Prostate Cancer Screening: New Urine Test vs PSA Alternatives
Prostate cancer screening has long been a vital part of men’s health, but recent advancements could revolutionize how we detect this common illness. Traditional methods, such as the PSA test, have been the go-to for diagnosing prostate cancer, yet they come with limitations that can lead to false positives and uncertainty. New research utilizing machine learning has introduced a promising urine test for prostate cancer, offering a non-invasive alternative that accurately identifies cancer biomarkers. This groundbreaking approach not only improves the accuracy of prostate cancer diagnosis but also has the potential to reveal the stage of the disease. As we continue to refine cancer detection methods, incorporating innovations like biomarkers in urine could transform the landscape of prostate cancer screening for the better.
Detecting prostate cancer effectively remains a critical concern for men, especially with emerging techniques that may provide more reliable options than traditional methods. Instead of depending solely on blood tests like PSA, researchers are exploring advanced urine-based assessments that leverage machine learning for enhanced accuracy. The shift toward these non-invasive screenings, which could yield vital information regarding cancer markers, addresses some of the shortcomings associated with current diagnostic practices. By focusing on urine samples, these innovative approaches aim to identify prostate cancer early and more precisely, potentially leading to better treatment outcomes. As we seek alternatives for prostate cancer diagnosis, leveraging technology and biological insights signifies a promising future in healthcare.
Innovative Approaches to Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate cancer screening has traditionally relied on the PSA test, which measures the levels of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. However, new research is exploring the potential of urine tests to detect prostate cancer biomarkers. This approach, highlighted by Swedish researchers, uses advanced machine learning techniques that analyze urine samples from men diagnosed with prostate cancer, demonstrating a promising alternative to the PSA test. This method not only offers a more comfortable screening experience for patients but also enhances diagnostic accuracy by identifying specific biomarkers related to prostate cancer.
The introduction of urine tests for prostate cancer screening represents a significant stride towards more effective cancer diagnosis. By leveraging machine learning algorithms to interpret complex data from urine samples, researchers can discern vital cancer markers that PSA tests may miss. This innovative approach not only tackles the challenge of tumor heterogeneity but also provides a non-invasive option that can be performed quickly and cost-effectively. As experts emphasize, transforming prostate cancer screening stands to improve early detection and treatment, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
The Role of Urine Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Recent findings indicate that urine biomarkers can be pivotal in accurately diagnosing prostate cancer. Unlike the traditional PSA test, which has limitations in specificity, biomarkers identified in urine samples can provide a clearer indication of the presence of cancerous cells. These biomarkers are substances in urine that are linked to prostate cancer, offering a new avenue for clinicians to improve diagnostic precision. Research led by the Karolinska Institutet showcases how analyzing urine samples can help identify the cancer’s malignancy and aggressiveness, paving the way for personalized treatment plans based on actual cancer profiles.
Furthermore, the utilization of urine biomarkers could revolutionize prostate cancer screening by offering an alternative that is both non-invasive and patient-friendly. As more studies validate the effectiveness of these biomarkers, healthcare providers can harness this knowledge to potentially replace or supplement the PSA test. This transition not only fosters a more comprehensive understanding of prostate cancer but also addresses existing concerns regarding the safety and reliability of current screening practices. The ongoing evolution of urine testing represents a hopeful shift towards more sensitive and specific prostate cancer diagnosis.
Machine Learning and Its Impact on Cancer Detection
The application of machine learning in cancer detection is transforming how medical professionals approach prostate cancer screening. In the recent study, researchers applied sophisticated algorithms to a vast dataset of urine samples, successfully identifying markers associated with prostate cancer. This method improves upon traditional screening techniques, which are often limited by factors such as tumor heterogeneity and the subjective interpretation of results. By refining the detection process using machine learning, the risk of false positives—which can lead to unnecessary biopsies and stress for patients—could be significantly reduced.
Machine learning technologies allow for more nuanced analysis of biological data, leading to earlier and more precise identification of prostate cancer. As more data is gathered and analyzed, these algorithms become increasingly effective at recognizing patterns that may elude human observers. Furthermore, the integration of machine learning into clinical settings promises to enhance the overall efficiency of prostate cancer screening and diagnosis, offering a pathway to more tailored treatment options based on individual patient profiles.
Alternatives to the PSA Test in Prostate Cancer Screening
While the PSA test has been the cornerstone of prostate cancer screening for decades, its limitations have led to a search for more reliable alternatives. The recent research advocates for urine tests that identify specific cancer biomarkers, presenting a potential replacement for PSA testing. These urine-based diagnostics harness the power of machine learning to enhance screening accuracy without the invasiveness associated with blood tests. As experts argue, these novel methodologies not only hold promise for better diagnostic clarity but also mitigate the anxiety and discomfort associated with traditional screening techniques.
