just society.
Future Directions in Addressing Conflict-Related Sexual Violence
As the global spotlight on sexual violence in conflict continues to grow, there is a pressing need for innovative solutions and strategies. Future efforts must focus on establishing more robust definitions and frameworks for recognizing various forms of gender-based violence, particularly as new conflict dynamics emerge. This includes transitioning from reactive measures to proactive approaches that encompass prevention strategies, including education and community outreach initiatives aimed at reducing vulnerabilities in conflict zones. Collaborations between humanitarian organizations, governments, and local communities are crucial in enhancing the overall effectiveness of these preventive efforts.
Furthermore, continuous monitoring and reporting mechanisms must be strengthened to hold parties accountable for violations of international law regarding sexual violence. Establishing transparent channels for survivors to speak out about their experiences is vital, as it can inform future interventions and best practices. The international community must leverage technology and data collection methods to gain insights into the trends and challenges regarding conflict-related sexual violence, allowing stakeholders to adapt their strategies accordingly. Looking ahead, the goal must be to create a world where sexual violence is decisively addressed and eradicated, securing a future of dignity and safety for all individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is conflict-related sexual violence and why is it a concern?
Conflict-related sexual violence refers to sexual violence that occurs in the context of armed conflict, often used as a weapon of war to intimidate, control, or punish populations. It is a significant concern due to its devastating impact on survivors, especially women and girls, who represent 92 percent of the victims as reported by the UN. This type of violence contributes to deep social stigma and marginalization, making recovery and reintegration into society particularly difficult for survivors.
How prevalent is sexual violence in conflict zones according to the UN report?
According to the UN report on sexual violence in conflict, there was a steep rise in incidents in 2024, with over 4,600 survivors reported. The increase represents a 25% rise compared to the previous year, highlighting the alarming escalation of gender-based violence in conflict-affected areas, particularly in regions like the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
What measures are being taken to address war crimes and sexual violence in conflict?
To combat war crimes and sexual violence in conflict, the UN report emphasizes accountability and compliance with international humanitarian law. It calls for Security Council sanctions against identified perpetrators and urges all conflict parties to adopt clear prohibitions against sexual violence. Effective monitoring and unimpeded access for humanitarian aid services are also recommended to assist survivors.
What specific groups and countries are highlighted for their involvement in sexual violence in conflict?
The report identifies various state and non-state actors responsible for patterns of sexual violence. Newly listed groups include the Résistance pour un Etat de Droit (RED) in the DRC for mass rape incidents, and individuals associated with the Hamas group for sexual violence against hostages. Additionally, significant concerns have been raised regarding patterns of sexual violence by Israeli and Russian armed forces.
How does sexual violence in conflict affect survivors and their communities?
Survivors of sexual violence in conflict face severe repercussions, including social stigma, physical injuries, and mental health issues. Communities often marginalize these individuals, further complicating their recovery and reintegration. The UN emphasizes that the violence extends beyond the act itself, affecting families and future generations, and calls for a more robust response to address these impacts and support survivors.
What role do humanitarian organizations play in addressing sexual violence in conflict?
Humanitarian organizations play a crucial role in providing support to survivors of sexual violence in conflict. They facilitate access to medical care, psychological support, and legal assistance. However, the UN report notes that access can be impeded by conflict parties blocking humanitarian efforts, underlining the need for protective measures to ensure support reaches those affected.
What is the significance of the UN’s resolutions on conflict-related sexual violence?
The UN’s resolutions on conflict-related sexual violence serve to reaffirm the commitment to prevent and combat such violence, holding violators accountable. They outline the standards that parties to conflict must adhere to and emphasize the need for comprehensive measures to protect survivors and enable their rights to justice and assistance.
How can individuals and communities help support survivors of sexual violence in conflict?
Individuals and communities can support survivors of sexual violence by advocating for their rights and providing a safe and supportive environment. This includes raising awareness about the issues surrounding conflict-related sexual violence, offering emotional and practical support, and ensuring access to resources such as healthcare and legal advice.
| Key Points |
|---|
| UN reports a 25% rise in sexual violence in conflict zones in 2024, with over 4,600 survivors documented. |
| Victims are predominantly women and girls (92%), but men, boys, LGBTQ+ individuals, and racial/ethnic minorities are also affected. |
| Extreme physical violence accompanies many attacks, with societal stigma further marginalizing survivors. |
| Increase in sexual violence in detention noted, used by non-State groups as a tactic of control. |
| Report documents low compliance with international humanitarian law; 63 actors suspected of sexual violence. |
| Israel and Russia placed on ‘notice’ for potential future accountability regarding sexual violence. |
| Urgent calls for accountability and effective action to prevent and eradicate sexual violence in conflict. |
Summary
Sexual violence in conflict has reached alarming levels, with the UN highlighting a significant rise in 2024. The acts of sexual violence serve as a brutal tactic in warfare, affecting tens of thousands of victims, predominantly women and children, while often remaining unpunished. As international awareness grows, there is an urgent need for accountability and effective strategies to combat these crimes, ensuring dignity and support for survivors.