Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s: A Conductor’s Journey
Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment option for individuals grappling with the debilitating effects of the disease. Focused on enhancing symptoms and improving the overall quality of life, this innovative neurostimulation technique involves implanting a device that delivers targeted electrical currents to specific areas of the brain. Through advancements like adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS), patients can experience real-time adjustments to their therapy, leading to better symptom management for Parkinson’s. This exciting development is giving hope to many, showcasing how modern Parkinson’s disease treatment is evolving at a remarkable pace. For patients like Rand Laycock, a music conductor who has bravely battled Parkinson’s, DBS therapy has proven to be a transformative lifeline.
The advent of neurostimulation techniques, particularly in the realm of Parkinson’s care, has unveiled a new horizon for managing this challenging condition. Terms like implantable pulse generators and electrical brain modulation describe the intricacies of therapies aimed at alleviating the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. As patients seek effective solutions for symptom relief, treatment options like deep brain stimulation have gained prominence. This form of intervention not only provides hope for improved daily functioning but also represents a significant stride in adapting therapies to meet individual needs. With advancements such as dynamic or adaptive stimulation, this approach to symptom control continues to evolve, enhancing the lives of those affected by Parkinson’s.
Understanding Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson’s Disease
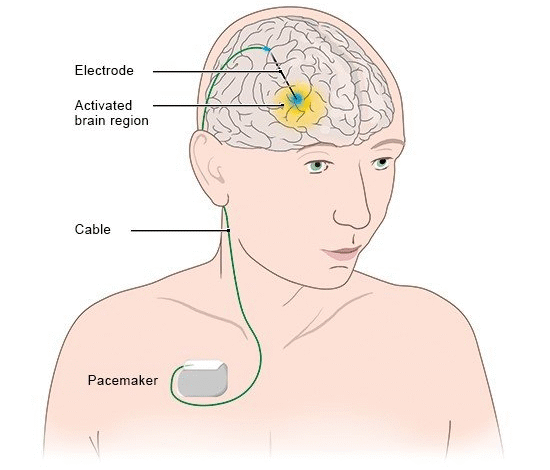
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has emerged as a revolutionary treatment for individuals battling Parkinson’s disease. This innovative therapy involves implanting a device that sends targeted electrical impulses to specific brain areas, helping to mitigate symptoms like tremors and stiffness. The technology has gained traction due to its efficacy in improving the quality of life for patients who have exhausted other treatment options. For many, including music conductor Rand Laycock, DBS has been transformative, allowing individuals to reclaim their passions and activities that Parkinson’s once hindered.
The procedure itself, often referred to as a ‘pacemaker for the brain,’ is designed to enhance neuron activity in areas affected by Parkinson’s. As patients undergo the DBS procedure, they find relief from debilitating symptoms, launching a journey towards improved symptom management and overall well-being. Doctors like Michal Gostkowski emphasize that DBS is not merely an option but a lifeline for those seeking effective Parkinson’s disease treatment, significantly altering how patients interact with their environments and loved ones.
The Role of Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) in Treatment
Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) represents the next evolution in neurostimulation technology, providing a more personalized approach to DBS therapy. Unlike traditional DBS, which delivers a constant signal, aDBS has the ability to adjust stimulation in real-time based on the patient’s specific neural activity. This innovative capability is crucial for addressing the fluctuating symptoms often experienced by Parkinson’s patients, like Rand Laycock. As a music conductor, the ability for his device to adapt to his needs during performances has proven invaluable, enabling him to manage tremors without interruption.
The introduction of aDBS may simplify the significantly complex management of Parkinson’s symptoms. By tracking brain frequencies, aDBS can lower or increase stimulation levels as necessary, which drastically improves symptom control. This form of therapy aligns with the growing trend toward personalized medicine, wherein treatments can be finely tuned to suit individual patient profiles. As more patients explore this advanced therapeutic option, they rejoice in newfound abilities, experiencing a life closer to normalcy while battling Parkinson’s disease.
Benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation Beyond Medications
For patients dealing with Parkinson’s, traditional medication regimens can become complicated, leading to side effects such as dyskinesias—uncontrolled movements that often complicate their lives. Deep brain stimulation provides an effective alternative or complement to pharmacological treatments. As highlighted in Laycock’s experience, following the implementation of DBS therapy, many patients report significant improvements in symptom management, dramatically reducing their dependency on medications. This not only alleviates issues with medication side effects but also offers a pathway to regaining control over their lives.
Moreover, DBS is becoming synonymous with better quality of life for patients with Parkinson’s disease. The therapy can dramatically enhance patients’ abilities to engage in daily activities and cherished hobbies. As patients experience a reduction in symptoms such as tremors, they often rediscover their passions, reigniting their desire to participate in work and hobbies. For music conductor Rand Laycock, the benefits of DBS have transcended mere symptom relief—they have restored joy and enthusiasm in his life, showcasing the dual importance of addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of coping with Parkinson’s.