In addition to urine tests, researchers are exploring various biomarkers that may serve as indicators of prostate cancer progression. Alternatives to the PSA test emphasize the need for precision in diagnosis, steering away from generalized testing toward more personalized approaches. The ongoing development of these alternatives aims to improve screening protocols, reduce the incidence of false positives, and ultimately lead to better outcomes for patients by detecting high-grade cancers at earlier stages.
Understanding Prostate Cancer Tumor Heterogeneity
Tumor heterogeneity poses a significant challenge in accurately diagnosing and treating prostate cancer. This term refers to the diverse characteristics of tumors, which can vary significantly among patients and even in different regions of the same tumor. The implications of tumor heterogeneity are profound, as they complicate the interpretation of diagnostic tests and the efficacy of treatment plans. The recent research emphasizes the importance of identifying biomarkers that can effectively represent the variety present in prostate cancer cases.
By focusing on markers in urine rather than relying solely on PSA levels, researchers aim to tackle the complexities of tumor heterogeneity. This approach not only broadens the scope of what can be detected but also enhances the chances of finding suitable targets for treatment. Understanding the nuances of tumor heterogeneity will ultimately lead to more tailored and effective prostate cancer treatment strategies, reducing morbidity and improving patient quality of life.
Future Directions in Prostate Cancer Research
Looking ahead, the future of prostate cancer research is promising, particularly with the recent advancements in urine testing and machine learning. Researchers recognize the need for larger and more diverse sample sizes to validate their findings and ensure applicability across various populations. The ongoing studies aim to establish comprehensive screening methods that are not only accurate but also patient-friendly. In light of the challenges posed by traditional methods, this focus on innovative detection techniques marks a turning point in the fight against prostate cancer.
Future research will likely expand beyond prostate cancer to explore similar applications in diagnosing other cancer types. The foundational work on urine biomarkers showcased in the study leaves room for expansion and adaptation of these methodologies across different cancers. The hope is that with continued innovation and research, we can develop efficient and comprehensive cancer screening programs that contribute to improved early detection, higher cure rates, and less invasive treatment protocols.
The Implications of PSA Test Limitations
Despite the PSA test’s longstanding role in prostate cancer screening, its limitations raise concerns among healthcare professionals. This blood test can produce false positives, leading to unnecessary biopsies and heightened anxiety for patients who may not actually have cancer. Research, including insights from experts such as Matthew C. Abramowitz, reinforces the urgency for alternative screening methods that provide greater specificity and lower the burden of unnecessary procedures. Understanding the implications of the PSA test’s limitations is crucial in pushing for advancements in cancer detection.
The quest for alternatives that minimize false positives while maximizing sensitivity is ongoing. Urine tests that detect biomarkers associated with prostate cancer present a compelling solution to the limitations of the PSA test. As researchers continue to refine these methodologies, the focus will remain on ensuring that screening processes effectively distinguish between different degrees of cancer risk while maintaining patient comfort—a key element that could redefine prostate cancer screening in the coming years.
Understanding False Positives in Prostate Cancer Screening
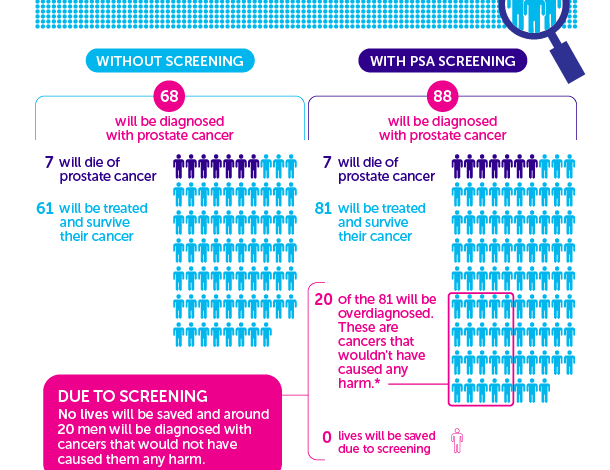
False positives in prostate cancer screening, particularly with the PSA test, represent a significant hurdle in achieving accurate diagnoses. Approximately 6% to 7% of PSA test results can lead to a false positive, meaning that a significant number of men may undergo invasive procedures like biopsies without having cancer. Understanding the statistics surrounding these false positives is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to navigate the complexities of prostate cancer screening effectively.
