GLP-1 Medications: Relief for Arthritis Symptoms
GLP-1 medications, also known as glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists, are rapidly gaining attention not only for their role in controlling diabetes but also for their potential benefits in weight management and arthritis treatment. These innovative drugs, such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, mimic a natural hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, providing a multifaceted approach to health. Recent studies suggest that GLP-1 medications could play a critical role in relieving rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, highlighting their effectiveness beyond traditional diabetes medications. This exciting discovery underscores their potential as weight loss drugs while also potentially alleviating the challenges faced by those with autoimmune diseases, which often manifest through painful inflammation. With a growing body of evidence supporting their broader therapeutic effects, GLP-1s may well reshape the landscape of treatment for both diabetes and related conditions.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists are a pioneering category of treatment that has emerged as a game changer not only for managing high blood sugar but also for promoting weight loss and offering arthritis symptoms relief. Commonly referred to as GLP-1 medications, these therapeutic agents imitate a vital hormone, enhancing glucose regulation and satiation. Their evolving role in rheumatoid arthritis treatment showcases an exciting intersection between metabolic health and autoimmune disease management. By helping patients shed excess weight, these medications may indirectly address the inflammation and discomfort frequently experienced by those with joint issues. As research continues to unveil their diverse benefits, the impact of GLP-1 receptor agents is poised to extend far beyond their initial applications.
Understanding GLP-1 Medications for Weight Loss and Beyond
GLP-1 medications, notably those like semaglutide and tirzepatide, are gaining recognition not only for their pivotal role in diabetes management but also for their potential benefits in weight loss and alleviating arthritis symptoms. As a class of drugs classified as GLP-1 receptor agonists, they work by mimicking the effects of the glucagon-like peptide-1, which plays a significant role in glucose metabolism. Beyond managing blood sugar levels, these medications can promote satiety and weight reduction, which may significantly impact conditions associated with obesity, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Studies have increasingly shown that individuals struggling with obesity and rheumatoid arthritis may experience an exacerbation of symptoms linked to their weight. Given the observed correlation between elevated Body Mass Index (BMI) and inflammatory conditions, GLP-1 medications are being re-evaluated for their ability to not only aid in weight management but also in reducing the inflammatory burden caused by excess fat. With patients reporting considerable improvement in their symptoms, healthcare professionals are beginning to explore GLP-1s as a dual solution for both diabetes and chronic inflammatory diseases.
The Role of Weight Loss Drugs in Relieving Arthritis Symptoms
Weight loss drugs have become a focal point in managing various conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, due to their cross-functional benefits. As obesity is known to contribute to systemic inflammation and worsen arthritis symptoms, effectively managing weight through medications can provide surprising relief for many patients. This relationship between weight and inflammatory markers suggests that reducing body fat is crucial for mitigating symptoms of autoimmune diseases. In this capacity, GLP-1 medications stand out not just for their weight loss potential but also for their ability to disrupt the cycle of inflammation tied to obesity.
The evidence supporting the efficacy of weight loss drugs in improving arthritis symptoms is compelling. Research indicates that for many patients, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can lead to fewer instances of pain and reduced need for anti-inflammatory medications. Moreover, as patients lose weight through the help of GLP-1 medications, they may find themselves experiencing a transition from dependency on rheumatoid arthritis treatments to a more manageable state, potentially reducing or eliminating the need for traditional medications.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Connection to Obesity
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is increasingly being recognized as a condition where weight management plays a crucial role in symptom control. Obesity is not only a risk factor for the development of RA but also exacerbates the existing symptoms through increased inflammatory responses in the body. This inflammatory role of excess fat highlights the importance of weight loss strategies as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for individuals diagnosed with RA. By addressing obesity, patients may find their arthritis symptoms less debilitating, leading to improved quality of life.
Furthermore, various studies have indicated that losing even a small percentage of body weight can help lessen the severity of arthritis symptoms. This is particularly important as the chronic nature of RA often necessitates long-term medication use, which can come with side effects and complications. By utilizing GLP-1 medications, patients may not only achieve weight loss but also directly impact their rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, showcasing the interconnected nature of these health issues.
Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Medications
GLP-1 medications have emerged as a promising avenue for exploration due to their potential anti-inflammatory effects. While these medications are primarily known for their role in managing diabetes and facilitating weight loss, research suggests they may also reduce inflammation beyond the typical metabolic pathways. This has garnered attention from the medical community, particularly concerning conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases characterized by excessive inflammation. The underlying mechanism relates to how fat cells produce cytokines that can stimulate inflammatory responses.
As GLP-1 medications may help in regulating these cytokines, they could effectively reduce the inflammation that contributes to arthritis symptoms. This intriguing possibility serves as a cornerstone for further investigation into their diverse applications in medicine. Observing the experiences of patients who report significant symptom relief after transitioning to GLP-1s lends credence to the potential of these medications as a multi-faceted treatment option for obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory diseases.