Exploring Neurostimulation Techniques for Parkinson’s Patients
Neurostimulation techniques reflect an exciting frontier in the management of Parkinson’s disease, with deep brain stimulation being one of the most extensively studied and utilized methods. Beyond DBS, researchers and clinicians are continuously exploring innovative neurostimulation approaches that might offer additional hope to those living with this condition. These techniques aim not only to alleviate symptoms but also to provide targeted interventions that could potentially slow the progression of the disease. As the field of neurostimulation evolves, patients are becoming more informed, allowing for collaborative discussions regarding their treatment plans.
The exploration of neurostimulation also leads to the discovery of various technologies, including non-invasive options that complement or enhance the effects of DBS. For instance, external neurostimulation devices and therapies might assist in modulation during critical moments of vulnerability. By integrating new technologies with existing methods like aDBS, patients may find more efficient ways to manage their symptoms. Such developments highlight the critical role of continuous research and innovation in the field of Parkinson’s disease treatment, ultimately resulting in a more tailored experience for those affected.
Coping with Parkinson’s: Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with Parkinson’s disease goes beyond managing physical symptoms; emotional and psychological support plays a pivotal role in treatment outcomes. Many patients, including those benefiting from deep brain stimulation, often experience feelings of frustration, isolation, and helplessness due to their condition. Establishing support systems, whether through family, friends, or support groups, can foster a sense of community and understanding, transforming the way patients cope with their diagnosis. Engaging in activities that bring joy can further enhance emotional resilience, allowing patients to maintain a positive outlook.
As patients like Rand Laycock regain their identities through treatments like aDBS, they also find the importance of holistic approaches that incorporate mental wellness into their care. Therapies such as counseling, art, and music therapy can significantly reduce anxiety and improve overall mental health, complementing the physical benefits of DBS. By intertwining physical and emotional care strategies, Parkinson’s patients can embark on a more comprehensive healing journey, fundamentally changing their quality of life.
The Future of Deep Brain Stimulation Therapies
As research into Parkinson’s disease continues to evolve, the future of deep brain stimulation therapies appears promising. Emerging technologies in neurostimulation aim to develop even more refined instruments for delivering precise treatments tailored to individual patient needs. For instance, advancements in brain imaging and artificial intelligence may pave the way for more accurate mapping of brain areas affected by Parkinson’s, maximizing the benefits of DBS. As these technologies mature, patients can anticipate not just improvement in symptom management, but potential new breakthroughs in treating the disease itself.
Moreover, the ongoing clinical trials and studies focused on deep brain stimulation seek to expand its indications beyond Parkinson’s disease. As we understand more about brain function and neuroplasticity, there may soon be applications of DBS therapy for associated conditions such as Alzheimer’s and severe depression. The continuous exploration of DBS and related therapies promises to alter the trajectory of several neurologic disorders, hinting at a future where patients experience a comprehensive approach to their health and wellness, transforming the landscape of treatment options available.
Patient Experiences: Transformative Stories of Recovery
Patient stories, like that of Rand Laycock, illuminate the transformative potential of deep brain stimulation therapies. His journey underscores the profound impact that DBS can have, providing renewed hope and capabilities to those living with Parkinson’s disease. As he recounts his experiences, Laycock shows how this therapy has allowed him to continue conducting his orchestra and engaging fully with his passions, which is a testament to the potential of DBS to change lives. His narrative serves as inspiration for others who may be hesitant about exploring surgical interventions due to fears surrounding the procedures.
The importance of personal testimonials in the field of Parkinson’s treatment cannot be overstated. They provide not just insight into the success of therapies like DBS, but also offer solidarity and encouragement to individuals grappling with similar challenges. As more patients share their recovery stories, the dialogue surrounding deep brain stimulation grows richer, enhancing our understanding of its role in effective Parkinson’s disease treatment and the hope it brings to individuals and families alike.
Engaging with Healthcare Providers About Treatment Options
Effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential for navigating the complexities of Parkinson’s disease treatment, including deep brain stimulation. Patients must feel empowered to engage in discussions about their symptoms, medication side effects, and the possibility of advanced treatments like DBS or aDBS. Open communication creates opportunities for personalized care, where patients receive tailored strategies that genuinely reflect their needs and aspirations. This collaborative approach fosters better understanding and management of symptoms, allowing for improved quality of life.
Moreover, as patients like Laycock have discovered, being proactive in discussions with neurologists and specialists can lead to better outcomes. Patients should not hesitate to explore all available treatment options during consultations and foster a dialogue about their unique experiences. By advocating for themselves and asking informed questions, individuals can cultivate a stronger partnership with their healthcare team, ensuring they are steered towards the most effective and modern therapies available for managing Parkinson’s disease.