The incorporation of urine biomarkers could drastically reduce the rates of false positives by providing specific indications of prostate cancer presence. Researchers are confident that moving forward with urine testing, which uses advanced methodologies and machine learning, can offer a more discriminatory screening process. As this research evolves, it is essential to continue educating patients about the significance of false positives and the advantages of emerging testing alternatives in informing early interventions.
The Importance of Comprehensive Screening Programs
Establishing comprehensive screening programs for prostate cancer is vital for early detection and improved treatment outcomes. Recent advancements in urine testing methodologies align with the growing consensus on the need for more specific and reliable screening options. By integrating urine biomarker analysis into standard testing protocols, healthcare providers can enhance early detection efforts, which are crucial for effective cancer treatment.
Moreover, comprehensive screening programs must also consider the diverse demographics and risk factors present in different populations. Future studies will be essential in refining these screening approaches to ensure inclusivity and applicability across various patient groups. As researchers work toward developing efficient screening methods, the ultimate goal remains clear: to detect high-grade prostate cancer early, thereby improving prognosis and reducing treatment-related complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is prostate cancer screening and why is it important?
Prostate cancer screening is the process of testing for prostate cancer in asymptomatic individuals to detect the disease early when treatment is most effective. Early detection through methods such as the PSA test or emerging urine tests for prostate cancer biomarkers can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
How does the urine test for prostate cancer work?
The urine test for prostate cancer analyzes specific biomarkers present in urine samples. Recent studies have shown that this non-invasive method can accurately detect prostate cancer, potentially outperforming traditional PSA tests, and assess the disease’s stage.
What are some potential PSA test alternatives for prostate cancer screening?
Alternatives to the PSA test include advanced urine tests that leverage machine learning to identify prostate cancer biomarkers, providing a more specific diagnosis while being non-invasive and often more accurate for certain patient populations.
What role does machine learning play in prostate cancer detection?
Machine learning enhances prostate cancer detection by analyzing large datasets, like urine samples, to identify patterns and biomarkers associated with prostate cancer more precisely. This technology has the potential to revolutionize prostate cancer screening methods by improving accuracy over traditional blood tests.
Are there specific biomarkers in urine that can indicate prostate cancer?
Yes, researchers have identified specific biomarkers in urine that can signal the presence of prostate cancer. These biomarkers are crucial for developing non-invasive screening tests that can accurately diagnose prostate cancer and determine its severity.
What are the limitations of current prostate cancer screening methods?
Current prostate cancer screening methods, particularly the PSA test, can lead to false positives and overdiagnosis, which can result in unnecessary procedures. Additionally, the PSA test lacks specificity, meaning it may indicate prostate issues that are not cancerous. Emerging urine tests aim to overcome these limitations.
How effective is the urine test for prostate cancer compared to the PSA test?
Studies suggest that the urine test for prostate cancer can achieve a higher accuracy in detecting cancer and its grade compared to the PSA test. This advancement offers a promising alternative that is non-invasive, painless, and potentially more reliable for cancer detection.
What is the future of prostate cancer screening?
The future of prostate cancer screening may include more efficient methods that utilize urine tests and machine learning technologies, leading to early detection of high-grade cancers. Research is ongoing to validate these methods and extend their applicability beyond prostate cancer.
What should men know about prostate cancer diagnosis and screening?
Men should understand the importance of prostate cancer screening, especially those at higher risk. Awareness of both traditional methods like the PSA test and emerging urine tests for prostate cancer can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
| Key Points |
|---|
| A new urine test uses machine learning to analyze samples for prostate cancer biomarkers, offering a non-invasive alternative to the PSA test. |
| The study involved over 2,000 men and showed high accuracy in detecting cancer and grading its stage. |
| Lead author Martin Smelik emphasizes the test’s advantages: non-invasive, painless, and relatively inexpensive compared to current blood tests. |
| The heterogeneity of tumors posed a challenge in identifying specific biomarkers for all patients. |
| Experts agree that a transformative advance in prostate cancer screening is needed, as the PSA test has limitations. |
| Findings point to the potential for broader applications in detecting other types of cancer beyond prostate cancer. |
| Further research with larger sample sizes is essential to validate these promising findings. |
| The goal is to develop efficient screening programs to improve prostate cancer detection rates. |
Summary
Prostate cancer screening is on the verge of a significant shift thanks to a new urine test that leverages machine learning to identify biomarkers linked to the disease. This innovative approach offers a non-invasive and accurate alternative to the traditional PSA test, which has been long criticized for its limitations. As research progresses, we may see the emergence of more effective screening methods that enhance our ability to detect prostate cancer in its early stages and improve patient outcomes.




