US Measles Cases Reach Highest Levels in 30 Years
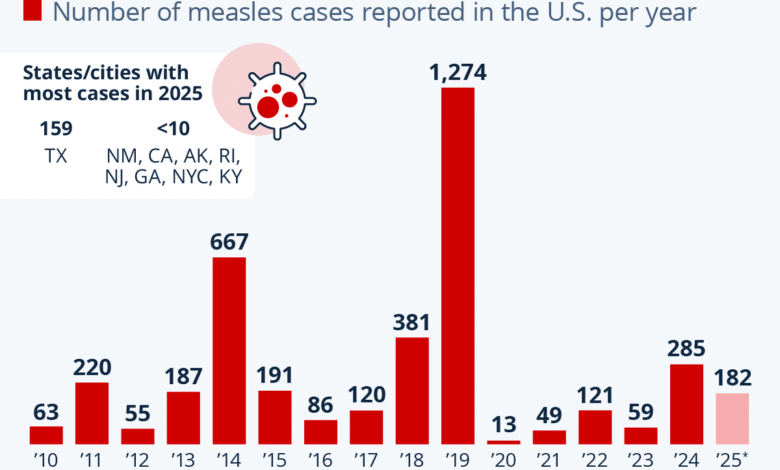
US measles cases have surged to their highest levels in over three decades, alarming public health officials and raising concerns about vaccination rates and immunity across the nation. Recent CDC measles data revealed that 1,288 confirmed infections have been reported across 38 states, with Texas experiencing the most significant outbreak, tallying over 700 cases alone. This troubling trend follows last year’s low of just 285 cases, highlighting a stark increase in measles outbreaks, particularly in 2025 where 27 outbreaks have already been documented. The effectiveness of the MMR vaccine remains crucial, especially as 92% of those infected this year are either unvaccinated or their vaccination status remains unknown. Awareness of measles symptoms and proactive measures, including improved vaccination rates, are imperative to stem this alarming rise in US measles cases.
The prevalence of measles in the United States has recently resurfaced as a critical public health issue, prompting discussions around vaccination practices and disease prevention strategies. Reports indicate a dramatic increase in confirmed measles infections within the country, capturing attention from health authorities and parents alike. With a significant portion of the population remaining unvaccinated, the risk of widespread transmission looms, especially amid recent outbreaks this year. Health experts emphasize the importance of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine’s effectiveness in preventing these infections. Families are urged to stay informed about measles symptoms, vaccination rates, and the potential implications of the ongoing measles outbreak phenomenon.
The Alarming Rise of US Measles Cases in 2025
In 2025, the United States is witnessing an unprecedented surge in measles cases, tallying up to 1,288 confirmed instances, marking the highest rate in over three decades according to the CDC. Various states have contributed to this outbreak, with Texas leading significantly with over 700 reported cases alone. This dramatic increase from last year, which saw only 285 cases documented, raises concerns about the state of public health and vaccination effectiveness across the nation.
Comparatively, the 2019 data reveals similar alarm with 1,274 recorded cases, but it is essential to note that the current statistics not only surpass the previous year but also echo numbers from as far back as 1992—with 2,126 cases reported then. This resurgence emphasizes the urgent need for awareness and improved measles vaccination rates, as the CDC delineates 27 measles outbreaks in 2025, a significant jump from the 16 outbreaks in 2024.
Analyzing CDC Measles Data: A Wake-Up Call
The CDC’s comprehensive data surrounding measles reveals startling trends. With 88% of confirmed cases being outbreak-associated, it is evident that the contagious nature of measles is a pressing issue. Such statistics underline that 1,130 out of 1,288 cases can be traced back to specific outbreaks, drawing attention to the role of community immunity. The increasing outbreaks signal that collective action through vaccination is more necessary than ever.