How Diabetes Medications Are Changing Arthritis Treatment
The treatment landscape for rheumatoid arthritis is evolving with the integration of diabetes medications, particularly GLP-1 drugs. The connection between metabolic health and chronic inflammatory diseases is becoming clearer, resulting in innovative approaches to patient care. Rather than just focusing on traditional anti-inflammatory agents, healthcare providers are now considering how glycemic control and weight management influence rheumatoid arthritis outcomes. This shift underscores a more holistic understanding of treating autoimmune diseases and their interplay with metabolic disorders.
Emphasizing the role of diabetes medications in rheumatology is revolutionary. Patients who struggle with both conditions now have newfound hope as they can address their diabetes while simultaneously managing their arthritis through weight loss achieved with GLP-1s. This novel approach not only diversifies treatment options but also minimizes the reliance on potentially harmful long-term use of conventional arthritis therapies. As ongoing research continues to unveil the benefits of combining these treatments, it paves the way for more individualized patient care.
Navigating the Risks of GLP-1 Approvals for Non-Diabetic Conditions
As GLP-1 medications gain popularity for multiple health conditions, embracing these drugs for non-diabetic uses, particularly in treating rheumatoid arthritis, warrants careful scrutiny. The mechanism by which these drugs exert their effects on inflammation remains an area requiring extensive study. Medical professionals are advocating for prudence, as any medication, including GLP-1s, carries risks and benefits that must be weighed on a case-by-case basis. Monitoring is essential, especially for non-diabetic individuals, to prevent potential adverse reactions.
Moreover, the accessibility of GLP-1 medications across various platforms raises concerns. Patients seeking relief from arthritis symptoms might be enticed by online pharmacy options that lack proper medical oversight. Ensuring that individuals using these medications receive appropriate guidance from knowledgeable healthcare providers is critical for their safety and treatment efficacy. Ensuring patients are well-informed about their options will ultimately lead to better management of both diabetes and arthritis symptoms.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations of GLP-1 Applications
While GLP-1 medications are heralded for their advantages in weight management and arthritis symptom relief, it is crucial to be cognizant of their potential side effects. Common pharmaceutical practices caution against overlooking side effects, especially as these medications alter metabolic pathways and immune responses within the body. Patients considering GLP-1s must engage in thorough discussions with their physicians to ensure they understand both the benefits and the risks associated with these treatments.
Particularly for patients transitioning from rheumatoid arthritis medications to GLP-1s, monitoring for adverse responses is paramount. It is essential for medical practitioners to maintain an open line of communication, allowing patients to report any unexpected changes in their health, especially symptoms related to inflammation or other reactions. As the dialogue around GLP-1s expands, ongoing patient education and healthcare partnerships will optimally manage expectations and promote safe usage.
The Future of Rheumatoid Arthritis Management with GLP-1s
The advancements in managing rheumatoid arthritis using GLP-1 medications signal a significant shift towards more integrative approaches in healthcare. As continuing research reveals their potential in enhancing both metabolic and inflammatory parameters, the future seems promising for those affected by chronic conditions. The capacity of GLP-1 drugs to address weight issues concomitant with autoimmune diseases illustrates an essential step toward personalized medicine, where treatment regimens are tailored to the individual patient’s health profile.
As clinical studies continue to emerge, the landscape of arthritis management will likely incorporate a model where weight loss drugs such as GLP-1s become standardized options in rheumatoid arthritis treatment protocols. This evolution could mean less dependency on multiple medications and a move towards comprehensive care that bridges the gap between endocrinology and rheumatology. The future will be characterized by holistic, patient-centered strategies that recognize the multifaceted nature of chronic diseases.
Conclusion: The Multifaceted Benefits of GLP-1 Medications
The exploration of GLP-1 medications reveals their multifaceted capabilities beyond their primary use in diabetes management. Their role appears to extend into areas such as weight loss and the management of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, underscoring the importance of weight control in inflammatory conditions. As the medical community advocates for innovative treatment strategies that address interconnected health issues, GLP-1s represent a significant advancement in tackling both metabolic and autoimmune diseases.
As patients and healthcare professionals alike embrace this evolving landscape, the collaborative efforts will provide opportunities for enhancing the treatment and management of rheumatic conditions through weight loss strategies that improve overall health. The intersection of GLP-1 usage with arthritis therapy has the potential to redefine approaches to chronic diseases, leading to improved outcomes and better quality of life for patients navigating these often complex health challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are GLP-1 medications and how do they work for weight loss?