The Importance of Ongoing Research in Parkinson’s Treatment
The landscape of Parkinson’s disease treatment is ever-evolving, driven by ongoing research that seeks to provide better management strategies, including advanced therapies like deep brain stimulation. Scientific inquiries into the causes, symptoms, and treatment responses of Parkinson’s contribute significantly to the evolution of existing therapies and the development of innovative solutions. Research initiatives are crucial for understanding how best to deploy treatments such as aDBS in various patient populations, ultimately leading to more effective symptom management and improved quality of life.
Patients can take comfort in knowing that every advancement in treatment stems from rigorous research efforts and collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and patient advocates. As more trials emerge, promising new interventions are likely to arise, expanding the horizons for those living with Parkinson’s. Recognition of the significance of research can inspire patients to participate in studies or advocate for increased funding and support toward evolving therapeutic pathways.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is deep brain stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson’s disease treatment?
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure that involves implanting a device that delivers electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain. This technique is used as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease to help manage debilitating symptoms such as tremors and dyskinesias, improving overall quality of life.
How does adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) differ from traditional DBS therapy?
Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) is an advanced form of DBS that can adjust its stimulation output in real-time based on the patient’s brain activity. Unlike traditional DBS, which delivers constant stimulation, aDBS fine-tunes its effects to optimize symptom control, making it particularly beneficial for patients with fluctuating symptoms.
What symptoms of Parkinson’s can be managed with DBS therapy?
DBS therapy can effectively manage various symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, including motor symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, as well as reducing dyskinesias that may arise from long-term medication use, significantly enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
Is deep brain stimulation suitable for all Parkinson’s disease patients?
Not all Parkinson’s disease patients are candidates for deep brain stimulation. It is generally recommended for those whose symptoms are not adequately controlled by medication or who experience intolerable side effects. A thorough evaluation by a neurologist is essential to determine suitability for DBS.
What is the recovery process like after deep brain stimulation surgery for Parkinson’s?
After DBS surgery, patients typically stay in the hospital for a short period for monitoring. Initial recovery includes managing discomfort and adjusting to the implanted device. Follow-up appointments are necessary to fine-tune settings for optimal symptom management and recovery duration varies by individual.
Can deep brain stimulation completely eliminate Parkinson’s symptoms?
Deep brain stimulation does not cure Parkinson’s disease, but it can significantly reduce the severity of symptoms and improve daily functioning. Many patients experience considerable relief, allowing them to engage more fully in activities they enjoy.
What advancements are being made in neurostimulation for Parkinson’s disease?
Recent advancements in neurostimulation for Parkinson’s include the development of adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) technology, which allows for real-time adjustments of stimulation settings based on the patient’s condition and needs, providing more personalized symptom management.
How can deep brain stimulation improve quality of life for Parkinson’s patients?
Deep brain stimulation enhances quality of life for Parkinson’s patients by reducing debilitating symptoms like tremors and involuntary movements, which allows for improved daily functioning, greater independence, and the ability to engage in hobbies and social activities.
What should patients consider before opting for deep brain stimulation as a treatment for Parkinson’s?
Patients should carefully consider the potential benefits, risks, and long-term implications of undergoing deep brain stimulation. Consulting with healthcare professionals and discussing personal health goals and concerns is essential to making an informed decision.
Are there lifestyle changes recommended after starting deep brain stimulation therapy for Parkinson’s?
After starting deep brain stimulation therapy, it’s often recommended that patients maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and ongoing engagement in social and cognitive activities, which can help maximize the benefits of the therapy.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Patient Background | Rand Laycock, a 70-year-old orchestra director, has dealt with Parkinson’s for over a decade since his diagnosis shortly before turning 60. |
| Challenge Faced | Despite medication, Laycock’s symptoms worsened, leading to significant hand tremors and dyskinesias. |
| Alternative Treatment | Introduced to deep brain stimulation (DBS) by Dr. Michal Gostkowski as a potential treatment for his symptoms. |
| DBS Explained | Deep brain stimulation involves an implant that delivers electrical currents to specific brain areas to enhance neuron activity. |
| Adaptive DBS (aDBS) Benefits | aDBS adjusts stimulation in real-time based on the patient’s brain activity, improving symptom control dynamically. |
| Success of Treatment | After starting aDBS, Laycock reported nearly complete disappearance of tremors and manageable dyskinesia. |
| Quality of Life Improvement | Laycock expresses hope for the future as he continues conducting music with minimal symptoms, emphasizing the transformative nature of the treatment. |
Summary
Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s offers significant hope for patients struggling with their symptoms, as demonstrated by Rand Laycock, who experienced marked improvement after undergoing this treatment. The tailored approach of adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) not only enhanced his quality of life but also allowed him to continue his passion for music nearly free of tremors. As medical advancements in DBS technology progress, they provide a beacon of hope for many Parkinson’s patients seeking to reclaim their lives.