Moreover, the CDC reported a concerning trend in vaccination coverage among U.S. kindergartners, noting a decline from 95.2% during the 2019-2020 school year to just 92.7% in the 2023-2024 school year. This drop leaves approximately 280,000 kindergartners vulnerable to measles, illustrating the critical importance of maintaining high vaccination rates to avoid future outbreaks.
Understanding MMR Vaccine Effectiveness Against Measles
The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine has been lauded for its safety and effectiveness, yet the recent decline in vaccination rates raises grave concerns. According to the CDC, maintaining over 95% vaccination coverage is crucial for achieving herd immunity. When this threshold is met, it significantly reduces the risk of outbreaks by protecting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
Despite the MMR vaccine’s proven effectiveness, the decrease in vaccination rates among young children poses a real threat to public health. With measles re-emerging in recent years, particularly in unvaccinated populations, it is paramount to address vaccine hesitancy and misinformation. Engaging communities through education on the critical importance of the MMR vaccine can help prevent another surge in cases.
Symptoms and Complications of Measles
Measles begins to manifest symptoms 7 to 14 days post-infection, with initial signs including high fever, cough, and a distinctive rash. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for prompt intervention, especially considering the severe health complications that can arise, such as pneumonia, encephalitis, and diarrhea. The CDC emphasizes that children under five face a higher risk of developing these serious health issues.
As measles is highly contagious, awareness of its spread is vital. According to the CDC, it can be contracted through mere proximity to an infected person, even hours after they have left the room. This underscores the necessity of monitoring and managing outbreaks proactively, particularly in community and school settings where children congregate.
The Importance of Measles Vaccination Rates
Vaccination rates serve as a critical indicator of community health, especially during heightened outbreaks like those witnessed in 2025. The CDC’s findings indicate a concerning drop in measles vaccinations among kindergartners over recent years, which directly correlates with the rising number of measles cases across the United States. A sustained commitment to high vaccination rates is essential to protect not only individuals but also those who cannot vaccinate due to age or medical conditions.
Improving measles vaccination rates requires community engagement and educational initiatives that clarify the MMR vaccine’s effectiveness. With declining vaccination rates leading to increased vulnerabilities among children, collective responsibility plays a pivotal role in reversing current trends. Efforts to educate parents on vaccination schedules and the dangers of measles should be prioritized to combat misinformation.
Measles Outbreaks: Trends and Patterns in 2025
The current landscape of measles outbreaks in the U.S. reflects troubling trends; the rise in reported cases and the burgeoning number of outbreaks indicates a public health emergency. Throughout 2025, 27 outbreaks have been documented, significantly higher than previous years, highlighting the patterns of transmission and vulnerability within communities. The concentration of outbreaks in states like Texas illustrates geographic patterns that necessitate tailored public health responses.
Recognizing these outbreak patterns aids in developing effective strategies for prevention and control. The CDC’s comprehensive outbreak data forms the foundation for targeted public health responses and reinforces the urgent need for vaccination campaigns, especially in regions experiencing higher rates of outbreak-associated cases.
Combatting Measles: Public Health Strategies
Effective public health strategies are vital to combat the ongoing measles crisis. The CDC has been proactive in advocating for increased vaccination efforts and community awareness campaigns that engage families in understanding the importance of the MMR vaccine. These initiatives are crucial in reversing the alarming trends of declining vaccination rates and ensuring that herd immunity is achieved across the nation.
Additionally, health officials are emphasizing the need for outbreak management protocols that involve rapid response teams to effectively control and contain measles transmission. By leveraging data on measles symptoms and vaccination status, public health authorities can deploy resources where they are needed most, ultimately saving lives and enhancing community health.
Measles Transmission: Understanding the Contagious Nature
Measles is an extremely contagious disease, and understanding its transmission pathways is key to preventing outbreaks. The CDC highlights that it spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, with the potential for contact even hours after the initial exposure. This emphasizes the importance of swift identification and isolation of cases to minimize further spread within communities.