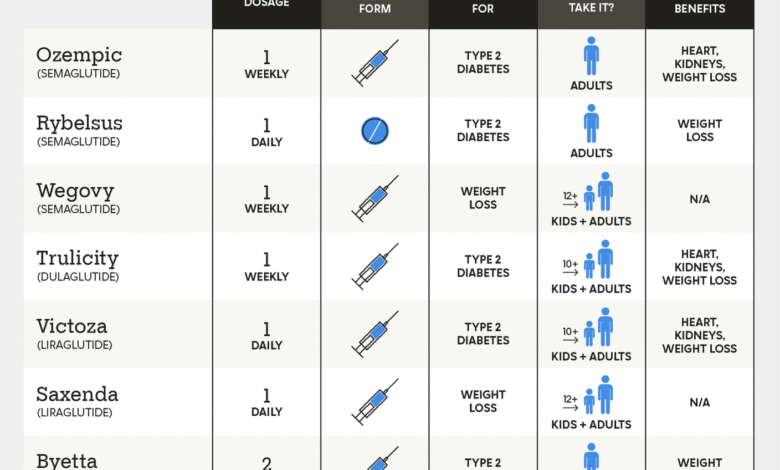
GLP-1 medications, also known as GLP-1 agonists, mimic the natural hormone glucagon-like peptide-1, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. These weight loss drugs, including semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound), can promote feelings of fullness, reduce appetite, and ultimately help in weight loss, making them effective for individuals with obesity or type 2 diabetes.
Can GLP-1 medications provide relief from arthritis symptoms?
Yes, GLP-1 medications have been shown to provide relief from arthritis symptoms, particularly in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Studies suggest that weight loss induced by GLP-1 drugs may alleviate some of the inflammation and pain associated with arthritis, helping to improve overall joint function.
Are GLP-1 medications effective for treating autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis?
GLP-1 medications may offer benefits for treating autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. While primarily designed for diabetes and weight management, these drugs have shown potential in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms in RA patients, possibly through weight loss and its effects on immune function.
How do GLP-1 medications affect patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking GLP-1 medications often experience significant relief from inflammation and pain. Many have reported the ability to discontinue traditional arthritis treatments after starting GLP-1 drugs, indicating a potential link between weight management and reduced symptoms.
Is there a link between obesity and rheumatoid arthritis in the context of GLP-1 medications?
Yes, a higher body mass index (BMI) is associated with an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. GLP-1 medications can aid in weight loss, which may help lower inflammation levels in the body and potentially reduce the risk or severity of arthritis symptoms.
What precautions should be taken when using GLP-1 medications for arthritis relief?
Patients considering GLP-1 medications for arthritis relief should consult with a knowledgeable physician for proper monitoring. These medications should be used under medical supervision, especially for individuals without obesity, to ensure safe and effective outcomes.
Can GLP-1 medications also impact conditions beyond diabetes and arthritis?
Yes, GLP-1 medications have been associated with reduced risks of other conditions, such as migraines, Alzheimer’s disease, and certain types of cancers, showcasing their potential therapeutic effects beyond just diabetes control and weight management.
What should individuals expect when starting GLP-1 medications for weight loss or arthritis?
Individuals starting GLP-1 medications should expect gradual weight loss and potential improvements in arthritis symptoms. However, results can vary, and it’s important to have regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Are there any side effects associated with GLP-1 medications when used for weight loss or arthritis?
Common side effects of GLP-1 medications include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and changes in appetite. While many find these manageable, it’s essential to communicate any adverse effects to a healthcare provider, especially if used for weight loss or arthritis relief.
Where can GLP-1 medications be obtained, and are online prescriptions safe?
GLP-1 medications should be obtained through a licensed healthcare provider. It is not advisable to get these medications from online platforms without a doctor’s supervision, as proper monitoring is crucial to ensure safe and effective treatment.
| Key Points |
|---|
| GLP-1 medications, like semaglutide and tirzepatide, regulate blood sugar and aid weight loss. |
| They may also relieve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). |
| RA is an autoimmune disease causing joint inflammation and pain. |
| Studies correlate obesity with a higher risk of developing RA. |
| Patients have reported significant relief from arthritis symptoms while using GLP-1s. |
| Cytokines produced by fat cells can increase inflammation; GLP-1 may help reduce levels. |
| While weight loss might contribute to symptom relief, this is still under study. |
| GLP-1s can lead to other health benefits, like reduced alcohol intake and lower reliance on certain medications. |
| Continuous monitoring by a physician is recommended when using GLP-1 medications. |
Summary
GLP-1 medications are showing promise not only in managing diabetes and promoting weight loss but also in relieving symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. These medications, such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, mimic natural biological processes that may lead to significant health improvements, including decreased inflammation and pain in joints. As research continues to uncover their full potential, GLP-1 medications stand out as a multifaceted approach to treating various health issues.