As public health officials work to educate the public about measles transmissibility, it is crucial to underscore that unvaccinated individuals are at the highest risk. Increased awareness about the risks of exposure, particularly in crowded or community settings, can play a significant role in controlling potential outbreaks and protecting vulnerable populations such as young children and those with compromised immune systems.
Looking Ahead: Future of Measles Vaccination in the U.S.
The trajectory of measles vaccination in the United States hinges on proactive public health measures and societal engagement. With evident disparities in vaccination rates, especially among younger populations, a concerted effort must be made to restore trust in vaccines and dispel myths that contribute to hesitancy. Health professionals and community leaders should work collaboratively to promote vaccination as an essential service.
In conclusion, the future of measles vaccination in the U.S. requires robust public health infrastructure and inclusive community education initiatives. With the continued rise in cases and outbreaks, strategic actions are paramount to safeguard the health of all citizens and to ensure that the lessons learned in 2025 are not repeated in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current US measles cases and how does this compare to recent years?
As of now, US measles cases have reached a record high with 1,288 confirmed cases across 38 states, the highest level in over 30 years. This is a significant increase from only 285 cases recorded last year and 1,274 cases in 2019.
What is the status of measles outbreaks in the US for 2025?
In 2025, there have been 27 reported outbreaks of measles in the US, with 88% of the confirmed cases associated with these outbreaks. This highlights the ongoing challenges in controlling the disease, especially among unvaccinated individuals.
How effective is the MMR vaccine in preventing US measles cases?
The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is very effective, providing a high level of protection when vaccination rates exceed 95%. Currently, a decline in vaccination coverage among kindergartners poses a risk, as it has dropped from 95.2% to 92.7%.
What are the typical measles symptoms to watch for?
Measles symptoms typically appear 7 to 14 days after infection and include a high fever, cough, and a distinctive rash. Identifying these symptoms early is crucial for preventing further spread of the disease.
What are the implications of low measles vaccination rates in US children?
Low measles vaccination rates result in increased vulnerability to outbreaks. Approximately 280,000 kindergartners are at risk as vaccination coverage has fallen to 92.7%. This decline can lead to higher numbers of measles cases and complications from the disease.
What serious health complications can arise from US measles cases?
Measles can lead to serious health complications, especially in children under five years old. Common complications include ear infections and diarrhea, while severe complications may involve pneumonia and encephalitis.
How does measles spread in the US?
Measles is highly contagious and spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. You can contract measles by being in a room where an infected person has been, even up to 2 hours after they have left.
How has CDC data influenced the understanding of US measles cases recently?
CDC data reveals alarming trends in US measles cases, showing the highest levels in decades, emphasizing the need for increased vaccination efforts and public awareness to combat outbreaks.
What actions can be taken to improve measles vaccination rates in the US?
To improve measles vaccination rates, public health campaigns focusing on educating parents about the safety and effectiveness of the MMR vaccine, as well as addressing misconceptions about vaccines, are crucial.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Current Measles Cases | 1,288 confirmed cases across 38 states, highest level in over 30 years. |
| Leading State | Texas has over 700 cases. |
| Previous Year Comparison | Only 285 cases reported last year. |
| Outbreaks | 27 outbreaks reported in 2025, with 88% of cases outbreak-associated. |
| Deaths | 3 deaths reported this year due to measles. |
| Vaccination Status | 92% of those infected are unvaccinated or have unknown status. |
| Vaccine Effectiveness | The MMR vaccine is safe and effective; herd immunity requires over 95% coverage. |
| Kindergarten Vaccination Rates | Coverage decreased from 95.2% to 92.7% from 2019-2024. |
| Contagion | Measles is highly contagious and can spread through the air. |
Summary
US measles cases are at their highest levels in over 30 years, as recent data from the CDC reveals extreme increases in infection rates and alarming trends in vaccination coverage. With rising cases leading to outbreaks and serious health complications, it’s crucial for communities to prioritize vaccination to achieve herd immunity and protect vulnerable populations. The current situation urges a renewed focus on public health measures to prevent further spread.




